nur für Forschungszwecke
Vadimezan (DMXAA) Vascular Disrupting Agent
Kat.-Nr.S1537
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 282.29
Qualitätskontrolle
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| human BJ cells | Cytotoxic assay | 24 h | Cytotoxicity against human BJ cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay, CC50=48.9 μM | 24518295 | ||
| HECPP cells | Function assay | 10 ug/mL | Activation of NF-kappaB in HECPP cells at 10 ug/mL | 17616114 | ||
| MCF7 | Antiproliferative assay | 24 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human MCF7 cells co-treated with pyranoxanthone at 1:1 molar ratio after 24 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 11.89 μM. | 29129511 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Antiproliferative assay | 24 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human MDA-MB-231 cells co-treated with pyranoxanthone at 1:1 molar ratio after 24 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 12.12 μM. | 29129511 | ||
| K562 | Antiproliferative assay | 24 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human K562 cells co-treated with pyranoxanthone at 1:1 molar ratio after 24 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 19.14 μM. | 29129511 | ||
| HepG2 | Antiproliferative assay | 24 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HepG2 cells co-treated with pyranoxanthone at 1:1 molar ratio after 24 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 21.25 μM. | 29129511 | ||
| COLO320 | Antiproliferative assay | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human COLO320 cells after 48 hrs by CCK8 assay, IC50 = 39.5 μM. | 28376372 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Antiproliferative assay | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human MDA-MB-231 cells after 48 hrs by CCK8 assay, IC50 = 48.4 μM. | 28376372 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibition assay | 24 hrs | Growth inhibition of human MDA-MB-231 cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 48.42 μM. | 29609121 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Antiproliferative assay | 24 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human MDA-MB-231 cells after 24 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 48.44 μM. | 29129511 | ||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Apoptosis assay | 24 to 96 uM | 48 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human MDA-MB-231 cells assessed as increase in cleaved caspase-3 expression at 24 to 96 uM after 48 hrs by Western blot analysis | 28376372 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Apoptosis assay | 24 to 96 uM | 48 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human MDA-MB-231 cells assessed as increase in cleaved PARP level at 24 to 96 uM after 48 hrs by Western blot analysis | 28376372 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function assay | 24 to 96 uM | 48 hrs | Decrease in caspase-3 level in human MDA-MB-231 cells at 24 to 96 uM after 48 hrs by Western blot analysis | 28376372 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function assay | 24 to 96 uM | 48 hrs | Increase in p53 level in human MDA-MB-231 cells at 24 to 96 uM after 48 hrs by Western blot analysis | 28376372 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function assay | 24 to 96 uM | 48 hrs | Decrease in caspase-9 level in human MDA-MB-231 cells at 24 to 96 uM after 48 hrs by Western blot analysis | 28376372 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function assay | 24 to 96 uM | 48 hrs | Decrease in MDM2 level in human MDA-MB-231 cells at 24 to 96 uM after 48 hrs by Western blot analysis | 28376372 | |
| HepG2 | Cell cycle arrest assay | 0.2 uM | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human HepG2 cells assessed as accumulation at S phase at 0.2 uM after 24 hrs by propidium iodide staining-based flow cytometric method relative to control | 29129511 | |
| HepG2 | Cell cycle arrest assay | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human HepG2 cells assessed as accumulation at S phase co-treated with pyranoxanthone at 1:1 molar ratio after 24 hrs by propidium iodide staining-based flow cytometric method | 29129511 | ||
| HepG2 | Apoptosis assay | 0.2 uM | 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human HepG2 cells assessed as increase in cleaved caspase-3 levels at 0.2 uM after 24 hrs by Western blot method | 29129511 | |
| HepG2 | Apoptosis assay | 0.2 uM | 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human HepG2 cells assessed as increase in cleaved caspase-9 levels at 0.2 uM after 24 hrs by Western blot method | 29129511 | |
| HepG2 | Apoptosis assay | 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human HepG2 cells assessed as increase in cleaved PARP levels co-treated with pyranoxanthone at 1:1 molar ratio after 24 hrs by Western blot method | 29129511 | ||
| HepG2 | Apoptosis assay | 0.2 uM | 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human HepG2 cells assessed as increase in cleaved PARP levels at 0.2 uM after 24 hrs by Western blot method | 29129511 | |
| HepG2 | Apoptosis assay | 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human HepG2 cells assessed as increase in cleaved caspase-3 levels co-treated with pyranoxanthone at 1:1 molar ratio after 24 hrs by Western blot method | 29129511 | ||
