nur für Forschungszwecke
Go6976 PKC Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S7119
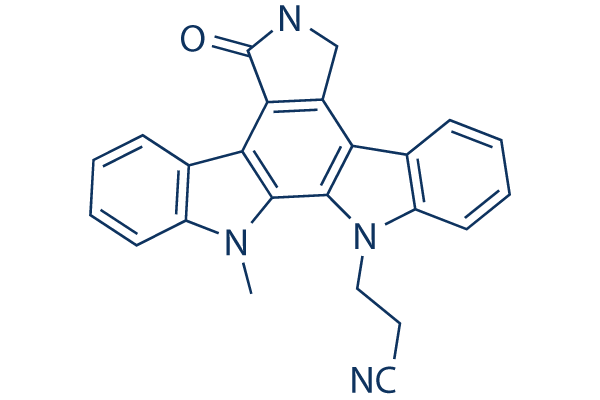
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 377.42
Qualitätskontrolle
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vero | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against African green monkey Vero cells assessed as reduction in cell viability measured on day 5 post dose by MTS/PMS based microscopic analysis, CC50=6μM. | 28689975 | |||
| primary microglial cells | Function assay | Inhibition of IFN-gamma-induced IFN-gamma regulatory factor levels in Sprague-Dawley rat primary microglial cells by Western blotting | 17395590 | |||
| primary microglial cells | Function assay | 1.3 uM | Suppression of IFN-gamma-induced PKCalpha/beta2 nuclear translocation in Sprague-Dawley rat primary microglial cells at 1.3 uM by Western blotting | 17395590 | ||
| primary microglial cells | Function assay | 1.3 uM | Suppression of IFN-gamma-induced IFN-gamma regulatory factor 1 nuclear translocation in Sprague-Dawley rat primary microglial cells at 1.3 uM by Western blotting | 17395590 | ||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 377.42 | Formel | C24H18N4O |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 136194-77-9 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | PD406976 | Smiles | CN1C2=CC=CC=C2C3=C4C(=C5C6=CC=CC=C6N(C5=C31)CCC#N)CNC4=O | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 44.7 mg/mL
(118.43 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
JAK2
(Cell-free assay) FLT3
(Cell-free assay) PKCα
(Cell-free assay) 2.3 nM
PKCβ1
(Cell-free assay) 6.2 nM
PKC
(Rat brain) 7.9 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Go6976 hat keine Wirkung auf die Kinaseaktivität der Ca(2+)-unabhängigen PKC-Subtypen Delta, Epsilon und Zeta. Neben WT JAK2 hemmt diese Verbindung auch die mutierten Formen (JAK2 V617F und TEL-JAK2), die bei hämatologischen Malignomen gefunden werden, und hat Aktivität gegen mutierte Formen von FLT3. In AML-Zellen reduziert diese Chemikalie das Überleben auf 55% der Kontrolle in FLT3-ITD-Fällen und auf 69% in FLT3-WT-Proben. Es hemmt potent die HIV-1-Induktion durch Bryostatin 1, Tumornekrosefaktor alpha und Interleukin 6.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
PKC-Aktivitätstest
|
|
Kurz gesagt, zur Messung von PKCα, PKCβ1 und PKC aus Rattenhirn enthält das Assay-Gemisch von 200 μl 50 mM HEPES (pH 7,5), 5 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, 1,25 mM EGTA, 1,32 mM CaC12, 1 mM Dithiothreitol, 1 μg Phosphatidylserin, 0,2 μg Diolein, 40 μg Histon Hi, 10 μM [γ-32P]ATP (1 μCi/ml) und 5-10 Einheiten (pmol Pi/min) PKC. Die Assays werden durch Zugabe von [γ-32P]ATP gestartet, 5 min bei 30 °C inkubiert, durch Zugabe von 2 ml 8,5 % H3PO4 gestoppt, durch 0,45-μm-Nitrocellulosefilter filtriert und durch Szintillationszählung ausgewertet.
|
|
| In vivo |
Go6976 (2,5 mg/kg i.p.) verhindert als PKD-Inhibitor wirksam LPS/D:-GalN-induzierte akute Leberschäden durch Hemmung der MAPKs-Aktivierung zur Reduzierung der TNF-α-Produktion und verbessert signifikant das Überleben von LPS/D-GalN-behandelten Mäusen.
|
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
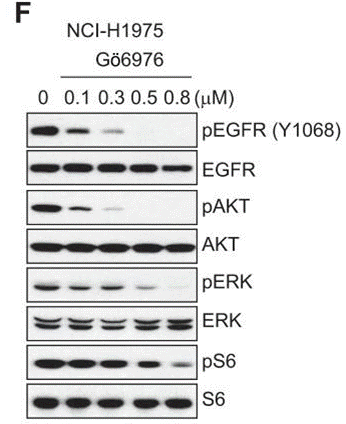
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-EGFR / EGFR / p-AKT / AKT / p-ERK / ERK / p-S6 / S6 |
|
23229345 |
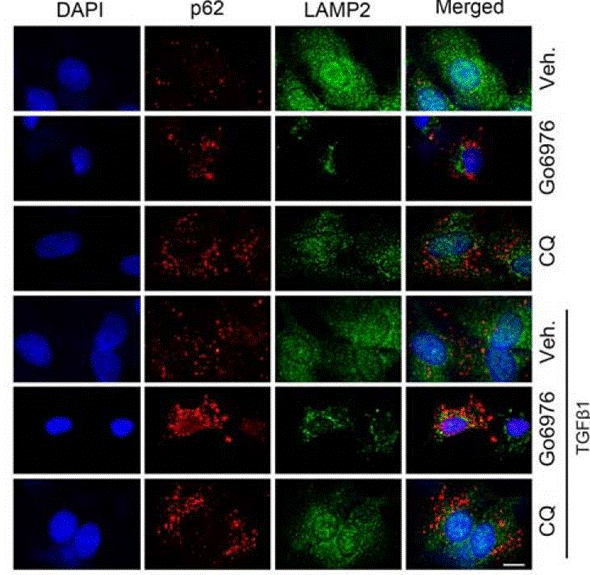
| Immunofluorescence | p62 / LAMP2 |
|
29794026 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
