uitsluitend voor onderzoeksdoeleinden
CC-5013 (Lenalidomide) Immunomodulator
Cat.Nr.S1029
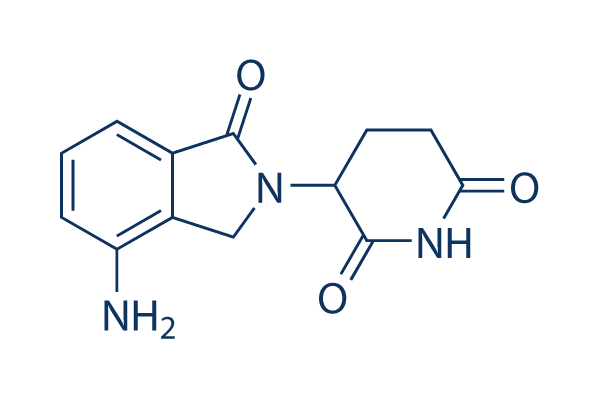
Chemische structuur
Moleculair gewicht: 259.26
Kwaliteitscontrole
| Gerelateerde doelwitten | Proteasome E1 Activating E3 Ligase DUB p97 SUMO E2 conjugating |
|---|---|
| Overige E3 ligase Ligand Inhibitoren | CC-99282 |
Celkweek, behandeling & werkconcentratie
| Cellijnen | Assaytype | Concentratie | Incubatietijd | Formulering | Activiteitsbeschrijving | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LB771-HNC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.15038 μM | SANGER | |||
| L-363 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.92212 μM | SANGER | |||
| JAR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.97001 μM | SANGER | |||
| EoL-1-cell | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.10515 μM | SANGER | |||
| BT-549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.21849 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-NEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.89512 μM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.67585 μM | SANGER | |||
| HMV-II | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.0172 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.4467 μM | SANGER | |||
| KASUMI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.571 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-28 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.9764 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.6241 μM | SANGER | |||
| T47D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.2099 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.48 μM | SANGER | |||
| A2058 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.8199 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW620 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.2473 μM | SANGER | |||
| LCLC-103H | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.4892 μM | SANGER | |||
| HAL-01 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.5796 μM | SANGER | |||
| PANC-08-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.9108 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-684 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.3979 μM | SANGER | |||
| DEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.499 μM | SANGER | |||
| K5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.1486 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.4652 μM | SANGER | |||
| ACN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.5297 μM | SANGER | |||
| H9 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.626 μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.143 μM | SANGER | |||
| HSC-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.6601 μM | SANGER | |||
| IGROV-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.783 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.9968 μM | SANGER | |||
| LN-405 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.9076 μM | SANGER | |||
| MSTO-211H | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.3573 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.5759 μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.1563 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.6963 μM | SANGER | |||
| SBC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.8696 μM | SANGER | |||
| CTV-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.0149 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuP-T3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.4009 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2218 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.5407 μM | SANGER | |||
| HDLM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.2026 μM | SANGER | |||
| ABC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.6974 μM | SANGER | |||
| MV-4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.7317 μM | SANGER | |||
| WM-115 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.3099 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW1990 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.33 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC70 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.7346 μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-520 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.8839 μM | SANGER | |||
| JEG-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.1614 μM | SANGER | |||
| C8166 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.2274 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-OV-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.6755 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H526 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.683 μM | SANGER | |||
| NKM-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.9568 μM | SANGER | |||
| ECC10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34.7443 μM | SANGER | |||
| A2780 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.3601 μM | SANGER | |||
| KY821 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.7681 μM | SANGER | |||
| MKN1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.2137 μM | SANGER | |||
| EKVX | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.4212 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-16 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.3885 μM | SANGER | |||
| CTB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=39.7789 μM | SANGER | |||
| COR-L105 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.4746 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.2069 μM | SANGER | |||
| Mewo | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.9871 μM | SANGER | |||
