nur für Forschungszwecke
Pomalidomide (CC-4047) Immunmodulatorisches Mittel
Kat.-Nr.S1567
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 273.24
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | Proteasome E1 Activating E3 Ligase DUB p97 SUMO E2 conjugating |
|---|---|
| Weitere E3 ligase Ligand Inhibitoren | CC-99282 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOLP-8 | Cytotoxicity Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | potently augments direct and indirect MM cell killing by SAR | 26338273 | |
| J-CD38 | Cytotoxicity Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | potently augments direct and indirect MM cell killing by SAR | 26338273 | |
| R-CD38 | Cytotoxicity Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | potently augments direct and indirect MM cell killing by SAR | 26338273 | |
| BC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 39-1250 nM | 5 d | DMSO | IC50=107 nM, inhibits cell IC50=107 nM, viability dose dependently | 26119939 |
| BCBL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 39-1250 nM | 5 d | DMSO | IC50=74 nM, inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 26119939 |
| JSC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 39-1250 nM | 5 d | DMSO | IC50=34 nM, inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 26119939 |
| VG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 39-1250 nM | 5 d | DMSO | IC50=101 nM, inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 26119939 |
| UMPEL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 39-1250 nM | 5 d | DMSO | IC50=32 nM, inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 26119939 |
| UMPEL-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 39-1250 nM | 5 d | DMSO | IC50=111 nM, inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 26119939 |
| BC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 39-1250 nM | 5 d | DMSO | IC50=744 nM, inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 26119939 |
| BCP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 39-1250 nM | 5 d | DMSO | IC50=396 nM, inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 26119939 |
| APK-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 39-1250 nM | 5 d | DMSO | IC50=226 nM, inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 26119939 |
| RPMI8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.01-50 μM | 48 h | DMSO | IC50=8 μM | 26097872 |
| OPM2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.01-50 μM | 48 h | DMSO | IC50=10 μM | 26097872 |
| RPMI8226 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 48 h | DMSO | strengthens cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling of mTOR and p-mTOR protein | 26097872 |
| OPM2 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 48 h | DMSO | strengthens cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling of mTOR and p-mTOR protein | 26097872 |
| RPMI8226 | Function Assay | 0.1-10 μM | 4 h | DMSO | increases VEGF mRNA expression | 25053990 |
| SH-SY5Y | Apoptosis Assay | 25 μg/mL | 1 h | causes statistically significant reduction in both CPF- and CPF+CM-induced apoptosis | 24975276 | |
| JJN3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1-100 μM | 72 h | DMSO | inhibits cell growth slightly | 23178378 |
| XG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1-100 μM | 72 h | DMSO | inhibits cell growth | 23178378 |
| CD138+ | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1-100 μM | 72 h | DMSO | inhibits cell growth | 23178378 |
| XG-1 | Function Assay | 2/100 μM | 24 h | DMSO | inhibits CCL3/MIP-1α mRNA expression | 23178378 |
| U266 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.01-10 μM | 48 h | DMSO | inhibits cell growth dose dependently | 22552008 |
| CRBN60 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.01-10 μM | 48 h | DMSO | inhibits cell growth dose dependently | 22552008 |
| CRNB75 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.01-10 μM | 48 h | DMSO | inhibits cell growth dose dependently | 22552008 |
| MM.1S | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.01-10 μM | 48 h | DMSO | significantly inhibits proliferation at concentrations as low as 0.01μM | 21389327 |
| OPM2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.01-10 μM | 48 h | DMSO | significantly inhibits proliferation at concentrations as low as 0.01μM | 21389327 |
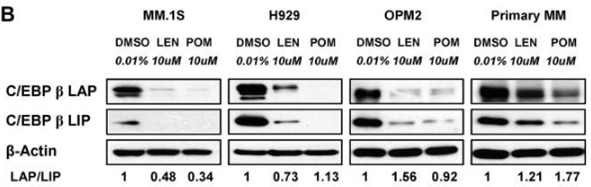
| MM.1S | Function Assay | 10 μM | 72 h | DMSO | significantly decreases the protein level of C/EBPβ isoforms | 21389327 |
| H929 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 72 h | DMSO | significantly decreases the protein level of C/EBPβ isoforms | 21389327 |
| OPM2 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 72 h | DMSO | significantly decreases the protein level of C/EBPβ isoforms | 21389327 |
| CT26 | Function Assay | 1/10 μM | 24 h | reduces the numbers of live colonies | 19638977 | |
| T-cells | Function assay | 2 to 3 days | Inhibition of IL-2 production in human T cells measured after 2 to 3 days by ELISA, EC50 = 0.008 μM. | 23168019 | ||
| DF15 | Function assay | 4 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated aiolos degradation in human DF15 cells expressing ePL-tagged aiolos after 4 hrs by luminometric analysis, EC50 = 0.022 μM. | 28425720 | ||
| DF15 | Function assay | 4 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated ikaros degradation in human DF15 cells expressing ePL-tagged ikaros after 4 hrs by luminometric analysis, EC50 = 0.024 μM. | 28425720 | ||
