Technische Daten
| Formel | C19H18FN3O.H3PO4 |
||||||
| Molekulargewicht | 421.36 | CAS-Nr. | 459868-92-9 | ||||
| Löslichkeit (25°C)* | In vitro | DMSO | 84 mg/mL (199.35 mM) | ||||
| Water | 2 mg/mL (4.74 mM) | ||||||
| Ethanol | Insoluble | ||||||
| In vivo (Lösungsmittel einzeln und der Reihe nach zum Produkt hinzufügen.) |
|
||||||
|
* <1 mg/ml bedeutet schwer löslich oder unlöslich. * Bitte beachten Sie, dass Selleck die Löslichkeit aller Verbindungen intern testet und die tatsächliche Löslichkeit geringfügig von veröffentlichten Werten abweichen kann. Dies ist normal und ist auf geringfügige Batch-zu-Batch-Variationen zurückzuführen. * Versand bei Raumtemperatur (Stabilitätstests zeigen, dass dieses Produkt ohne Kühlmaßnahmen versendet werden kann.) |
|||||||
Vorbereitung von Stammlösungen
Biologische Aktivität
| Beschreibung | Rucaparib phosphate ist ein Inhibitor von PARP mit einem Ki von 1,4 nM für PARP1 in einem zellfreien Assay und zeigt auch eine Bindungsaffinität zu acht anderen PARP-Domänen. Phase 3. | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ziele |
|
||
| In vitro | Rucaparib ist ein potenter Inhibitor der gereinigten humanen PARP-1 in voller Länge und zeigt eine höhere Hemmung der zellulären PARP in LoVo- und SW620-Zellen. Außerdem bindet Rucaparib nachweislich an acht weitere PARP-Domänen, darunter PARP2, 3, 4, 10, 15, 16, TNKS1 und TNKS2. Die Radiosensibilisierung durch Rucaparib beruht auf der nachgeschalteten Hemmung der NF-κB-Aktivierung und ist unabhängig von der SSB-Reparaturhemmung. Rucaparib könnte NF-κB angreifen, das durch DNA-Schäden aktiviert wird, und die bei klassischen NF-κB-Inhibitoren beobachtete Toxizität überwinden, ohne andere wichtige Entzündungsfunktionen zu beeinträchtigen. Rucaparib hemmt die PARP-1-Aktivität bei einer Konzentration von 1 μM in permeabilisierten D283Med-Zellen um 97,1 %. | ||
