nur für Forschungszwecke
Dorsomorphin Dihydrochloride AMPK/BMP-Signalweg-Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S7306
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 472.41
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | PI3K Akt mTOR GSK-3 ATM/ATR DNA-PK PDPK1 PTEN PP2A PDK |
|---|---|
| Weitere AMPK Inhibitoren | Dorsomorphin (Compound C) AICAR (Acadesine) A-769662 GSK621 WZ4003 Ex229 (Compound 991) Phenformin HCl BAY-3827 HTH-01-015 O-304 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2C12 | Function assay | 4 uM | Inhibition of BMPR1-mediated osteoblast differentiation in BMP4-stimulated mouse C2C12 cells assessed as decrease in alkaline phosphatase level at 4 uM by spectrophotometry | 18026094 | ||
| C2C12 | Function assay | 4 uM | Inhibition of BMPR1-mediated osteoblast differentiation in BMP6-stimulated mouse C2C12 cells assessed as decrease in alkaline phosphatase level at 4 uM by spectrophotometry | 18026094 | ||
| HepG2 | Function assay | 10 uM | 30 mins | Inhibition of BMPR1-mediated hepcidin mRNA expression in BMP2-stimulated human HepG2 cells at 10 uM treated 30 mins before BMP2 challenge measured after 16 hrs by qRT-PCR analysis | 18026094 | |
| Hep3B | Function assay | 10 uM | 30 mins | Inhibition of BMPR1-mediated hepcidin mRNA expression in IL6-stimulated human Hep3B cells at 10 uM treated 30 mins before IL6 challenge measured after 6 hrs by qRT-PCR analysis | 18026094 | |
| Hep3B | Function assay | 10 uM | 30 mins | Inhibition of BMPR1-mediated Id1 mRNA expression in IL6-stimulated human Hep3B cells at 10 uM treated 30 mins before IL6 challenge measured after 6 hrs by qRT-PCR analysis | 18026094 | |
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| KB-3-1 | qHTS assay | P-glycoprotein substrates identified in KB-3-1 adenocarcinoma cell line, qHTS therapeutic library screen | 31515284 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 472.41 | Formel | C24H25N5O.2HCl |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 1219168-18-9 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | BML-275 2HCl,Compound C 2HCl | Smiles | C1CCN(CC1)CCOC2=CC=C(C=C2)C3=CN4C(=C(C=N4)C5=CC=NC=C5)N=C3.Cl.Cl | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
Water : 47 mg/mL
DMSO
: Insoluble
Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
ALK2
ALK3
ALK6
AMPK
(Cell-free assay) 109 nM(Ki)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Dorsomorphin hemmt die ACC-Inaktivierung durch AICAR und schwächt auch die Wirkung von AICAR ab, die Fettsäureoxidation zu erhöhen oder lipogene Gene in Hepatozyten zu unterdrücken. Die Hemmung der AMPK-Aktivität durch Dorsomorphin hemmt die autophagische Proteolyse in HT-29-Zellen fast vollständig. Darüber hinaus hemmt Dorsomorphin selektiv die BMP-Typ-I-Rezeptoren ALK2, ALK3 und ALK6 und blockiert somit die BMP-vermittelte SMAD1/5/8-Phosphorylierung, die Transkription von Zielgenen und die osteogene Differenzierung. |
| Kinase-Assay |
AMPK-Partielle Reinigung und In-vitro-Kinase-Assay.
|
|
Leber-AMPK wird aus männlichen SD-Ratten bis zum Blue-Sepharose-Schritt teilweise gereinigt. Die 100-μl-Reaktionsmischung enthält 100 μM AMP, 100 μM ATP (0,5 μCi 33P-ATP pro Reaktion) und 50 μM SAMS in einem Puffer (40 mM HEPES, pH 7,0, 80 mM NaCl, 0,8 mM EDTA, 5 mM MgCl2, 0,025% BSA und 0,8 mM DTT). Die Reaktion wird mit Zugabe des Enzyms gestartet. Nach 30-minütiger Inkubation bei 30 °C wird die Reaktion durch Zugabe von 80 μl 1% H3PO4 gestoppt. Aliquots (100 μl) werden auf 96-Well MultiScreen-Platten übertragen. Die Platte wird dreimal mit 1% H3PO4 gewaschen, gefolgt von einer Detektion in einem Top-Count. Die In-vitro-AMPK-Hemmdaten, die mit Verbindung C — (6-[4-(2-Piperidin-1-yl-ethoxy)-phenyl)]-3-pyridin-4-yl-pyyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin — erhalten wurden, werden an die folgende Gleichung für kompetitive Hemmung durch nichtlineare Regression unter Verwendung eines Least-Squares-Marquardt-Algorithmus in einem Computerprogramm angepasst, das von N. Thornberry von Merck Research Laboratories geschrieben wurde: Vi/Vo = (Km + S)/[S + Km × (1 + I/Ki)], wobei Vi die gehemmte Geschwindigkeit ist, Vo die Anfangsgeschwindigkeit ist, S die Substrat (ATP)-Konzentration ist, Km die Michaelis-Konstante für ATP ist, I die Inhibitor (Verbindung C)-Konzentration ist und Ki die Dissoziationskonstante für Verbindung C ist.
|
|
| In vivo |
Dorsomorphin (10 mg/kg) reduziert die basalen Hepcidin-Expressionsspiegel und erhöht die Serumeisenkonzentrationen bei erwachsenen Mäusen. Dorsomorphin (0,2 mg/kg, i.v.) reduziert signifikant die VCAM-1- und ICAM-1-Expression in der thorakalen Aorta von LPS-behandelten Ratten. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
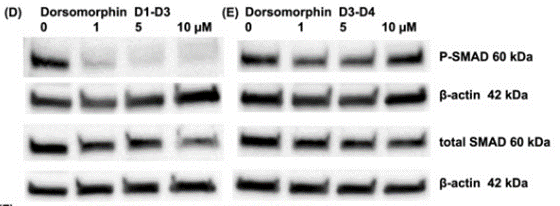
| Western blot | p-SMAD / SMAD Id1 / Id2 / Id3 pAMPK / AMPK / pACC / ACC / pRaptor / HIF1α p-ERK / ERK / Bcl2 / BAX / Cleaved caspase-3 LC3B I/ LC3B II |
|
30808965 |
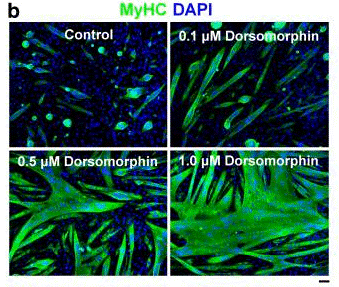
| Immunofluorescence | MyHC Id1 / MyoD |
|
20689554 |
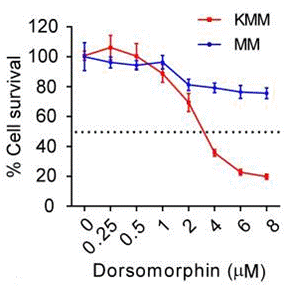
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability (MM cells) Cell viability (glioma cell lines) |
|
25010525 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
Is there any information you may provide as to WHICH AMPK SUBUNIT this compound is targeting in the AMPK complex?
Antwort:
According to the reference (see link below), it should target the AMPK alpha subunit through ALCAR or metformin. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20844250