| BCPAP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.7917 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-45 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.2776 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1693 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.6986 μM | SANGER | |||
| H-EMC-SS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.3224 μM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=50.3545 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=52.3142 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1304 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=52.7024 μM | SANGER | |||
| NOS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=52.8559 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2342 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=53.0508 μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-270 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=53.6364 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-135 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=55.1853 μM | SANGER | |||
| OE33 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=55.818 μM | SANGER | |||
| ML-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=55.9489 μM | SANGER | |||
| KMOE-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=56.2893 μM | SANGER | |||
| Daoy | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=56.3204 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=57.0142 μM | SANGER | |||
| NBsusSR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=57.5705 μM | SANGER | |||
| UACC-257 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=58.6264 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-139 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=58.826 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-85-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=58.8643 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H720 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=58.8942 μM | SANGER | |||
| MLMA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=59.091 μM | SANGER | |||
| A3-KAW | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=59.2809 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos-2G6-4C10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=59.6287 μM | SANGER | |||
| A388 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=60.449 μM | SANGER | |||
| LAMA-84 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=60.9905 μM | SANGER | |||
| GCT | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=61.0786 μM | SANGER | |||
| K-562 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=61.5333 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1666 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=61.875 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1993 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=63.4043 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H358 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=65.0121 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=65.988 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCE-T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=67.0798 μM | SANGER | |||
| DOK | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=67.4948 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1376 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=69.8314 μM | SANGER | |||
| NEC8 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=70.1243 μM | SANGER | |||
| G-402 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=70.9395 μM | SANGER | |||
| GR-ST | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=71.172 μM | SANGER | |||
| QIMR-WIL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=71.4434 μM | SANGER | |||
| CHP-212 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=71.965 μM | SANGER | |||
| KU812 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=72.9702 μM | SANGER | |||
| Becker | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=73.1489 μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=74.7486 μM | SANGER | |||
| A498 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=74.9308 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H69 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=75.7663 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H209 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=78.6147 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-33 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=78.9939 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-680N | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=79.1007 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-283MED | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=79.812 μM | SANGER | |||
| ATN-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=81.1187 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-N87 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=81.7296 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-NB-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=81.8849 μM | SANGER | |||
| HEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=82.4134 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB69 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=83.0033 μM | SANGER | |||
| MPP-89 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=83.2575 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-829 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=85.4912 μM | SANGER | |||
