nur für Forschungszwecke
Nitazoxanide Influenza Virus Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1627
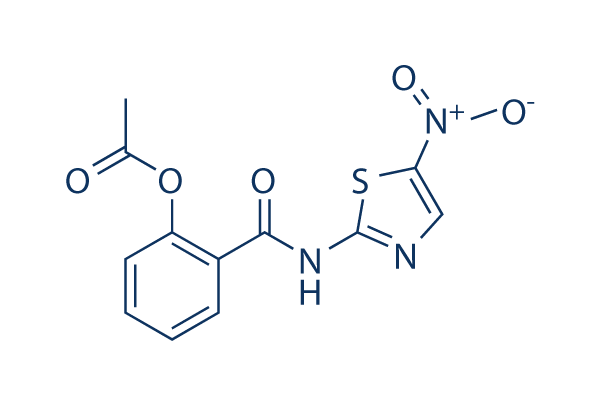
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 307.28
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | Integrase Bacterial Antibiotics Anti-infection Fungal Antiviral COVID-19 Parasite Reverse Transcriptase HIV |
|---|---|
| Weitere Influenza Virus Inhibitoren | Arbidol HCl Nucleozin D-Pinitol (-)-Arctigenin Adamantane Cetylpyridinium chloride monohydrate Chebulinic acid |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2(2.2.15) | Antiviral assay | Antiviral activity against Hepatitis B virus infected in human HepG2(2.2.15) cells assessed as decrease in extracellular viral DNA measured 24 hrs after last dose, EC50=0.12μM | 21553812 | |||
| HepG2(2.2.15) | Antiviral assay | Antiviral activity against HBV infected in human HepG2(2.2.15) cells assessed as inhibition of extracellular viral DNA level, IC50=0.12μM | 28383274 | |||
| Ava5 | Antiviral assay | 3 days | Antiviral activity against HCV genotype 1b infected in Ava5 cells assessed as inhibition of viral replication after 3 days by blot hybridization analysis, EC50=0.21μM | 22059983 | ||
| Huh7.5 | Antiviral assay | 3 days | Antiviral activity against HCV genotype 1a infected in Huh7.5 cells assessed as inhibition of viral replication after 3 days by blot hybridization analysis, EC50=0.33μM | 22059983 | ||
| HepG2(2.2.15) | Antiviral assay | Antiviral activity against Hepatitis B virus infected in human HepG2(2.2.15) cells assessed as decrease in intracellular viral DNA measured 24 hrs after last dose, EC50=0.59μM | 21553812 | |||
| HepG2(2.2.15) | Antiviral assay | Antiviral activity against Hepatitis B virus infected in human HepG2(2.2.15) cells assessed as decrease in extracellular viral DNA measured 24 hrs after last dose, EC90=0.83μM | 21553812 | |||
| Ava5 | Antiviral assay | 3 days | Antiviral activity against HCV genotype 1b infected in Ava5 cells assessed as inhibition of viral replication after 3 days by blot hybridization analysis, EC90=0.93μM | 22059983 | ||
| Huh7.5 | Antiviral assay | 3 days | Antiviral activity against HCV genotype 1a infected in Huh7.5 cells assessed as inhibition of viral replication after 3 days by blot hybridization analysis, EC90=1.1μM | 22059983 | ||
| BHK-21 | Antiviral assay | Antiviral activity against Chikungunya virus 0611aTw infected in BHK-21 cells by RT-qPCR analysis, EC50=1.96μM | 28689975 | |||
| HepG2(2.2.15) | Antiviral assay | Antiviral activity against Hepatitis B virus infected in human HepG2(2.2.15) cells assessed as decrease in intracellular viral DNA measured 24 hrs after last dose, EC90=2.1μM | 21553812 | |||
| HCT8 | Antiparasitic assay | 48 hrs | Antiparasitic activity against Cryptosporidium parvum SPL infected in human HCT8 cells incubated for 48 hrs by FITC/DAPI staining based fluorescence assay, EC50=2.3μM | 29469575 | ||
| Vero E6 | Function assay | 48 hrs | IC50 for antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 in the Vero E6 cell line at 48 h by immunofluorescence-based assay (detecting the viral NP protein in the nucleus of the Vero E6 cells), IC50=2.81838μM | 32353859 | ||
| HCT8 | Antiparasitic assay | 48 hrs | Antiparasitic activity against Cryptosporidium parvum BGF infected in human HCT8 cells incubated for 48 hrs by FITC/DAPI staining based fluorescence assay, EC50=2.9μM | 29469575 | ||
| BHK-21 | Antiviral assay | Antiviral activity against Chikungunya virus infected in BHK-21 cells by RT-qPCR analysis, EC50=2.96μM | 28689975 | |||
| U2OS | Antiviral assay | Antiviral activity against Chikungunya virus infected in human U2OS cells by RT-qPCR analysis, EC50=3.01μM | 28689975 | |||
| HCT8 | Antiparasitic assay | Antiparasitic activity against Cryptosporidium parvum in HCT8 cells, IC50=3.25μM | 16480281 | |||
| HCT-8 | Antimicrobial assay | Antimicrobial activity against Cryptosporidium parvum infected in human HCT-8 cells, IC50=3.8μM | 18591280 | |||
