IκBs are a family of related proteins that have an N-terminal regulatory domain, followed by six or more ankyrin repeats and a PEST domain near their C terminus. IκBα is the best-studied and major IκB protein. [show the full text]
IκB/IKK
| Kat.-Nr. | Produktname | Informationen | Publikationen | Validierung |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S8922 | TBK1/IKKε-IN-5 | TBK1/IKK -IN-5 (Verbindung 1) ist ein dualer Inhibitor der TANK-binding Kinase 1 (TBK1) und I B Kinase- (IKK /IKK-i) mit IC50-Werten von 1,0 nM und 5,6 nM für TBK1 bzw. IKK . Die TBK1/IKK -Hemmung verstärkt die Reaktion auf die PD-1-Blockade, was die Tumorantwort in vivo effektiv vorhersagt. |
|
|
| S9042 | Wedelolactone | Wedelolactone, eine aus einer Heilpflanze gewonnene Naturverbindung, ist ein Inhibitor von IKK, das entscheidend für die Aktivierung von NF-κB durch Vermittlung der Phosphorylierung und des Abbaus von IκBα ist. Diese Verbindung ist auch ein Inhibitor von caspase-11. |
|
|
| S8078 | Bardoxolone Methyl (RTA 402) | Bardoxolone Methyl (RTA 402, TP-155, NSC 713200, CDDO Methyl Ester, CDDO-Me) ist ein IKK-Inhibitor, der potente proapoptotische und entzündungshemmende Aktivitäten zeigt; Auch ein potenter Nrf2-Aktivator und Nuklearer Faktor-κB (NF-κB)-Inhibitor. Bardoxolone Methyl hebt die Ferroptosis auf. Bardoxolone Methyl induziert Apoptose und Autophagie in Krebszellen. |
|
|
| S1396 | Resveratrol (trans-Resveratrol) | Resveratrol hat ein breites Spektrum an Targets, darunter Cyclooxygenasen (d.h. COX, IC50=1,1 μM), Lipoxygenasen (LOX, IC50=2,7 μM), Kinasen, Sirtuine und andere Proteine. Es hat krebshemmende, entzündungshemmende, blutzuckersenkende und andere positive kardiovaskuläre Effekte. Resveratrol induziert mitophagy/autophagy und Autophagie-abhängige Apoptose. |
|
|
| S2882 | IKK-16 | IKK-16 ist ein selektiver IκB-Kinase (IKK)-Inhibitor für IKK-2, IKK complex und IKK-1 mit einer IC50 von 40 nM, 70 nM bzw. 200 nM in zellfreien Assays. IKK-16 hemmt auch die LRRK2 Ser935-Phosphorylierung in Zellen und die LRRK2-Kinaseaktivität in vitro mit einer IC50 von 50 nM. |
|
|
| S2824 | TPCA-1 | TPCA-1 (GW683965) ist ein IKK-2-Inhibitor mit einem IC50-Wert von 17,9 nM in einem zellfreien Assay, hemmt den NF-κB-Signalweg und zeigt eine 22-fache Selektivität gegenüber IKK-1. TPCA-1 ist auch ein STAT3-Inhibitor und verstärkt die Apoptosis. |
|
|
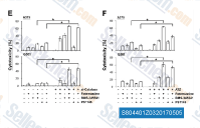
| S8044 | BMS-345541 | BMS-345541 ist ein hochselektiver Inhibitor der katalytischen Untereinheiten von IKK-2 und IKK-1 mit einer IC50 von 0,3 μM bzw. 4 μM in zellfreien Assays. |
|
|
| S7352 | Bay 11-7085 | BAY 11-7085 (Bay 11-7083) ist ein irreversibler Inhibitor der TNF -induzierten I B -Phosphorylierung mit einer IC50 von 10 M. |
|

|
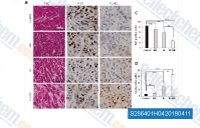
| S2864 | IMD 0354 | IMD-0354 (IKK2 Inhibitor V) ist ein IKKβ-Inhibitor und blockiert die IκBα-Phosphorylierung im NF-κB-Signalweg. |
|
|
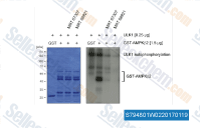
| S7948 | MRT67307 HCl | MRT67307 ist ein potenter dualer IKKϵ- und TBK1-Inhibitor mit IC50-Werten von 160 bzw. 19 nM. MRT67307 hemmt potent ULK1 und ULK2 und blockiert die Autophagy. |
|
|
IκB (Inhibitor of κB) functions as a primary inhibitor of NF-κB activation, with an N-terminal regulatory domain, followed by six or more ankyrin repeats and a PEST domain near their C terminus. [1] IκB family contains eight known members, IκBα, IκBβ, IκBε, Bcl-3 (B-cell lymphoma 3), IκBζ, and IκBns (NF-κBδ), as well as the precursor Rel proteins p100 (NF-κB2) and p105 (NF-κB1) due to the presence of multiple ankyrin repeats in their C-terminal halves. IκBα and IκBβ are broadly expressed in all type of cells, whereas IκBε is expressed only in hematopoietic cells. Bcl-3, IκBζ and IkBNS are atypical IκB proteins that exhibit limited expression following NF-κB activation. The regulation of IκB proteins varies by protein type, and each IκB moiety exhibits a unique affinity for NF-κB complexes. [2]
In unstimulated cells, the IκBα proteins mask the nuclear localization signals (NLS) of NF-κB proteins, keeping them sequestered in an inactive state in the cytoplasm. In response to stimuli, IκB kinase (IKK) phosphorylates IκBα leading to the degradation of IκBα, and subsequent NF-κB activation. IκBα expression can be activated by NF-κB to generate a negative feedback loop. Similar to IκBα, IκBβ acts by sequestering p65- and c-Rel-containing complexes in the cytoplasm. However, nuclear localized IκBβ also binds to p65:c-Rel heterodimers, promoting continued binding to specific κB sites, and augmenting late transcription of select target genes (i.e. TNF and IL-1β). IκBε is induced slowly, and selectively regulates p65 homodimers and c-Rel:p65 heterodimers. Bcl-3 functions as a transcriptional co-activator that may both inhibit and facilitate NF-κB-dependent transcription in a context-specific manner. Like Bcl-3, IκBζ can enhance transcription in association with p50 NF-κB dimmers despite the prescence of distinct mechanisms. IκBns selectively inhibits NF-κB-dependent pro-inflammatory gene expression by stabilizing p50 homodimers at κB sites. In addition to exclusively stabilizing RelB dimers, p100 itself can act more broadly in inhibiting NF-κB dimers. The p105 also acts like a typical IκB protein, and is additionally associated with the activation of the MAPK-ERK signaling pathway through the binding of MAP3K8 (TPL2). Moreover, the functions of individual IκB family members are quite heterogeneous and are not limited to this particular role in regulating NF-κB signaling. [2]
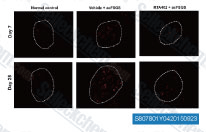
In oncology, the direct activation of NF-κB complexes through the loss of the inhibitory proteins IκBα and IκBε has been observed in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Since the NF-κB signal pathway plays a critical role in tumorigenesis bv way of abberant IκB activity, a variety of compounds targeting IKK and its associated enzymes are in clinical development. [3] For instance, the proteasome inhibitor Bortezomib (Velcade®) has been approved by the FDA for use in haematological malignancies. [4] In addition, Bortezomib is currently being explored in clinical development for its efficacy against solid tumors (clinicaltrials.gov; NCT00479128).
