nur für Forschungszwecke
Fludarabine STAT1 Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1491
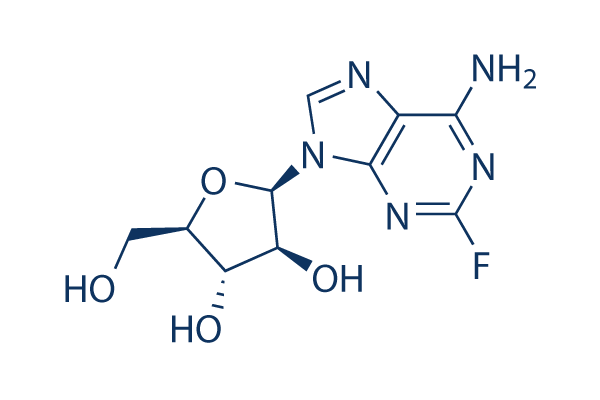
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 285.23
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | EGFR JAK Pim |
|---|---|
| Weitere STAT Inhibitoren | Napabucasin (BBI608) Stattic NSC 74859 (S3I-201) Cryptotanshinone (Tanshinone C) C188-9 (TTI-101) SH-4-54 BP-1-102 AS1517499 Nifuroxazide HO-3867 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jeko-1 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 24 h | inhibits expression of IDO | 25940712 | |
| MV-4-11 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| THP-1 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| MOLM 13 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| KBM3/Bu2506 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 25111583 | |
| Nalm-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Reh | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30 μM | 25061101 | |||
| U2937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Mec-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50>500 μM | 25061101 | |||
| RPMI-8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=500 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Molt-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=180 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Nalm-6-FluR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=250 μM | 25061101 | |||
| Raji | Function Assay | 3 μM | 24/48/72 h | induces accumulations of p53, p63 and p73 | 24940695 | |
| PBMC | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 24 h | DMSO | inhibits STAT1 phosphorylation | 24911872 |
| MDA-231 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 24 h | DMSO | decreases IDO expression | 24911872 |
| 624.38mel | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24 h | DMSO | decreases IDO expression | 24911872 |
| MDA-231 | Function Assay | 50-200 μM | 24 h | DMSO | inhibits IDO activity independently of mRNA levels | 24911872 |
| 624.38mel | Function Assay | 50-200 μM | 24 h | DMSO | inhibits IDO activity independently of mRNA levels | 24911872 |
| HMECs | Function Assay | 100 μM | 36 h | inhibits IFNγ and LPS induced STAT1 phosphorylation and IRF1 expression | 24211327 | |
| HMECs | Function Assay | 100 μM | 36 h | inhibits IFNα mediated phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT3, but not of STAT2 | 24211327 | |
| BJAB | Apoptosis Assay | 5 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis | 24057147 | |
| I-83 | Apoptosis Assay | 5 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis | 24057147 | |
| NALM6 | Apoptosis Assay | 5 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis | 24057147 | |
| DU-145 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-10 μg/ml | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner | 23734815 | |
| Nalm-6 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 1/2/4 h | induces autophagy | 23681223 | |
| Reh | Function Assay | 10 μM | 1/2/4 h | induces autophagy | 23681223 | |
| Nalm-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50 ∼10 μM | 23681223 | |||
| Reh | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50 ∼10 μM | 23681223 | |||
| HEC1A | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100-500 μM | 24 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| AN3CA | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100-500 μM | 24 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| HEC50B | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100-500 μM | 24 h | inhibits cell growth slightly | 23595697 | |
| HEC1A | Apoptosis Assay | 20/100 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| AN3CA | Apoptosis Assay | 20/100 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner | 23595697 | |
| HEC50B | Apoptosis Assay | 20/100 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 23595697 | |
| EHEB | Apoptosis Assay | 40 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 23497075 | |
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.7±2.8 µM | 23377192 | |||
| A549 GAPDH-deficient | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5±2.3 µM | 23377192 | |||
| CLL | Apoptosis Assay | 10 μM | 24-96 h | induces apoptotic cell death | 22207686 | |
| MEC1 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 μM | 72 h | induces apoptosis significantly | 22132973 | |
| U937 | Apoptosis Assay | 0.8 μM | 4-48 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22074700 | |
| U937 | Apoptosis Assay | 1 μM | 96 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22023523 | |
| Daudi | Apoptosis Assay | 20 μM | 96 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22023523 | |
| J45.01 | Apoptosis Assay | 1 μM | 96 h | induces apoptosis slightly | 22023523 | |
| RPMI 8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.9 ± 3.7 μM | 21948264 | |||
| CEM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.4 ± 0.4 μM | 21948264 | |||
| Raji | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.47 ± 0.04 μM | 21948264 | |||
