Nur für Forschungszwecke
Phospho-RKIP (Ser153) Antibody [J22F24]
Kat.-Nr.: F3700
Anwendung:
Reaktivität:
Experimentiergrundlagen
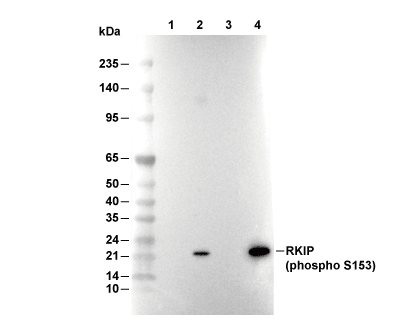
WB
Recommended wet transfer conditions: 200 mA, 60 min.
Recommended wet transfer conditions: 200 mA, 60 min.
Nutzungsinformationen
| Verdünnung |
|---|
|
| Anwendung |
|---|
| WB |
| Reaktivität |
|---|
| Rat, Human |
| Quelle |
|---|
| Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Lagerpuffer |
|---|
| PBS, pH 7.2+50% Glycerol+0.05% BSA+0.01% NaN3 |
| Lagerung (ab dem Datum des Erhalts) |
|---|
| -20°C (avoid freeze-thaw cycles), 2 years |
| Vorhergesagtes Molekulargewicht Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht |
|---|
| 21 kDa 21 kDa |
| *Warum unterscheiden sich das vorhergesagte und das tatsächliche Molekulargewicht? Die folgenden Gründe können Unterschiede zwischen dem vorhergesagten und dem tatsächlichen Protein-Molekulargewicht erklären. |
| Positivkontrolle | HeLa cells (PMA, 100ng/ml, 48 h); C6 cells (TPA, 0.5uM, 3 h) |
|---|---|
| Negativkontrolle | HeLa cells; C6 cells |
Experimentelle Methoden
| WB |
|---|
Experimental Protocol:
Sample preparation
1. Tissue: Lyse the tissue sample by adding an appropriate volume of ice-cold RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail),and homogenize the tissue at a low temperature. 2. Adherent cell: Aspirate the culture medium and wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 3. Suspension cell: Transfer the culture medium to a pre-cooled centrifuge tube. Centrifuge and aspirate the supernatant. Wash the cells with ice-cold PBS twice. Lyse the cells by adding an appropriate volume of RIPA/NP-40 Lysis Buffer (containing Protease Inhibitor Cocktail, Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail) and put the sample on ice for 5 min. 4. Place the lysate into a pre-cooled microcentrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 4°C for 15 min. Collect the supernatant;
5. Remove a small volume of lysate to determine the protein concentration;
6. Combine the lysate with protein loading buffer. Boil 20 µL sample under 95-100°C for 5 min. Centrifuge for 5 min after cool down on ice.
Electrophoretic separation
1. According to the concentration of extracted protein, load appropriate amount of protein sample and marker onto SDS-PAGE gels for electrophoresis. Recommended separating gel (lower gel) concentration: 10%. Reference Table for Selecting SDS-PAGE Separation Gel Concentrations 2. Power up 80V for 30 minutes. Then the power supply is adjusted (110 V~150 V), the Marker is observed, and the electrophoresis can be stopped when the indicator band of the predyed protein Marker where the protein is located is properly separated. (Note that the current should not be too large when electrophoresis, too large current (more than 150 mA) will cause the temperature to rise, affecting the result of running glue. If high currents cannot be avoided, an ice bath can be used to cool the bath.)
Transfer membrane
1. Take out the converter, soak the clip and consumables in the pre-cooled converter;
2. Activate PVDF membrane with methanol for 1 min and rinse with transfer buffer;
3. Install it in the order of "black edge of clip - sponge - filter paper - filter paper - glue -PVDF membrane - filter paper - filter paper - sponge - white edge of clip"; 4. The protein was electrotransferred to PVDF membrane. ( 0.45 µm PVDF membrane is recommended ) Reference Table for Selecting PVDF Membrane Pore Size Specifications Recommended conditions for wet transfer: 200 mA, 60 min. ( Note that the transfer conditions can be adjusted according to the protein size. For high-molecular-weight proteins, a higher current and longer transfer time are recommended. However, ensure that the transfer tank remains at a low temperature to prevent gel melting.)
Block
1. After electrotransfer, wash the film with TBST at room temperature for 5 minutes;
2. Incubate the film in the blocking solution ( recommending 5% BSA solution)
for 1 hour at room temperature;
3. Wash the film with TBST for 3 times, 5 minutes each time.
Antibody incubation
1. Use 5% skim milk powder to prepare the primary antibody working liquid (recommended dilution ratio for primary antibody 1:1000), gently shake and incubate with the film at 4°C overnight; 2. Wash the film with TBST 3 times, 5 minutes each time;
3. Add the secondary antibody to the blocking solution and incubate with the film gently at room temperature for 1 hour;
4. After incubation, wash the film with TBST 3 times for 5 minutes each time.
Antibody staining
1. Add the prepared ECL luminescent substrate (or select other color developing substrate according to the second antibody) and mix evenly;
2. Incubate with the film for 1 minute, remove excess substrate (keep the film moist), wrap with plastic film, and expose in the imaging system. |
Biologische Beschreibung
| Spezifität |
|---|
| Phospho-RKIP (Ser153) Antibody [J22F24] detects endogenous levels of total RKIP protein only when it is phosphorylated at Ser153. |
| Subzelluläre Lokalisierung |
|---|
| Cytoplasm |
| Uniprot ID |
|---|
| P30086 |
| Klon |
|---|
| J22F24 |
| Synonym |
|---|
| PBP; PEBP; PEBP1; Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1; PEBP-1; HCNPpp; Neuropolypeptide h3; Prostatic-binding protein; Raf kinase inhibitor protein; RKIP |
| Hintergrund |
|---|
| Phospho-RKIP (Ser153) is the protein kinase C (PKC)-phosphorylated form of Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP), a member of the phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein (PEBP) family. In its unphosphorylated state, RKIP inhibits Raf-1/MEK/ERK signaling by binding Raf-1 via a conserved ligand-binding pocket containing a flexible helix with Ser153. Upon phosphorylation at Ser153, primarily by PKCζ downstream of GPCR activation, the helix unfolds, disrupting Raf-1 association and exposing interfaces that facilitate GRK2 binding and RKIP homodimerization through symmetric phosphorylated monomer interactions. This phosphorylation relieves RKIP-mediated inhibition of the Raf-MEK-ERK cascade, leading to enhanced MAPK activation and promoting cell proliferation, migration, and survival. Concurrently, phospho-RKIP sequesters GRK2, preventing GPCR desensitization and internalization, thereby sustaining GPCR signaling and facilitating persistent Raf-1 phosphorylation. Phospho-RKIP modulates the NF-κB pathway by interacting with NIK/TAK1/IKK complexes and influences apoptosis and cytokine signaling suppression (SOCS induction). Pathologically, elevated phospho-Ser153 RKIP is linked to cancer progression and metastasis (e.g., prostate, colorectal) through increased ERK activity, tumor invasion, and impaired immune surveillance owing to reduced SOCS/NF-κB suppression. It also correlates with chemoresistance and poor prognosis and contributes to inflammatory diseases such as arthritis via unchecked GPCR signaling. |
| Referenzen |
|---|
|
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.