| BHK-21 | Antiviral assay | Antiviral activity against Chikungunya virus 0810bTw infected in BHK-21 cells by RT-qPCR analysis, EC50=4.95μM | 28689975 | |||
| Vero | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against african green monkey Vero cells assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by WST-1 assay, IC50=10.74μM | 23787289 | ||
| BHK21 | Cytotoxicity assay | 16 hrs | Cytotoxicity against BHK21 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 16 hrs by CCK-8 assay, CC50=25μM | 28689975 | ||
| U2OS | Cytotoxicity assay | 16 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human U2OS cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 16 hrs by CCK-8 assay, CC50=25μM | 28689975 | ||
| Ava5 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | Cytotoxicity against human Ava5 cells after 3 days by neutral red dye assay, CC50=35μM | 22059983 | ||
| Huh7.5 | Cytotoxicity assay | 3 days | Cytotoxicity against human Huh7.5 cells after 3 days by neutral red dye assay, CC50=49μM | 22059983 | ||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 307.28 | Formel | C12H9N3O5S |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 55981-09-4 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | NTZ, NSC 697855 | Smiles | CC(=O)OC1=CC=CC=C1C(=O)NC2=NC=C(S2)[N+](=O)[O-] | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 62 mg/mL
(201.77 mM)
Ethanol : 62 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
PFOR
mTORC1
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Nitazoxanide reduziert das Parasitenwachstum in Zellkulturen um mehr als 90 % mit geringen Anzeichen einer medikamentenassoziierten Zytotoxizität. Diese Verbindung ist ein neues thiazolides Antiparasitikum, das eine ausgezeichnete In-vitro-Aktivität gegen eine Vielzahl von Protozoen und Helminthen zeigt. Es und sein Metabolit Tizoxanide sind in vitro aktiver als Metronidazol gegen G. intestinalis, E. histolytica und T. vaginalis. Dieser Wirkstoff zeigt eine potente Hemmung sowohl der HBV- als auch der HCV-Replikation. Er verstärkt die Wirkung einer nachfolgenden Behandlung mit dieser Verbindung plus IFN, aber nicht dieser Chemikalie plus 2'CmeC, in HCV-Replikon-haltigen Zellen. Diese Chemikalie induziert eine Reduktion mehrerer HBV-Proteine (HBsAg, HBeAg, HBcAg), die von 2.2.15-Zellen produziert werden, beeinflusst jedoch nicht die HBV-RNA-Transkription. Es zeigt IC50- und IC90-Werte von 0,017 bzw. 0,776 mg/mL gegen E. histolytica, 0,004 bzw. 0,067 mg/mL gegen G. intestinalis und 0,034 bzw. 2,046 mg/mL gegen T. vaginalis. Diese Verbindung ist toxischer als Metronidazol und Albendazol gegen E. histolytica. |
| In vivo |
Nitazoxanide ist teilweise wirksam bei der Reduzierung der Parasitenlast in einem gnotobiotischen Ferkeldiarrhoe-Modell, wenn es oral 11 Tage lang mit 250 mg/kg/Tag verabreicht wird, jedoch nicht mit 125 mg/kg/Tag. Diese Verbindung induziert bei Ferkeln eine medikamentenbedingte Diarrhoe, die die therapeutische Wirksamkeit beeinflusst haben könnte. |
Literatur |
|
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06049901 | Recruiting | Metastatic Colorectal Cancer |
Tanta University |
March 1 2023 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05701423 | Recruiting | Multiple Sclerosis |
Biogen |
February 8 2023 | -- |
| NCT05368935 | Completed | Renal Impairment|Renal Disease|Kidney Disease |
Genfit |
April 25 2022 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05116826 | Completed | Moderate Hepatic Impairment|Severe Hepatic Impairment|Liver Diseases |
Genfit |
November 5 2021 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03656068 | Completed | Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis|Fatty Liver|Fibrosis Liver|Compensated Cirrhosis |
Pinnacle Clinical Research PLLC |
December 4 2018 | Phase 2 |
| NCT02684240 | Completed | Tuberculosis |
Weill Medical College of Cornell University |
February 2016 | Phase 2 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
