AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) plays a pivotal role in the regulation of cellular energy homeostasis as the principal energy sensor in most eukaryotic cells. In response to stress, AMPK activation switches on catabolic pathways that generate ATP while simultaneously inactivating biosynthetic pathways that consume ATP. [show the full text]
AMPK Aktivatoren/Inhibitoren (AMPK Activators/Inhibitors)
| Kat.-Nr. | Produktname | Informationen | Publikationen | Validierung |
|---|---|---|---|---|
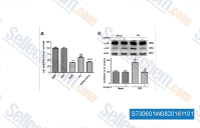
| S7306 | Dorsomorphin Dihydrochloride | Dorsomorphin 2HCl ist ein potenter, reversibler, selektiver AMPK-Inhibitor mit einem Ki von 109 nM in zellfreien Assays, der keine signifikante Hemmung mehrerer strukturell verwandter Kinasen wie ZAPK, SYK, PKCθ, PKA und JAK3 aufweist. Hemmt auch die Aktivität des Typ-I-BMP-Rezeptors. Dorsomorphin induziert Autophagy in Krebszelllinien. |
|
|
| S1208 | Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) Hydrochloride | Doxorubicin (DOX) HCl ist ein Antibiotikum, das die menschliche DNA Topoisomerase II mit einer IC50 von 2,67 μM hemmt. Doxorubicin reduziert die basale Phosphorylierung von AMPK. Doxorubicin wird in der begleitenden Behandlung von HIV-infizierten Patienten eingesetzt, birgt jedoch ein hohes Risiko einer HBV-Reaktivierung.Dieses Produkt kann beim Auflösen in PBS-Lösung ausfallen. Es wird empfohlen, die Stammlösung in reinem Wasser herzustellen und mit reinem Wasser oder Salzlösung zu verdünnen, um die Arbeitslösung zu erhalten.Doxorubicin (Adriamycin) HCl kann zur Induktion von Tiermodellen für Nierenerkrankungen verwendet werden. |
|
|
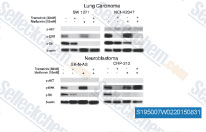
| S1950 | Metformin Hydrochloride | Metformin Hydrochloride (1,1-Dimethylbiguanid-Hydrochlorid) ist ein hochwirksames Antihyperglycemic Agent, das in erster Linie die Hyperglykämie in Hepatozyten reduziert, indem es die hepatische Gluconeogenese (Glukoseproduktion durch die Leber) unterdrückt. Es fördert auch Mitophagy in mononukleären Zellen und induziert die Apoptose von Lungenkrebszellen durch die Aktivierung des JNK/p38 MAPK Signalwegs und GADD153. |
|
|
| S8161 | ON123300 | ON123300 ist ein potenter und multi-zielgerichteter Kinase-Inhibitor mit IC50 von 3,9 nM, 5 nM, 26 nM, 26 nM, 9,2 nM und 11 nM für CDK4, Ark5/NUAK1, PDGFRβ, FGFR1, RET (c-RET) bzw. Fyn. |
|
|
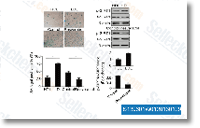
| S1396 | Resveratrol (trans-Resveratrol) | Resveratrol hat ein breites Spektrum an Targets, darunter Cyclooxygenasen (d.h. COX, IC50=1,1 μM), Lipoxygenasen (LOX, IC50=2,7 μM), Kinasen, Sirtuine und andere Proteine. Es hat krebshemmende, entzündungshemmende, blutzuckersenkende und andere positive kardiovaskuläre Effekte. Resveratrol induziert mitophagy/autophagy und Autophagie-abhängige Apoptose. |
|
|
| S7840 | Dorsomorphin (Compound C) | Dorsomorphin ist ein potenter, reversibler, selektiver AMPK-Inhibitor mit einem Ki von 109 nM in zellfreien Assays, der keine signifikante Hemmung mehrerer strukturell verwandter Kinasen wie ZAPK, SYK, PKCθ, PKA und JAK3 zeigt. Dorsomorphin hemmt selektiv die BMP-Typ-I-Rezeptoren ALK2, ALK3 und ALK6. Dorsomorphin wird zur Förderung spezifischer Zelldifferenzierung und zur Induktion der Autophagie von Krebszelllinien eingesetzt. Für Zelltests wird das wasserlösliche S7306 Dorsomorphin (Compound C) 2HCl empfohlen. |
|
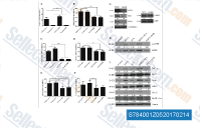
|
| S1802 | AICAR (Acadesine) | AICAR (Acadesine, NSC105823, AICA Riboside), ein AMPK-Aktivator, führt zur Akkumulation von ZMP, das die stimulierende Wirkung von AMP auf AMPK und AMPK-Kinase nachahmt. Diese Verbindung induziert mitophagy. Phase 3. |
|
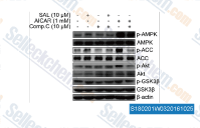
|
| S2697 | A-769662 | A-769662 ist ein potenter, reversibler AMPK-Aktivator mit einem EC50 von 0,8 μM in zellfreien Assays, mit geringem Einfluss auf die GPPase/FBPase-Aktivität. |
|
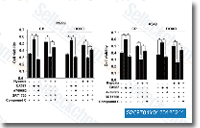
|
| S5958 | Metformin (1,1-Dimethylbiguanide) | Metformin (1,1-Dimethylbiguanid), ein weit verbreitetes Medikament zur Behandlung von Typ-2-Diabetes, aktiviert die AMP-aktivierte Proteinkinase (AMPK) in Hepatozyten. Metformin fördert die Mitophagy in mononukleären Zellen. Metformin induziert die Apoptose von Lungenkrebszellen durch Aktivierung des JNK/p38 MAPK-Signalwegs und GADD153. |