| In vivo | Rucaparib ist nicht toxisch, verstärkt aber signifikant die Temozolomid-induzierte TGD in DNA-Reparatur-kompetenten D384Med-Xenotransplantaten. Pharmakokinetische Studien zeigen auch, dass Rucaparib im Gehirngewebe nachgewiesen wird, was darauf hindeutet, dass Rucaparib Potenzial in der intrakraniellen Malignomtherapie hat. Rucaparib verstärkt signifikant die Zytotoxizität von Topotecan und Temozolomid in NB-1691-, SH-SY-5Y- und SKNBE(2c)-Zellen. Rucaparib verstärkt die Antitumoraktivität von Temozolomid und zeigt eine vollständige und anhaltende Tumorregression in NB1691- und SHSY5Y-Xenotransplantaten. | ||
| Merkmale | Der erste PARP-Inhibitor, der in klinischen Studien in Kombination mit Temozolomid eingesetzt wurde. |
Protokoll (aus Referenz)
| Kinase-Assay:[1] |
|
|---|---|
| Zell-Assay:[4] |
|
| Tierstudie:[4] |
|
Referenzen
|
Kundenproduktvalidierung
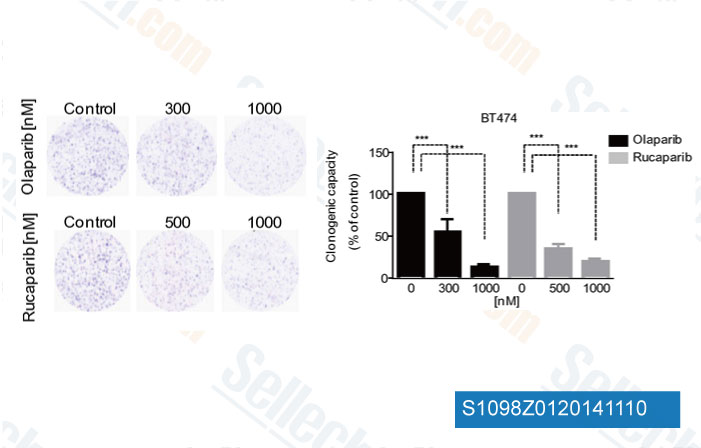
-
Daten von [ Eur J Cancer , 2014 , 50(15), 2725-34 ]
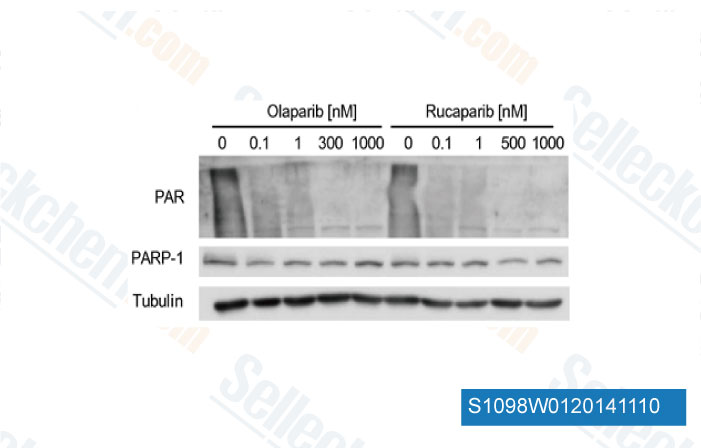
-
Daten von [ Eur J Cancer , 2014 , 50(15), 2725-34 ]
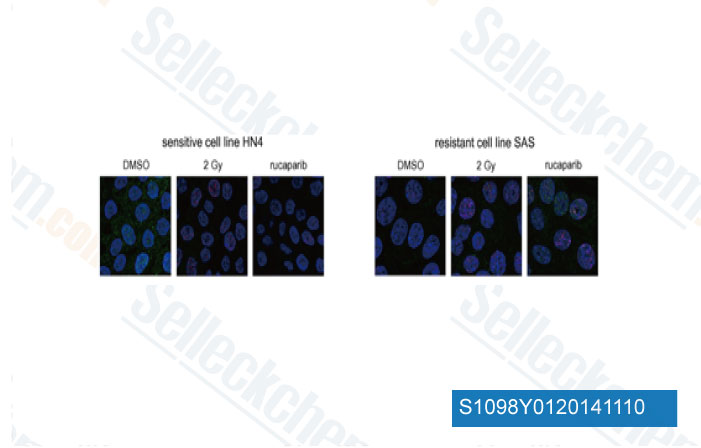
-
Daten von [ Oral Oncol , 2014 , 50(9), 825-31 ]
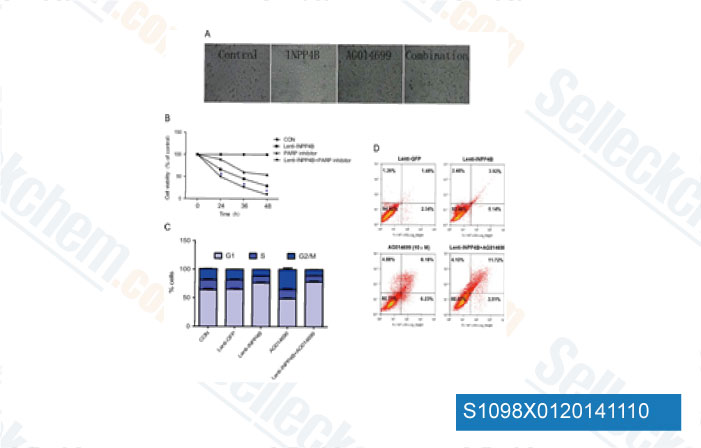
-
Daten von [ Urol Oncol , 2014 , 32(5), 720-6 ]
Sellecks Rucaparib phosphate Wurde zitiert von 136 Publikationen
| Uracil processing by SMUG1 in the absence of UNG triggers homologous recombination and selectively kills BRCA1/2-deficient tumors [ Mol Cell, 2025, S1097-2765(25)00098-X] | PubMed: 40010343 |
| PARG Mutation Uncovers Critical Structural Determinant for Poly(ADP-Ribose) Hydrolysis and Chromatin Regulation in Embryonic Stem Cells [ Cells, 2025, 14(14)1049] | PubMed: 40710302 |
| PARP inhibitors differentially regulate immune responses in distinct genetic backgrounds of high-grade serous tubo-ovarian carcinoma models [ Cancer Res Commun, 2025, 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-24-0515] | PubMed: 39851178 |
| Patient-derived rhabdomyosarcoma cells recapitulate the genetic and transcriptomic landscapes of primary tumors [ iScience, 2024, 27(10):110862] | PubMed: 39319271 |
| Human Fallopian Tube-Derived Organoids with TP53 and RAD51D Mutations Recapitulate an Early Stage High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Phenotype In Vitro [ Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(2)886] | PubMed: 38255960 |
