nur für Forschungszwecke
PX-12 Thioredoxin Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S7947
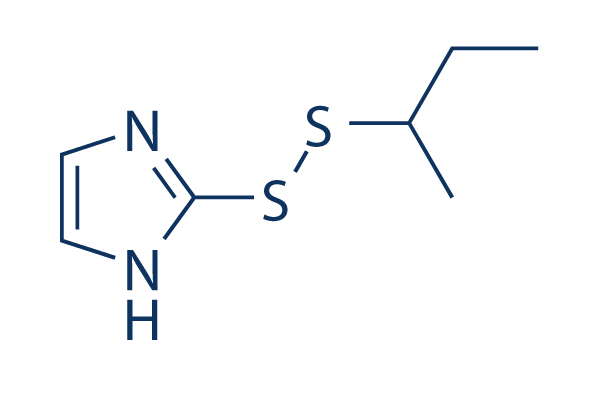
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 188.31
Qualitätskontrolle
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T84 | Function assay | 3 hrs | Inhibition of human recombinant thioredoxin-mediated TG2 activation expressed in T84 cells assessed as blockade of 5-biotinamidopentylamine incorporation after 3 hrs by fluorescence microscopic analysis, IC50=2.11μM | 23327656 | ||
| MEF | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against mouse MEF cells, LD50=2.7μM | 22128876 | |||
| Ramos | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human Ramos cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, LD50=3.4μM | 22128876 | ||
| PancO2 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against mouse PancO2 cells after 72 hrs by crystal violet staining, LD50=3.9μM | 22128876 | ||
| T24 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human T24 cells after 72 hrs by crystal violet staining, LD50=4.6μM | 22128876 | ||
| B78 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against mouse B78 cells after 72 hrs by crystal violet staining, LD50=5μM | 22128876 | ||
| CT26 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against wild type mouse CT26 cells after 72 hrs by crystal violet staining, LD50=5.2μM | 22128876 | ||
| K562 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human K562 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, LD50=5.5μM | 22128876 | ||
| M21 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human M21 cells, GI50=8.3μM | 18502639 | |||
| MCF7 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human MCF7 cells, GI50=8.3μM | 18502639 | |||
| MCF7 | Antiproliferative assay | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human MCF7 cells after 48 hrs by sulforhodamine B method, GI50=8.3μM | 18617414 | ||
| M21 | Antiproliferative assay | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human M21 cells after 48 hrs by sulforhodamine B method, GI50=8.3μM | 18617414 | ||
| Raji | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human Raji cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, LD50=8.8μM | 22128876 | ||
| EMT6 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against mouse EMT6 cells after 72 hrs by crystal violet staining, LD50=11.6μM | 22128876 | ||
| HT29 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human HT29 cells, GI50=25μM | 18502639 | |||
| HT29 | Antiproliferative assay | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HT29 cells after 48 hrs by sulforhodamine B method, GI50=25μM | 18617414 | ||
| M21 | Function assay | 25 nM | 16 hrs | Stimulation of nuclear translocation of thioredoxin-1 from cytosol in human M21 cells at 25 nM after 16 hrs by immunocytofluorescence | 18617414 | |
| Raji | Function assay | 5 to 10 uM | 4 to 24 hrs | Induction of Trx mRNA expression in human Raji cells at 5 to 10 uM after 4 to 24 hrs by RT-PCR analysis | 22128876 | |
| Raji | Function assay | 10 to 20 uM | 4 to 8 hrs | Induction of Trx protein expression in human Raji cells at 10 to 20 uM after 4 to 8 hrs by Western blot analysis | 22128876 | |
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 188.31 | Formel | C7H12N2S2 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 141400-58-0 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | DB05448, 1-methyl propyl 2-imidazolyl disulfide | Smiles | CCC(C)SSC1=NC=CN1 | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 38 mg/mL
(201.79 mM)
Ethanol : 38 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Trx-1
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
In MCF-7- und HT-29-Zellen verhindert PX-12 den Hypoxie (1% Sauerstoff)-induzierten Anstieg des HIF-1alpha-Proteins und verringert die HIF-1-transaktivierende Aktivität, die VEGF-Bildung und die induzierbare Stickoxidsynthase. Diese Verbindung hemmt auch das Wachstum von MCF-7- und HT-29-Zellen mit IC50-Werten von 1,9 μM bzw. 2,9 μM. Es hemmt auch die HIF-1α-Proteinspiegel durch eine Nrf2/PMF-1-vermittelte Erhöhung. In A549-Zellen hemmt diese Chemikalie das Zellwachstum über G2/M-Phasenarrest und Bax-vermittelte und ROS-abhängige Apoptose. In Hepatozellulären Karzinomzellen übt es einen synergistischen Effekt mit 5-FU aus, um die Tumorigenität signifikant zu unterdrücken.
|
| In vivo |
Bei Mäusen mit MCF-7-Tumor-Xenotransplantaten reduziert PX-12 (12 mg/kg, i.p.) die HIF-1α- und VEGF-Proteinspiegel und die Mikrovessel-Dichte.
|
Literatur |
|
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00736372 | Completed | Metastatic Cancer|Advanced Cancer |
Cascadian Therapeutics Inc.|Seagen Inc. |
June 2008 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00417287 | Terminated | Pancreatic Neoplasms |
Cascadian Therapeutics Inc.|National Cancer Institute (NCI)|Translational Genomics Research Institute|Seagen Inc. |
December 2006 | Phase 2 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
