Wnt proteins form a family of highly conserved secreted signaling molecules that regulate cell-to-cell interactions during embryogenesis. Wnt signalling pathway plays a key role in the development of CSC(Cancer stem cell) and it may be a significant step in the development of a large number of tomours. As currently understood, Wnt proteins bind to receptors of the Frizzled and LRP families on the cell surface. [show the full text]
Wnt/beta-catenin Inhibitoren/Aktivatoren (Wnt/beta-catenin Inhibitors/Activators)
Weitere Stem Cells & Wnt Inhibitoren
- Ausgewählte Inhibitoren
- Inhibitoren (34)
- Modulatoren (3)
- Agonisten (4)
- Aktivatoren (11)
- Agonisten (4)
| Kat.-Nr. | Produktname | Informationen | Publikationen | Validierung |
|---|---|---|---|---|
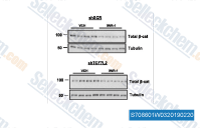
| S7086 | IWR-1-endo | IWR-1-endo (endo-IWR 1, IWR-1) ist ein Wnt-Signalweginhibitor mit einer IC50 von 180 nM in Wnt3A-exprimierenden L-Zellen, induziert die Axin2-Proteinspiegel und fördert die β-Catenin-Phosphorylierung durch Stabilisierung von Axin-Gerüst-Destruktionskomplexen. |
|
|
| S8968 | PRI-724 (Foscenvivint) | Foscenvivint (PRI-724) ist ein potenter und spezifischer Inhibitor, der die Interaktion von β-Catenin und CBP stört. |
|
|
| S7085 | IWP-2 | IWP-2 ist ein Inhibitor der Wnt-Verarbeitung und -Sekretion mit einem IC50-Wert von 27 nM in einem zellfreien Assay, selektiver Blockierung der Porcn-vermittelten Wnt-Palmitoylierung, beeinflusst Wnt/β-catenin im Allgemeinen nicht und zeigt keine Wirkung gegen Wnt-stimulierte zelluläre Reaktionen. IWP-2 hemmt spezifisch CK1δ. |
|
|
| S0733 | Tegatrabetan (BC-2059) | Tegatrabetan (BC-2059, Tegavivint), ein Antagonist von β-Catenin, stört die Bindung von β-Catenin an das Gerüstprotein Transducin-β-ähnliches 1 (TBL1) und den proteasomalen Abbau, was zu einer Abnahme der nukleären β-Catenin-Spiegel führt. |
|
|
| S3842 | Isoquercitrin | Isoquercitrin (Hirsutrin, 3-Glucosylquercetin, Quercetin 3-o-glucopyranosid), eine Flavonoidverbindung mit Antikrebsaktivität, isoliert aus Bidens bipinnata L, ist ein Inhibitor von Wnt/ A-Catenin, der nachgeschaltet der nukleären Translokation von A-Catenin wirkt. |
|
|
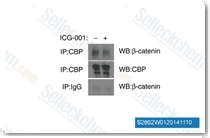
| S2662 | ICG-001 | ICG-001 antagonisiert die Wnt/β-Catenin/TCF-vermittelte Transkription und bindet spezifisch an das CREB-bindende Protein (CBP) mit einem IC50 von 3 μM, jedoch nicht an den verwandten transkriptionellen Koaktivator p300. ICG-001 induziert Apoptose. |
|
|
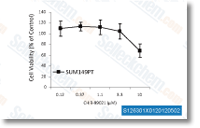
| S1263 | CHIR-99021 (Laduviglusib) | Laduviglusib (CHIR-99021, CT99021) ist ein GSK-3α- und GSK-3β-Inhibitor mit IC50-Werten von 10 nM bzw. 6,7 nM. Es zeigt keine Kreuzreaktivität gegen Cyclin-abhängige Kinasen (CDKs) und eine 350-fache Selektivität gegenüber GSK-3β im Vergleich zu CDKs. Diese Verbindung fungiert als Wnt/β-catenin-Aktivator und induziert Autophagy. |
|
|
| S2924 | Laduviglusib (CHIR-99021) Hydrochloride | Laduviglusib (CHIR-99021; CT99021) HCl ist das Hydrochlorid von CHIR-99021, einem GSK-3α/β-Inhibitor mit einer IC50 von 10 nM/6,7 nM; CHIR-99021 zeigt eine über 500-fache Selektivität für GSK-3 im Vergleich zu seinen engsten Homologen Cdc2 und ERK2. CHIR-99021 ist ein potenter pharmakologischer Aktivator des Wnt/beta-Catenin-Signalwegs. CHIR-99021 rettet signifikant die lichtinduzierte Autophagy und erhöht GR, RORα und Autophagy-bezogene Proteine. |
|
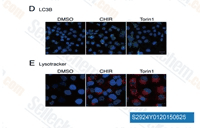
|
| S1180 | XAV-939 | XAV-939 (NVP-XAV939) hemmt selektiv die Wnt/β-catenin-vermittelte Transkription durch Tankyrase1/2-Hemmung mit einer IC50 von 11 nM/4 nM in zellfreien Assays, reguliert die Axin-Spiegel und beeinflusst CRE, NF-κB oder TGF-β nicht. |
|
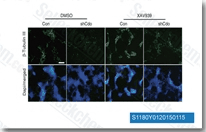
|
| S5992 | Heparan Sulfate | Heparan sulfate (HS, Heparitin sulfate, Alpha-idosane, HHS 5, N-Acetylheparan Sulfate, Suleparoid, Tavidan), ein Bestandteil von HS-Proteoglykanen (HSPGs), ist ein lineares Polysaccharid, das auf der Zelloberfläche vorhanden ist. Heparan sulfate beeinflusst die Bindungsaffinität von Darmepithelzellen (IECs) an Wnt, wodurch die Aktivierung der kanonischen Wnt-Signalübertragung gefördert und die Regeneration der Krypten des Dünndarms nach Epithelschäden erleichtert wird. |
|
|
The Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway is an important mechanism of study for researchers of human diseases as it plays a role in oncology when overactivated, however, reduced signalling of this pathway also results in abnormal bone development and neurodegenerative illnesses. Depending on the indication of use, development of inhibitors or activators of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway is an important area of focus.
Normally, regulation of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway occurs by a large protein assembly called the β-catenin destruction complex that maintains low concentrations of β-catenin in the cytoplasm, and consequently in the nucleus. The β-catenin destruction complex is comprised of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3α/ GSK3β), casein kinase Iα (CKIα), Axin1/Axin2 scaffolding, and adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) – a tumor suppressor protein. Recruitment of β-catenin to the destruction complex leads to the phosphorylation of β-catenin N-terminus residues by CKIα and GSK3, following which ubiquitination and degradation events occur. Sequestering β-catenin at several N-terminal serine and threonine residues to the β-catenin destruction complex are Axin and APC. Similarly, it is believed these constituents of the β-catenin destruction complex regulate β-catenin efflux from the nucleus. The low concentration of β-catenin in the cell restricts β-catenin to the essential role of cadherin-mediated cell adhesion. An additional mechanism controlling the expression of Wnt signalling in the cell involves the inhibition of Wnt specific gene transcription by the T-cell factor (TCF) family of proteins.[1]
Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway is signified by the formation of a “Wnt signalosome” – a large protein complex that develops following the recognition of Wnt protein on the cell surface by a set of proteins called the seven-pass transmembrane Frizzled (Fz) family and its co-receptor, low density lipoprotein receptor related protein (LRP5/LRP6).ii The Wnt signalosome inhibits the activity of the β-catenin destruction complex by recruiting several components of the destruction complex to the membrane. As a consequence, the buildup of β-catenin’s unphosphorylated form results in the cytoplasm and subsequently in the nucleus. It is in the nucleus where rising concentrations of β-catenin combine with TCF proteins to transform this protein from an inhibitory protein to an activator of Wnt-signalling pathway by encouraging the transcription of the Wnt-responsive gene.[1]
Among cancer research, Wnt/β-catenin signalling is an area of focus since loss-of-function mutations in the APC gene results in β-catenin stabilization. Deletions within a chromosomal region containing the APC gene is understood to be associated with a hereditary disease known as familial adenomatous polyposis that yield intestinal polyps in large numbers that ultimately gives rise to tumors. Alternatively, mutations that promote gain-of-function of the APC gene inhibit the β-catenin destruction complex from limiting β-catenin concentrations in the cell. Additionally, some cancers have been correlated to a loss of Axin1 or Axin2 function. Overexpression of the Wnt/ β-catenin signalling pathway results in the constitutive activation of c-myc, and is most commonly linked to colorectal cancer.[2]
Since the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway plays a critical role in cancer, clinical research has yielded several new targets that may positively influence Wnt/β-catenin signalling where its absence is related to disease. Potential new drug targets include two lipid kinases that were found with the accumulation of β-catenin among HEK293T cells transfected with short inhibitory RNAs (siRNAs) targeting human kinases, these include: (1) phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type IIα (PI4KIIα), and (2) phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase type Iβ (PIP5Kiβ). Additionally, three human homologs of Drosophila PAR-1 can also provide useful drug targets as these elements activate Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway as well.[2]
There are many enzymes involved in the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and knowing whether activation or repression is best suited will determine the molecular strategy to explore for therapeutic benefit.