| HepG2 | Apoptosis assay | 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human HepG2 cells assessed as increase in cleaved caspase-9 levels co-treated with pyranoxanthone at 1:1 molar ratio after 24 hrs by Western blot method | 29129511 | ||
| HepG2 | Apoptosis assay | 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human HepG2 cells assessed as downregulation of Bcl-xL expression co-treated with pyranoxanthone at 1:1 molar ratio after 24 hrs by Western blot method | 29129511 | ||
| HepG2 | Apoptosis assay | 24 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human HepG2 cells assessed as upregulation of Bid expression co-treated with pyranoxanthone at 1:1 molar ratio after 24 hrs by Western blot method | 29129511 | ||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 282.29 | Formel | C17H14O4 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 117570-53-3 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | ASA404, NSC 640488 | Smiles | CC1=C(C2=C(C=C1)C(=O)C3=CC=CC(=C3O2)CC(=O)O)C | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 16 mg/mL
(56.67 mM)
Mit 50°C Wasserbad erwärmt;
Ultraschallbehandelt;
7.5%Sodium bicarbonate : 10 mg/mL (Ultrasonic and heating for 5 minutes.) Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
DT-diaphorase
(Cell-free assay) 20 μM(Ki)
DT-diaphorase
(Cell-free assay) 20 μM(Ki)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
In DLD-1-Zellen des menschlichen Kolonkarzinoms hemmt Vadimezan (DMXAA) die DT-Diaphorase-Aktivität ohne signifikante Auswirkungen auf die Aktivität der Cytochrom-b5-Reduktase und der Cytochrom-P450-Reduktase. Die Kombination von Menadion und dieser Verbindung führt zu einer Erhöhung der antiproliferativen Aktivität von DLD-1-Zellen. Als Antiviral-Mittel hemmt es die VSV-induzierte Zytotoxizität und die Influenza-Virusreplikation in RAW 264.7-Makrophagen. Eine aktuelle Studie zeigt, dass DMXAA nicht-immunvermittelte hemmende Effekte gegen mehrere Kinase-Mitglieder des VEGFR (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor) aufweist, wie z.B. die VEGFR2-Signalgebung in menschlichen Nabelschnurvenenendothelzellen.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
DT-Diaphorase-Aktivität und kinetische Analyse der Enzyminhibition
|
|
Die Aktivität des gereinigten DT-Diaphorase-Enzyms wird durch Messung der Reduktion von Cytochrom c bei 550 nm an einem Beckman DU 650 Spektrophotometer bestimmt. Jeder Assay enthält Cytochrom c (70 μM), NADH (variable Konzentrationen), gereinigte DT-Diaphorase (0,032 μg) und Menadion (variable Konzentrationen) in einem Endvolumen von 1 ml Tris-HCl-Puffer (50 mM, pH 7,4), der 0,14 % BSA enthält. Die Reaktion wird durch Zugabe von NADH gestartet. Die Reduktionsraten werden über den Anfangsteil der Reaktionskurve (30 Sekunden) berechnet, und die Ergebnisse werden in μmol Cytochrom c reduziert/min/mg Protein ausgedrückt, wobei ein molarer Extinktionskoeffizient von 21,1 mM−1 cm−1 für reduziertes Cytochrom c verwendet wird. Enzymtests werden bei Raumtemperatur durchgeführt und alle Reaktionen dreifach. Die Hemmung der Aktivität der gereinigten DT-Diaphorase erfolgt durch Zugabe von Vadimezan (DMXAA) in verschiedenen Konzentrationen zur Reaktion, und die Hemmungseigenschaften werden durch Variation der NADH-Konzentration (konstantes Menadion) oder der Menadion-Konzentration (konstantes NADH) bei mehreren Konzentrationen dieser Verbindung bestimmt. Ki-Werte werden durch Auftragen von 1/V gegen erhalten. Die Aktivität der DT-Diaphorase in DLD-1-Zellen wird durch Messung der Dicumarol-sensitiven Reduktion von DCPIP bei 600 nm bestimmt. Kurz gesagt, DLD-1-Zellen im mittleren exponentiellen Wachstum werden durch Abschaben in eiskalten Puffer (Tris-HCl, 25 mM, pH 7,4 und 250 mM Saccharose) geerntet und auf Eis sonifiziert. Die Enzymtestbedingungen sind 2 mM NADH, 40 μM DCPIP, 20 μl Dicumarol (falls erforderlich) in einem Endvolumen von 1 ml Tris-HCl (25 mM, pH 7,4), das BSA (0,7 mg/ml) enthält. Die Ergebnisse werden als Dicumarol-sensitive Reduktion von DCPIP unter Verwendung eines molaren Extinktionskoeffizienten von 21 mM−1 cm−1 ausgedrückt. Proteinkonzentrationen werden mit dem Bradford-Assay bestimmt.
|
|
| In vivo |
Vadimezan (DMXAA)-Behandlung schützt C57BL/6J-Mäuse, die i.n. mit 200 p.f.u. Maus-adaptiertem H1N1-Influenza-PR8-Virus infiziert wurden, signifikant mit einer Überlebensrate von 60 %, während die Kontrollgruppe nur eine Überlebensrate von 20 % aufwies. Diese Verbindung verzögert signifikant das durch chemische Karzinogene induzierte Tumorwachstum, verlängert die Zeit bis zur Tumorverdopplung und verlängert die Zeit von der Behandlung bis zur Euthanasie. Nach ihrer Behandlung wurden die mediane Tumorverdopplungszeit, die mediane Tumorverdreifachungszeit und die mediane Zeit von der Behandlung bis zur Euthanasie bei tumortragenden Tieren um das ca. 4,4-, 1,8- bzw. 2,7-fache erhöht.
|
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
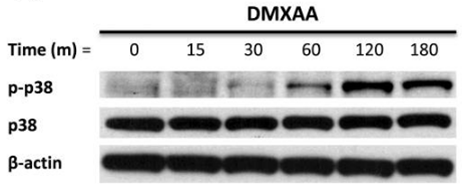
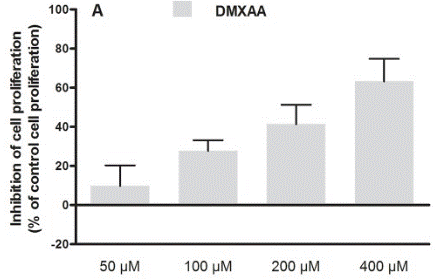
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-p38 / p38 p-MK2 / pERK / p-JNK |
|
21819972 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell proliferation |
|
30138430 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00856336 | Completed | Refractory Tumors |
Antisoma Research |
May 2003 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00863733 | Completed | Solid Tumors |
Cancer Research UK|Cancer Society Auckland |
May 1996 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