| Exosomal miR-664a-5p as a therapeutic target biomarker for PARP inhibitor response in prostate cancer [ Am J Cancer Res, 2024, 14(8):3789-3799] | PubMed: 39267686 |
| CK2-HTATSF1-TOPBP1 signaling axis modulates tumor chemotherapy response [ J Biol Chem, 2024, 300(6):107377] | PubMed: 38762174 |
| BRCA2 Germline Mutations Identify Gastric Cancers Responsive to PARP Inhibitors [ Cancer Res, 2023, 83(10):1699-1710] | PubMed: 37129948 |
| Pharmacological depletion of RNA splicing factor RBM39 by indisulam synergizes with PARP inhibitors in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma [ Cell Rep, 2023, 42(10):113307] | PubMed: 37858464 |
| The Sensitization of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers to Poly ADP Ribose Polymerase Inhibition Independent of BRCA1/2 Mutation Status by Chemically Modified microRNA-489 [ Cells, 2023, 13(1)49] | PubMed: 38201253 |
RÜCKGABERICHTLINIE
Die bedingungslose Rückgaberichtlinie von Selleck Chemical gewährleistet unseren Kunden ein reibungsloses Online-Einkaufserlebnis. Wenn Sie in irgendeiner Weise mit Ihrem Kauf unzufrieden sind, können Sie jeden Artikel innerhalb von 7 Tagen nach Erhalt zurückgeben. Im Falle von Produktqualitätsproblemen, sei es protokollbezogene oder produktbezogene Probleme, können Sie jeden Artikel innerhalb von 365 Tagen ab dem ursprünglichen Kaufdatum zurückgeben. Bitte befolgen Sie die nachstehenden Anweisungen, wenn Sie Produkte zurücksenden.
VERSAND UND LAGERUNG
Selleck-Produkte werden bei Raumtemperatur transportiert. Wenn Sie das Produkt bei Raumtemperatur erhalten, seien Sie versichert, dass die Qualitätskontrollabteilung von Selleck Experimente durchgeführt hat, um zu überprüfen, dass die normale Temperaturplatzierung von einem Monat die biologische Aktivität von Pulverprodukten nicht beeinträchtigt. Nach dem Sammeln lagern Sie das Produkt bitte gemäß den in der Datenblatt beschriebenen Anforderungen. Die meisten Selleck-Produkte sind unter den empfohlenen Bedingungen stabil.
NICHT FÜR DIE ANWENDUNG AM MENSCHEN, FÜR VETERINÄRMEDIZINISCHE DIAGNOSTIK ODER THERAPEUTISCHE ZWECKE.
