nur für Forschungszwecke
Berberine chloride Anti-infection chemisch
Kat.-Nr.S2271
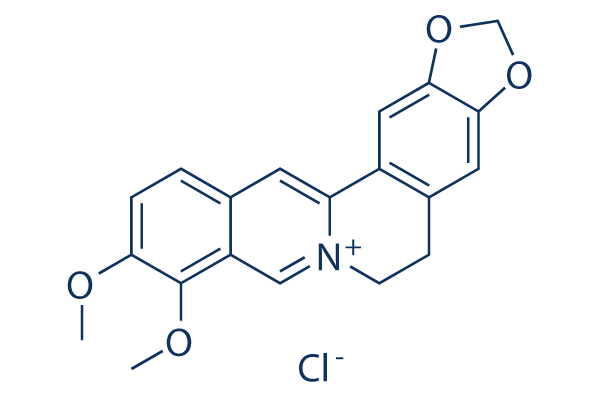
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 371.81
Qualitätskontrolle
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRC5 cells | Function assay | Antiviral activity against HCMV in MRC5 cells by plaque reduction assay, IC50=0.68 μM | ||||
| MRC5 cells | Proliferation assay | 10 μM | 54 hrs | Inhibition of HCMV proliferation in MRC5 cells after 54 hrs post-infection at 10 uM by plaque assay | ||
| MRC5 cells | Proliferation assay | 10 μM | 24 h | Inhibition of HCMV proliferation in MRC5 cells after 24 hrs post-infection at 10 uM by plaque assay | ||
| Bel7402 cells | Function assay | 12 h | Induction of LDLR protein in human Bel7402 cells after 12 hrs by RT-PCR assay relative to control | |||
| HepG2 cells | Function assay | 10 ug/mL | 12 h | Induction of LDLR protein expression in human HepG2 cells at 10 ug/mL after 12 hrs by flow cytometry | ||
| KB cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human KB cells after 72 hrs, IC50=7.32 μM | |||
| HL60 cells | Apoptosis assay | 48 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human HL60 cells after 48 hrs using annexin V-propidium iodide staining by FACS analysis | |||
| A549 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells by SRB assay, IC50=6.27 μM | ||||
| SKOV3 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human SKOV3 cells by SRB assay, IC50=16.44 μM | ||||
| SK-MEL-2 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human SK-MEL-2 cells by SRB assay, IC50=13.76 μM | ||||
| HCT15 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human HCT15 cells by SRB assay, IC50=16.59 μM | ||||
| CEM cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human CEM cells expressing green fluorescent protein after 48 hrs by MTT assay, CC50=2.09 μM | |||
| human CEM cells | Function assay | 7 days | Antiviral activity against 0.05 MOI Human immunodeficiency virus 1 NL4.3 infected in human CEM cells expressing green fluorescent protein assessed as p24 antigen production measured 7 days post infection by ELISA, EC50=0.13 μM | |||
| SKN cells | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | Growth inhibition against human SKN cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=15.88 μM | |||
| RKN cells | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | Growth inhibition against human RKN cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=49.6 μM | |||
| G402 cells | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | Growth inhibition against human G402 cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, GI50=11.87 μM | |||
| A10 cells | Function assay | 30 μM | 24 hrs | Downregulation of Scd2 mRNA expression in rat A10 cells at 30 uM after 24 hrs by quantitative RT-PCR analysis | ||
| A10 cells | Function assay | 30 μM | 24 hrs | Down regulation of Prim2 mRNA expression in rat A10 cells at 30 uM after 24 hrs by quantitative RT-PCR analysis | ||
| A10 cells | Function assay | 30 μM | 24 hrs | Downregulation of Impk mRNA expression in rat A10 cells at 30 uM after 24 hrs by quantitative RT-PCR analysis | ||
| HepG2-A16-CD81 cells | Function assay | 10 μM | NOVARTIS: Antimalarial liver stage activity measured as a greater than 50% reduction in Plasmodium yoelii schizont area in HepG2-A16-CD81 cells at 10uM compound concentration, determined by immuno-fluorescence. | |||
| HepG2-A16-CD81 cells | Function assay | 10 μM | NOVARTIS: Antimalarial liver stage activity measured as reduction in Plasmodium yoelii schizont area in HepG2-A16-CD81 cells by immuno-fluorescence, and median schizont size at 10uM compound concentration, IC50=0.548 μM | |||
| HepG2 cells | Function assay | 10 μM | 4 h | Increase in AMPKalpha phosphorylation in human HepG2 cells at 10 uM after 4 hrs by Western blot analysis relative to untreated control | ||
| HepG2 cells | Function assay | 10 μM | 4 h | Increase in total AMPKalpha level in human HepG2 cells at 10 uM after 4 hrs by Western blot analysis relative to untreated control | ||
| HepG2 cells | Function assay | 20 μM | 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human HepG2 cells assessed as morphological changes at 20 uM after 24 hrs using Hoechst 33258 staining by fluorescence microscopic analysis | ||
| HT-29 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HT-29 cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=8.45 μM | |||
| HepG2 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HepG2 cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=11.22 μM | |||
| HepG2 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HepG2 cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=8.32 μM | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 371.81 | Formel | C20H18NO4.Cl |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 633-65-8 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 25 mg/mL
(67.23 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Caspase-3
Caspase-8
PARP
cytochrome c
cIAP1
Bcl-2
Bcl-xL
JNK
p38 MAPK
ROS
Topo I
Topo II
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Im Vergleich zu Regorafenib allein hemmt die kombinierte Behandlung von Berberine (BBR) und Regorafenib signifikant die Proliferation von Leberzellkarzinom (HCC)-Zellen und induziert die zelluläre Apoptosis. |
| In vivo |
Die kombinierte Behandlungsgruppe mit Berberine (BBR) und Regorafenib hat eine dramatische Hemmwirkung auf das Wachstum von Leberzellkarzinom (HCC)-Xenograft-Tumoren in Nacktmäusen. Die erhöhte Apoptosis von Xenograft-Tumoren wird in der kombinierten Behandlungsgruppe beobachtet. |
Literatur |
|
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06273241 | Not yet recruiting | Pharmacokinetic Study in Healthy Volunteers |
University Medicine Greifswald |
March 4 2024 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05845931 | Recruiting | Pharmacokinetic Study in Healthy Volunteers |
University Medicine Greifswald |
May 5 2023 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05480670 | Completed | Polycystic Ovary Syndrome |
Ayub Teaching Hospital |
November 1 2022 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05463003 | Completed | Pharmacokinetic Study in Healthy Volunteers |
University Medicine Greifswald |
July 19 2022 | Not Applicable |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