| ONS-76 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=85.7908 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=86.2032 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=86.4336 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW900 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=87.2053 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=87.2243 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuP-T4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=91.0405 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1419 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=91.6374 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-72 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=92.0219 μM | SANGER | |||
| Mo-T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=92.7697 μM | SANGER | |||
| OC-314 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=92.8821 μM | SANGER | |||
| BHT-101 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=93.1 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=93.8462 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=94.3055 μM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-361 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=96.0516 μM | SANGER | |||
| DF15 | Function assay | 4 hrs | Induction of CRL4/CRBN ubiquitin ligase-mediated aiolos degradation in human DF15 cells expressing pLOC-ePL-tagged aiolos after 4 hrs by luminescence based beta-galactosidase enzyme fragmentation complementation assay, EC50 = 0.053 μM. | 28358507 | ||
| DF15 | Function assay | 4 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated ikaros degradation in human DF15 cells expressing ePL-tagged ikaros after 4 hrs by luminometric analysis, EC50 = 0.067 μM. | 28425720 | ||
| DF15 | Function assay | 4 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated aiolos degradation in human DF15 cells expressing ePL-tagged aiolos after 4 hrs by luminometric analysis, EC50 = 0.087 μM. | 28425720 | ||
| T-cells | Function assay | 2 to 3 days | Inhibition of IL-2 production in human T cells measured after 2 to 3 days by ELISA, EC50 = 0.15 μM. | 23168019 | ||
| NAMALWA | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human NAMALWA cells assessed as inhibition of [3H]thymidine incorporation after 72 hrs by scintillation counting, IC50 = 0.36 μM. | 23168019 | ||
| CD34+ progenitor cells | Function assay | 14 days | Decrease in erythroid differentiation of CD34+ progenitor cells from myelodysplastic syndrome del(5q) patient assessed as CD36 expression after 14 days | 17576924 | ||
| CD34+ progenitor cells | Function assay | 14 days | Decrease in myeloid differentiation of CD34+ progenitor cells from myelodysplastic syndrome del(5q) patient assessed as CD33 expression after 14 days | 17576924 | ||
| CD34+ progenitor cells | Function assay | 14 days | Decrease in erythroid differentiation of CD34+ progenitor cells from myelodysplastic syndrome del(5q) patient assessed as glycophorin A expression after 14 days | 17576924 | ||
| CD34+ progenitor cells | Growth inhibition assay | 14 days | Inhibition of cell proliferation of CD34+ progenitor cells from myelodysplastic syndrome del(5q) patient after 14 days | 17576924 | ||
| CD34+ progenitor cells | Growth inhibition assay | 14 days | Growth inhibition of CD34+ progenitor cells from non-del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome patient after 14 days | 17576924 | ||
| DF15 | Function assay | 0.1 to 10 uM | 5 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated aiolos degradation in human DF15 cells at 0.1 to 10 uM after 5 hrs by immunoblot analysis | 28425720 | |
| OPM2 | Function assay | 0.1 to 10 uM | 5 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated aiolos degradation in human OPM2 cells at 0.1 to 10 uM after 5 hrs by immunoblot analysis | 28425720 | |
| DF15 | Function assay | 0.1 to 10 uM | 5 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated ikaros degradation in human DF15 cells at 0.1 to 10 uM after 5 hrs by immunoblot analysis | 28425720 | |
| OPM2 | Function assay | 0.1 to 10 uM | 5 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated ikaros degradation in human OPM2 cells at 0.1 to 10 uM after 5 hrs by immunoblot analysis | 28425720 | |
| EC9706 | Antiproliferative assay | 150 ug/mL | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human EC9706 cells at 150 ug/mL after 48 hrs by CCK-8 assay | 28757066 | |
| Klik om meer experimentele gegevens over de cellijn te bekijken | ||||||
Chemische informatie, Opslag en Stabiliteit
| Moleculair gewicht | 259.26 | Formule | C13H13N3O3 |
Opslag (Vanaf de ontvangstdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-nr. | 191732-72-6 | SDF downloaden | Opslag van stamoplossingen |
|
|
| Synoniemen | CC-5013 | Smiles | C1CC(=O)NC(=O)C1N2CC3=C(C2=O)C=CC=C3N | ||
Oplosbaarheid
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 51 mg/mL
(196.71 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molariteitscalculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formuleringscalculator (Heldere oplossing)
Stap 1: Voer de onderstaande informatie in (Aanbevolen: Een extra dier voor het geval van verlies tijdens het experiment)
Stap 2: Voer de in vivo formulering in (Dit is alleen de calculator, geen formulering. Neem eerst contact met ons op als er geen in vivo formulering is in het gedeelte Oplosbaarheid.)
Berekeningsresultaten:
Werkconcentratie: mg/ml;
Methode voor het bereiden van DMSO-mastervloeistof: mg geneesmiddel vooraf opgelost in μL DMSO ( Concentratie mastervloeistof mg/mL, Neem eerst contact met ons op als de concentratie de DMSO-oplosbaarheid van de partij geneesmiddel overschrijdt. )
Methode voor het bereiden van in vivo formulering: Neem μL DMSO mastervloeistof, voeg vervolgens toeμL PEG300, mengen en helder maken, voeg vervolgens toeμL Tween 80, mengen en helder maken, voeg vervolgens toe μL ddH2O, mengen en helder maken.