| U937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.24 ± 0.04 μM | 21948264 | |||
| K562 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.44 ± 0.05 μM | 21948264 | |||
| NALM-6 | Apoptosis Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis slightly | 21699383 | |
| JMV-3 | Apoptosis Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | induces cell apoptosis slightly | 21699383 | |
| EHEB | Function Assay | 5-50 μM | 24 h | decreases p21 expression significantly | 21168391 | |
| JVM-2 | Function Assay | 30 μM | 24 h | decreases p21 expression | 21168391 | |
| KBM3/Bu2506 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=0.67 µM | 20933509 | |||
| KBM3/Bu2506 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.6 μM | 24 h | increases the cell fraction in S-phase | 20933509 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.0 μM | 20447390 | |||
| MCF-7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.0 μM | 20447390 | |||
| HLE-B3 | Function Assay | 25 μM | 48 h | blocks IFN-γ–induced STAT1 phosphorylation and IDO expression | 20435158 | |
| K562 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=3.3 nM | 20307198 | ||
| BW-225 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 ×10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| OH-65 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 ×10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| GR-145 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=2.74 × 10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=5.48 × 10−8 μM | 18661380 | |||
| CaSki | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 × 10−7 μM | 18661380 | |||
| ZMK-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC20=1.37 × 10−6 μM | 18661380 | |||
| SKW6.4 | Apoptosis Assay | 0.01-10 μM | 24/48 h | induces cell death in both time- and dose- dependent manner | 18092340 | |
| RPMI 8226 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 24 h | IC50=1.54 μM | 17976186 | ||
| MM.1S | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=13.48 μM | 17976186 | ||
| MM.1R | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=33.79 μM | 17976186 | ||
| U937 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3,200 ± 560 nM | 15930361 | |||
| CLL5 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL5 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 0.16 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| K562 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human paclitaxel-resistant K562 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 0.26 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| CLL3 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL3 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 0.35 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CLL4 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL4 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 0.64 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CEM-DNR-B | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human CEM-DNR-B cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 1.01 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| primary CLL | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human primary CLL cells, LD50 = 1.1 μM. | 25148392 | |||
| CLL6 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL6 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 1.6 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CLL2 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL2 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 2.66 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| HCT116 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human HCT116 cells after 72 hrs by SRB assay, IC50 = 6.6 μM. | 25462277 | ||
| PBMC | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against patient PBMC after 48 hrs by CellTitre-Blue assay in presenc of mouse M210B4 cells, IC50 = 10 μM. | 25562417 | ||
| CHO | Function assay | Binding affinity determined by displacement of specific binding of [125I]N-(4-amino-3-iodophenethyl)-adenosine in membranes of CHO cells stably transfected with the rat adenosine A3 receptor, Ki = 10.4 μM. | 7707320 | |||
| JVM2 | Antitumor assay | Antitumor activity against human JVM2 cells assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 10.4 μM. | 24673739 | |||
| HeLa | Antitumor assay | Antitumor activity against human HeLa cells assessed as cell viability by MTT assay, EC50 = 16 μM. | 24673739 | |||
| CLL1 | Antitumor assay | 48 hrs | Antitumor activity against CLL1 cells isolated from CLL patient assessed as cell viability after 48 hrs by FACS analysis, EC50 = 17.1 μM. | 24673739 | ||
| CEM | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human CEM cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 19.49 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| T47D | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human T47D cells after 72 hrs by SRB assay, IC50 = 46.2 μM. | 25462277 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 47.44 μM. | 20605656 | ||
