nur für Forschungszwecke
Go 6983 PKC Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S2911
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 442.51
Qualitätskontrolle
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC12 | Function assay | 0.5 μM | GO6983 blocked the effect of PMA on the activation of Akt and MAPK induced by IGF-1 | 10788447 | ||
| PC-3 | Function assay | 1 μM | 2 h | Gö6983 abrogates the TPA-induced RGFR transactivation response | 15897236 | |
| HCT116 | Function assay | 2 μM | 8 h | attenuated PMA-induced FLIP mRNA expression | 16052516 | |
| HT29 | Function assay | 2 μM | 8 h | attenuated PMA-induced FLIP mRNA expression | 16052516 | |
| KM20 | Function assay | 2 μM | 8 h | attenuated PMA-induced FLIP mRNA expression | 16052516 | |
| KM12C | Function assay | 2 μM | 8 h | attenuated PMA-induced FLIP mRNA expression | 16052516 | |
| Caco-2 | Function assay | 2 μM | 8 h | completely attenuated PMA-induced FLIP mRNA expression | 16052516 | |
| A549 | Function assay | 10 μM | 1 h | markedly inhibited ATPγS-stimulated NADPH oxidase activity and H2O2 and/or ROS generation | 23326583 | |
| HeLa | Function assay | 2 μM | 48 h | suppressed the effect of PMA on apicularen A-induced cytotoxicity | 24447339 | |
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| HEK293 | Function assay | Inhibition of Cav1.2 calcium current measured using whole cell patch clamp in human HEK293 cells transfected with rabbit L-type calcium channel subunits, IC50 = 20 μM. | ChEMBL | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 442.51 | Formel | C26H26N4O3 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 133053-19-7 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | GOE 6983, Gö 6983 | Smiles | CN(C)CCCN1C=C(C2=C1C=CC(=C2)OC)C3=C(C(=O)NC3=O)C4=CNC5=CC=CC=C54 | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 89 mg/mL
(201.12 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
PKCγ
(Cell-free assay) 6 nM
PKCα
(Cell-free assay) 7 nM
PKCβ
(Cell-free assay) 7 nM
PKCδ
(Cell-free assay) 10 nM
PKCζ
(Cell-free assay) 60 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Go 6983 (300 μM) unterdrückt die PKCμ-Autophosphorylierung um 20 % in NIH3T3-Zellen, die mit PKCμ transfiziert wurden. In Herzen, die mit PMNs und dieser Verbindung (100 nM) reperfundiert wurden, erholen sich der linksventrikuläre Entwicklungsdruck (LVDP) und die LVDP-Rate auf 89 % bzw. 74 % der Ausgangswerte, was signifikant höher ist als bei PMNs allein. Diese Chemikalie (100 nM) reduziert die Adhärenz von PMNs an das Endothel und die Infiltration in das Myokard signifikant im Vergleich zu Ischämie gefolgt von Reperfusion (I/R)+PMN-Herzen und hemmt die Superoxidfreisetzung aus PMNs signifikant um 90 %. Sie dämpft die post-I/R-kardiale Kontraktionsdysfunktion in Anwesenheit von PMNs, was teilweise mit einer verringerten Superoxidproduktion zusammenhängen könnte. Dieser Inhibitor hemmt signifikant die Antigen-induzierte Superoxidfreisetzung aus Leukozyten von Patienten, die zuvor gegen Baumpollen sensibilisiert wurden. Er hemmte die intrazelluläre Ca(2+)-Akkumulation in menschlichem Gefäßgewebe, was einen Mechanismus für seine gefäßerweiternden Eigenschaften nahelegt. Diese Verbindung (1 μM) in Kombination mit Ro-31-8425 (390 nM) hemmt die Angiotensin II-induzierte PLD2-Aktivität in PGSMCs leicht. Es ist ein isoform-spezifischer PKC-Inhibitor, der die ATP-Bindungsstelle angreift. Er hemmt die ΔPfPKB-Aktivität mit einer IC50 von 1 μM. In mit dieser Chemikalie (5 μM) behandelten Zellen ist die Anzahl der Ringe im folgenden Zyklus deutlich geringer im Vergleich zu den Kontrollkulturen. Diese Behandlung (5 μM) führt zu einer fast 60%igen Abnahme der Bildung neuer Ringe in P. falciparum-Kulturen. |
| Kinase-Assay |
Bindungstest
|
|
Phosphorylierungsreaktionen werden in einem Gesamtvolumen von 100 μL durchgeführt, enthaltend Puffer C (50 mM Tris-HC1, pH 7,5, 10 mM β-Mercaptoethanol), 4 mM MgCl2, 10 μg PS, 100 nM TPA, 5 μL eines Sf158-Zellextrakts als Quelle für rekombinante PKCμ oder von Sf9-Zellextrakten als Quelle für andere rekombinante PKC-Isoenzyme, 10 μg Syntid 2 als Substrat und 35 μM ATP, das 1 μCi [γ-32P]ATP enthält. In einigen Experimenten werden PS und TPA weggelassen oder verschiedene Inhibitoren in den im Text angegebenen Konzentrationen hinzugefügt. Nach Inkubation für 10 min bei 30℃ wird die Reaktion durch Übertragen von 50 μL der Testmischung auf ein 20 mm großes Phosphocellulosepapier beendet, das 3-mal in deionisiertem Wasser und zweimal in Aceton gewaschen wird. Die Radioaktivität auf jedem Papier wird durch Flüssigkeitsszintillationszählung bestimmt.
|
|
| In vivo |
Go6983 (22,0 μg/Maus, i.v.) hemmt die Tumormetastasierung in einem murinen pulmonalen B16BL6-Tumormodell stark um 51,2 %. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
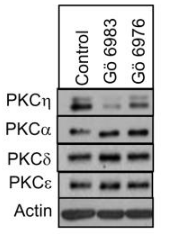
| Western blot | PKCη / PKCα / PKCδ / PKCε |
|
22892130 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