| DF15 | Function assay | 4 hrs | Induction of CRL4/CRBN ubiquitin ligase-mediated aiolos degradation in human DF15 cells expressing pLOC-ePL-tagged aiolos after 4 hrs by luminescence based beta-galactosidase enzyme fragmentation complementation assay, EC50 = 0.027 μM. | 28358507 | ||
| NAMALWA | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human NAMALWA cells assessed as inhibition of [3H]thymidine incorporation after 72 hrs by scintillation counting, IC50 = 0.03 μM. | 23168019 | ||
| HeLa | Function assay | Inhibition of IL-1-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation in HeLa cells assessed as blocking of p50/p65 nuclear translocation, IC50 = 1.27 μM. | 17845850 | |||
| DF15 | Function assay | 0.01 to 1 uM | 5 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated aiolos degradation in human DF15 cells at 0.01 to 1 uM after 5 hrs by immunoblot analysis | 28425720 | |
| OPM2 | Function assay | 0.01 to 1 uM | 5 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated ikaros degradation in human OPM2 cells at 0.01 to 1 uM after 5 hrs by immunoblot analysis | 28425720 | |
| DF15 | Function assay | 0.01 to 1 uM | 5 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated ikaros degradation in human DF15 cells at 0.01 to 1 uM after 5 hrs by immunoblot analysis | 28425720 | |
| OPM2 | Function assay | 0.01 to 1 uM | 5 hrs | Induction of cereblon-mediated aiolos degradation in human OPM2 cells at 0.01 to 1 uM after 5 hrs by immunoblot analysis | 28425720 | |
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 273.24 | Formel | C13H11N3O4 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 19171-19-8 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | CC-4047 | Smiles | C1CC(=O)NC(=O)C1N2C(=O)C3=C(C2=O)C(=CC=C3)N | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 100 mg/mL
(365.97 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Merkmale |
A derivative of thalidomide and up to 10,000 times more potent than thalidomide.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
CRBN
TNF-α
(PBMCs) 13 nM
|
| In vitro |
Pomalidomide hemmt die durch Lipopolysaccharid (LPS) stimulierte TNF-alpha-Freisetzung in menschlichen PBMC und in menschlichem Vollblut mit IC50-Werten von 13 nM bzw. 25 nM. Diese Verbindung hemmt das Wachstum von durch IL-2 stimulierten T-regulatorischen Zellen mit einer IC50 von ~1 μM. Die Behandlung mit dieser Chemikalie (6,4 nM-10 μM) erhöht die Produktion von IL-2 in menschlichen peripheren Blut-T-Zellen und ist in der CD4+-Untergruppe etwas potenter als in der CD8+-Untergruppe. Es ist signifikant potenter als CC-5013 bei der Erhöhung von IL-2-, IL-5- und IL-10-Spiegeln, aber nur geringfügig potenter als CC-5013 bei der Erhöhung von IFN-γ-Spiegeln. Dieses Mittel verstärkt die SEE- und Raji-Zellen induzierte AP-1-Transkriptionsaktivität in Jurkat-Zellen dosisabhängig, mit einer maximalen Verstärkung von 4-fach bei 1 μM. Die Exposition von Raji-Zellen gegenüber verschiedenen Konzentrationen dieser Verbindung (2,5-40 μg/mL) über 48 Stunden führt zu einer signifikanten Abnahme der Zellproliferation und DNA-Synthese. Es gibt eine Reduktion von ~40% im Vergleich zu Vehikel-behandelten Kontrollen. |
| Kinase-Assay |
Hemmung der TNF-α-Synthese
|
|
Die TNF-α-hemmende Aktivität wird in Lipopolysaccharid (LPS)-stimulierten PBMC gemessen. Pomalidomide wird den menschlichen PBMCs 1 Stunde vor der Zugabe von LPS (1 μg/mL) zugesetzt und die Inkubation für weitere 18-20 Stunden fortgesetzt. Die Überstände werden dann geerntet und die Konzentration von TNF-α in den Überständen wird mittels ELISA bestimmt. Die Konzentration dieser Verbindung, die die TNF-Produktion um 50% hemmt (IC50), wird mittels nichtlinearer Regressionsanalyse berechnet. Der menschliche Vollblut-TNF-Inhibitionsassay wird ähnlich wie der PBMC-Assay durchgeführt, außer dass heparinisiertes frisches menschliches Vollblut direkt in Mikrotiterplatten plattiert wird.
|
|
| In vivo |
Pomalidomide verstärkt die Antitumorwirkung von Rituximab gegen B-Zell-Lymphome in Mäusen mit schwerem kombiniertem Immundefekt. Die Verabreichung dieser Verbindung in Kombination mit Rituximab verleiht den Mäusen eine mediane Überlebenszeit von 74 Tagen im Vergleich zu 58 Tagen bei CC5013/Rituximab-Behandlung und 45 Tagen bei Rituximab-Monotherapie. Der synergistische Effekt dieser Verbindung und Rituximab kann durch die Depletion von NK-Zellen vollständig aufgehoben werden, was die Annahme unterstützt, dass die Expansion von NK-Zellen ein Mechanismus ist, durch den diese Verbindung die Antitumoraktivität von Rituximab verstärken kann. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | CEBPβ IKZF1 / IKZF3 / UBE2G1 / CRBN |
|
21389327 |
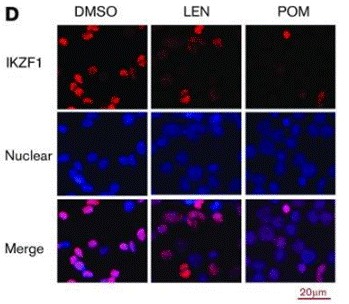
| Immunofluorescence | IKZF1 |
|
29496670 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04902443 | Recruiting | Viral Associated Malignancies|Kaposi Sarcoma|EBV/KSHV-associated Lymphomas |
National Cancer Institute (NCI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
December 10 2021 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
Is the formulation S1567 in 1% DMSO+30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80 suitable for its oral administration?
Antwort:
Its suspension in 1% DMSO+30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80 is for oral gavage.
Frage 2:
I would like to know if it is racemic or optically active?
Antwort:
Our S1567 is racemic.