Methode voor het bereiden van in vivo formulering: Neem μL DMSO mastervloeistof, voeg vervolgens toe μL Maïsolie, mengen en helder maken.
Opmerking: 1. Zorg ervoor dat de vloeistof helder is voordat u het volgende oplosmiddel toevoegt.
2. Zorg ervoor dat u het/de oplosmiddel(en) in de juiste volgorde toevoegt. U moet ervoor zorgen dat de verkregen oplossing, bij de vorige toevoeging, een heldere oplossing is voordat u verdergaat met het toevoegen van het volgende oplosmiddel. Fysische methoden zoals vortexen, echografie of een warmwaterbad kunnen worden gebruikt om het oplossen te bevorderen.
Werkingsmechanisme
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
CRBN
VEGF
TNF-α
(PBMCs) 13 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Lenalidomide induceert sterk IL-2 en sIL-2R productie. Deze door de verbinding geïnduceerde tyrosinefosforylatie van CD28 op T-cellen wordt gevolgd door een stroomafwaartse activering van NF-κB. Deze verbinding en pomalidomide remmen autoubiquitinatie van CRBN in HEK293 T-cellen die thalidomide-bindend competent wild-type CRBN tot expressie brengen, maar niet thalidomide-bindend defectief CRBN(YW/AA). Overexpressie van CRBN wild-type eiwit, maar niet CRBN(YW/AA) mutant eiwit, in KMS12 myeloomcellen, versterkt pomalidomide-gemedieerde reducties in c-myc en IRF4 expressie en verhoogt p21(WAF-1) expressie. Langdurige selectie voor resistentie tegen deze verbinding in H929 myeloomcellijnen gaat gepaard met een reductie in CRBN, terwijl in DF15R myeloomcellen die resistent zijn tegen zowel pomalidomide als deze chemische stof, CRBN-eiwit ondetecteerbaar is. Deze chemische stof voorkomt de inductie van defecten door de expressie van tumorcelremmende moleculen te downreguleren. Het voorkomt de inductie van tumor-geïnduceerde T-cel lytische synapsdysfunctie. Deze verbindingbehandeling blokkeert door CLL-cellen geïnduceerde T-cel actine synapsdysfunctie, bootst antilichaamblokkade na en downreguleert de expressie van CLL-remmende liganden en hun receptoren op T-cellen. Deze behandeling voorkomt tumor-geïnduceerde immuunsuppressie in FL, DLBCL, HL, MM, SCC en OC en downreguleert immunosuppressieve ligandexpressie op alle onderzochte tumorcellen. De CTL-doodfunctie neemt significant toe na antilichaamblokkade van CLL-remmende liganden of deze chemische behandeling vergeleken met controlebehandelingen. Behandeling van autologe CLL-T-cel co-culturen met dit middel keert de verminderde CD8+ T-cel lytische synapsvorming en granzyme B-trafficking om. |
| Kinase Assay |
Analyse voor remming van TNF-synthese door humane PBMC's
|
|
Humane PBMC's van normale donoren worden verkregen door Ficoll-Hypaque dichtheidsgradientcentrifugatie. Cellen (106 cellen/mL) worden gekweekt in RPMI aangevuld met 10 AB+ serum, 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/mL penicilline en 100 μg/mL streptomycine. Lenalidomide wordt opgelost in DMSO bij 20 mg/mL; verdere verdunning gebeurt met kweekmedium. De uiteindelijke DMSO-concentratie in alle analyses, inclusief de controles, is 0,25%. Deze verbinding wordt 1 uur voorafgaand aan de toevoeging van LPS aan cellen toegevoegd. PBMC's (106 cellen/mL) worden gestimuleerd met 1 μg/mL LPS van Salmonella minnesota R595. Cellen, in drievoud, worden gedurende 18-20 uur bij 37 °C in 5% CO2 met LPS geïncubeerd. Supernatanten worden vervolgens geoogst en geanalyseerd op cytokineniveaus. In sommige experimenten worden supernatanten tot gebruik bij -70 °C ingevroren. De cellevensvatbaarheid wordt bepaald door de Trypanblauwe exclusiekleurstofmethode. De concentratie van TNFα in de kweeksupernatanten wordt bepaald door ELISA. Deze chemische stof wordt in minimaal drie afzonderlijke experimenten getest. Het percentage remming wordt bepaald als 100 × [1 - (cytokine(experimenteel)/cytokine(controle))].