| CCRF-CEM | Function assay | 10 uM | 1 to 60 mins | Drug transport in human CCRF-CEM cells assessed as ENT1-mediated uptake at 10 uM after 1 to 60 mins by liquid scintillation counting analysis | 23388705 | |
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Daoy | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for Daoy cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D caspase screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 285.23 | Formel | C10H12FN5O4 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 21679-14-1 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | FaraA, Fludarabinum, NSC 118218 | Smiles | C1=NC2=C(N=C(N=C2N1C3C(C(C(O3)CO)O)O)F)N | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 57 mg/mL
(199.83 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
STAT1
(Vascular smooth muscle cells) |
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Fludarabine hemmt effizient die Proliferation von RPMI 8226-Zellen mit einer IC50 von 1,54 μg/mL. Die IC50 dieser Verbindung gegen MM.1S- und MM.1R-Zellen beträgt 13,48 μg/mL bzw. 33,79 μg/mL. Im Gegensatz dazu sind U266-Zellen resistent gegen diese Chemikalie mit einer IC50 von 222,2 μg/mL. Diese Verbindung führt zu einer erhöhten Anzahl von Zellen in der G1-Phase des Zellzyklus, begleitet von einer gleichzeitigen Reduktion von Zellen in der S-Phase des Zellzyklus in einer zeitabhängigen Weise. Sie induziert einen Zellzyklus-Block und löst Apoptose in MM-Zellen aus. Sie löst eine zeitabhängige Spaltung von Caspase-8, -9, und -3, -7 aus, gefolgt von einer PARP-Spaltung. Sie erhöht die Expression von Bax auf zeitabhängige Weise, während die Expression von Bak sich nicht ändert. Nach Exposition gegenüber dieser Chemikalie für 12 Stunden zeigen RPMI 8226-Zellen einen Verlust des Membranpotenzials, wobei 61,05 % der Zellen eine geringe Fluoreszenz von Rhodamin 123 exprimieren, verglichen mit 8,62 % der Zellen in der unbehandelten Kontrolle. Um die Löslichkeit zu verbessern, wird es als Monophosphat (F-ara-AMP, fudarabine) formuliert, das bei intravenöser Infusion sofort und quantitativ zum Mutternukleosid dephosphoryliert wird. Im Zellinneren erfolgt eine Rephosphorylierung, die zu Fluoroadenin-Arabinosid-Triphosphat (F-ara-ATP) führt, dem wichtigsten zytotoxischen Metaboliten von F-ara-A. Es kann auch eine proinflammatorische Stimulation monozytischer Zellen induzieren, bewertet durch erhöhte Expression von ICAM-1 und IL-8-Freisetzung. Diese Verbindung beeinflusst das Wachstum von Ovarialkarzinomzelllinien nicht, während sie eine ausgeprägte und dosisabhängige Hemmung der Proliferation in Melanomzelllinien induziert. Es ist ein Inhibitor von STAT1, der STAT1 spezifisch reduziert, ohne andere Mitglieder der STAT-Familie zu beeinflussen. Zusätzlich zur zytoplasmatischen Akkumulation induziert wiederholtes Cisplatin in niedriger Dosis (RLDC) die HMGB1-Expression, die durch STAT1-Knockdown stark unterdrückt wird. Konsistent unterdrückt diese Chemikalie die HMGB1-Expression während der RLDC-Behandlung dosisabhängig in RLDC-behandelten Nieren-Tubuluszellen. |
| In vivo |
Mit PBS behandelte Tumore wachsen schnell auf etwa das 10-fache ihres ursprünglichen Volumens in 25 Tagen an, während die Tumore, die mit Fludarabine bei 40 mg/kg behandelt wurden, weniger als das 5-fache zunahmen. Ein signifikanter Antitumor-Effekt von 40 mg/kg dieser Verbindung auf das RPMI8226-Tumorwachstum wird gezeigt. RPMI8226-Tumore, die am Tag 10 mit 40 mg/kg dieser Chemikalie behandelt wurden, zeigen eine Zunahme apoptotischer Zellkerne. Diese Verbindung ist wirksam bei der Unterdrückung von RPMI8226-Myelom-Xenografts in SCID-Mäusen. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | procaspase-9 / procaspase-3 p-p53 / p53 STAT1 |
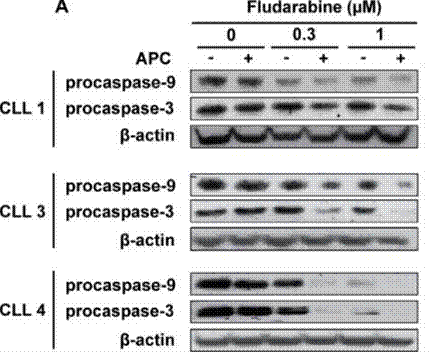
|
27223263 |
| Immunofluorescence | α-SMA / Vimentin |
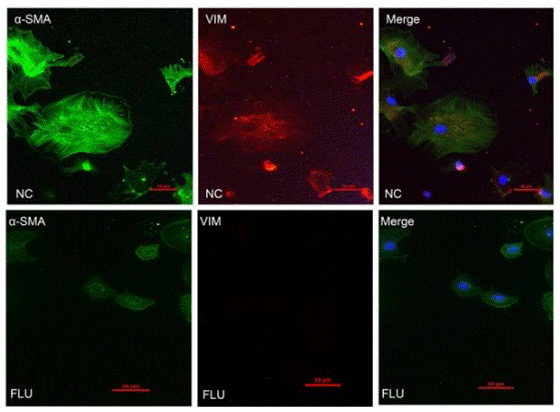
|
28322315 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
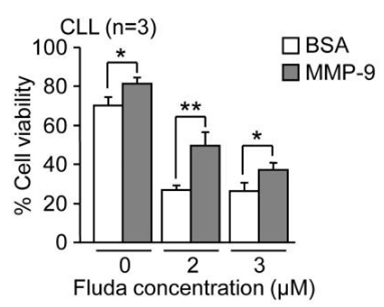
|
24956101 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05390814 | Recruiting | Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma |
Assistance Publique - Hôpitaux de Paris |
December 18 2023 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05201183 | Withdrawn | Acute Myeloid Leukemia|Chronic Myeloid Leukemia|Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia|Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
Naoyuki G. Saito M.D. Ph.D.|Indiana University |
October 2023 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT05917405 | Recruiting | Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Remission |
Nantes University Hospital |
September 14 2023 | Phase 2 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
how to re-suspend and deliver it for in vivo experiments?
Antwort:
For S1491, we tested a vehicle: 30% Propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W that you can resuspend this compound in at up to 30mg/ml. It is a suspension and can only be given via oral gavage.