|
|
| S7898 | GSK621 | GSK621 ist ein spezifischer und potenter AMPK-Aktivator. |
|
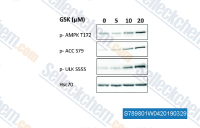
|
AMPK exists as a heterotrimeric protein complex composed of a catalytic α-subunit (α1 or α2) and regulatory β-subunit (β1 or β2) and γ- subunit (γ1, γ2 or γ3). The structure of the α-subunit consists of a conventional Ser/Thr kinase domain at the N-terminal, an auto-inhibitory domain (AID), an extended linker peptide and the α-subunit C-terminal domain (α-CTD). The β-subunit contains a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM), with the β-subunit C-terminal domain (β-CTD) interacting with both the α-CTD and the amino terminus of the γ-subunit, thus forming the core of the complex. The γ-subunit includes four tandem repeats of a sequence motif, termed a CBS repeat (cystathionine β-synthase, CBS1-4), that forms a flattened disk with one repeat in each quadrant to create four potential ligand binding sites in the centre (site 1-4). AMPK activity increases more than 100-fold when the conserved Thr172 residue in the activation loop of the catalytic α-subunit is phosphorylated by upstream AMPK kinases (AMPKK) such as LKB1 requiring the change in AMP or ADP levels, and CaMKKβ (CaMKK2) in response to increases in cell Ca2+. AMP binding to ligand binding site 1 of the γ subunit allosterically activates the AMPK complex by facilitating the phosphorylation of Thr172 in the catalytic α-subunit, whereas binding of AMP or ADP to site 3 modulates the phosphorylation state of Thr172. In addition to allosteric activation by AMP, the effects on phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of Thr172 can also be produced by ADP, which requires N-terminal myristylation of the β-subunit. [1][2]
AMPK is activated by various types of metabolic stress (glucose deprivation, hypoxia, ischemia, metabolic poisons, or muscle contraction), as well as drugs and xenobiotics (metformin, resveratrol, or berberine) through the classical or canonical mechanisms, which involve increases in cellular AMP, ADP or Ca2+. The metformin for the treatment of people with type 2 diabetes indirectly activates AMPK by increasing cellular AMP and ADP, usually by inhibiting mitochondrial ATP synthesis. Additionally, AMPK activated by resveratrol or metformin upregulates genes involved in oxidative metabolism and oxidative stress resistance by regulating transcription factors of the abnormal dauer formation 16 (DAF-16)/forkhead box O (FOXO) family, contributing to its effects on extending healthy lifespan. Some types of cellular stress such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) and DNA damaging agents (etoposide, doxorubicin and ionizing radiation) activate AMPK by non-canonical mechanisms that involve ATM rather than the increases in AMP, ADP or Ca2+ levels. Activation of AMPK enhances both the transcription and translocation of GLUT4, resulting in an increase in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake. In LKB1-knockout but not AMPKα1-knockout mice, the effects of both AICAR and contraction on glucose uptake are lost. In addition, AMPK also stimulates other catabolic processes such as fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis via inhibition of ACC2 and activation of PFKFB. AMPK is also involved in the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis through the activation of PGC1α, and the turnover of mitochondria via the special form of autophagy termed mitophagy by activating ULK1, and subsequently triggering autophagy. In addition, mTOR complex-1 (TORC1) can be inhibited by AMPK mediated phosphorylation of both its upstream regulator, TSC2, and the TORC1 subunit Raptor. Consistent with its role in cellular energy homeostasis, AMPK also conserves ATP by switching off almost all anabolic pathways, including the biosynthesis of lipids, carbohydrates, proteins and ribosomal RNA. Moreover, AMPK also functions beyond metabolism through regulation of the cell cycle and modulation of membrane excitability. As LKB1 is a tumor suppressor and is frequently mutated in spontaneous cancers, AMPK-activating drugs such as metformin or A-769662 significantly protect against the development of cancer. [1][2]