|
|
| In vivo |
De inductie van angiogenese door bFGF wordt significant geremd door orale behandeling met Lenalidomide op een dosisafhankelijke manier. Deze verbinding vermindert significant het percentage gevasculariseerd gebied van 5,16% (controlegroep) tot 2,58% (50 mg/kg). Het vermindert significant de berekende totale MVL van 21,07 (controle) tot 8,11 (50 mg/kg). Deze chemische stof remt significant de migratie van HUVEC's door de fibronectine-gecoate membranen naar 0,1 ng/mL bFGF bij 100 μM, 1 ng/mL VEGF bij concentraties van 10 μM en 100 μM. |
Referenties |
|
Toepassingen
| Methoden | Biomarkers | Afbeeldingen | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | phospho-IKKβ / IKKβ MDM2 / p-MDM2 / p-p53 / p53 |
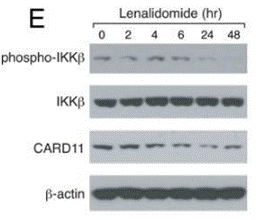
|
22698399 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
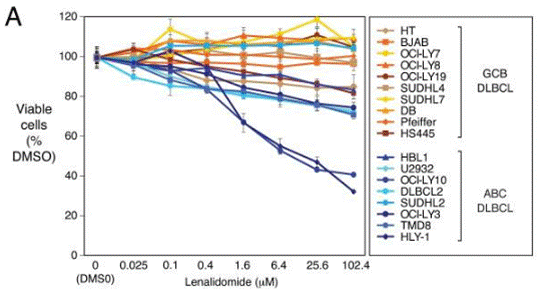
|
22698399 |
Informatie klinische proef
(gegevens van https://clinicaltrials.gov, bijgewerkt op 2024-05-22)
| NCT-nummer | Rekrutering | Aandoeningen | Sponsor/Medewerkers | Startdatum | Fasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06177028 | Not yet recruiting | Cognitive Impairment Mild|Cognitive Dysfunction|Amyloid Plaque|Neurodegenerative Disease Hereditary|Inflammation Brain |
St. Joseph''s Hospital and Medical Center Phoenix|Texas Tech University |
January 2 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06149286 | Recruiting | Relapsed/Refractory Follicular Lymphoma|Marginal Zone Lymphoma (MZL) |
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals |
December 28 2023 | Phase 3 |
| NCT06299553 | Recruiting | DLBCL - Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma |
Incyte Biosciences Italy S.r.l |
December 4 2023 | -- |
Technische ondersteuning
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Als u nog andere vragen heeft, kunt u een bericht achterlaten.
Veelgestelde vragen
Vraag 1:
What is the formulation for its injection (i.p.) in mice?
Antwoord:
This paper has the information you need: http://link.springer.com/article/10.1208/s12248-012-9401-2. Add it to the appropriate volume of sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 1% hydrochloric acid (HCl). The pH of this preparation was adjusted to 7.0–7.6 using sodium hydroxide and sterile filtered using a 0.22 μm Steriflip filter.
Vraag 2:
what is the procedure to resuspend it?
Antwoord:
This compound can be resuspended by DMSO, with a solubility of about 52 mg/mL (200.57 mM). For in vivo study, the working solution can be prepared with the vehicle of: 30% PEG400/0.5% Tween80/5% propylene glycol for oral administration.
