nur für Forschungszwecke
PF-3758309 PAK Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S7094
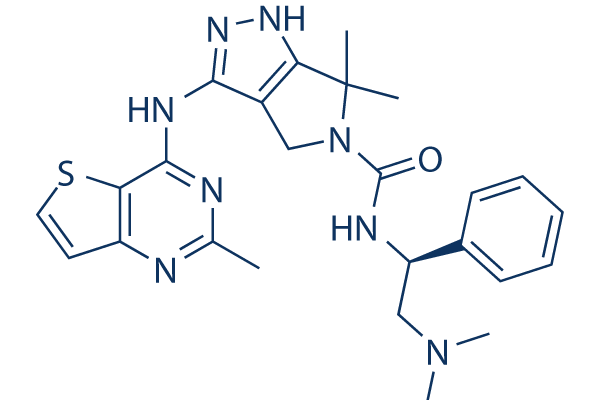
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 490.62
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | Akt Wnt/beta-catenin PKC HSP ROCK Microtubule Associated Integrin Bcr-Abl Actin FAK |
|---|---|
| Weitere PAK Inhibitoren | IPA-3 FRAX597 FRAX486 FRAX1036 LCH-7749944 NVS-PAK1-1 Hydrastine GNE 2861 G-5555 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| human MDA-MB-436 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 24-48 h | Cytotoxicity against human MDA-MB-436 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 24 to 48 hrs by Celltiter-glo luminescence assay, IC50=0.79 nM | 24432870 | ||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative activity against | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT116 cells after 72 hrs by CCK8 assay, IC50=0.039μM. | 29886323 | ||
| A549 | Antiproliferative activity against | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human A549 cells after 72 hrs by CCK8 assay, IC50=0.463μM. | 29886323 | ||
| TC32 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| fibroblast cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for control Hh wild type fibroblast cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 490.62 | Formel | C25H30N8OS |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 898044-15-0 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | PF-03758309 | Smiles | CC1=NC2=C(C(=N1)NC3=NNC4=C3CN(C4(C)C)C(=O)NC(CN(C)C)C5=CC=CC=C5)SC=C2 | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 98 mg/mL
(199.74 mM)
Ethanol : 98 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Merkmale |
PF-3758309 is potent toward a broad array of tumor cell lines from different tumor types.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
PAK1
(Cell-free assay) 13.7 nM(Ki)
PAK6
(Cell-free assay) 17.1 nM(Ki)
PAK5
(Cell-free assay) 18.1 nM(Ki)
PAK4
(Cell-free assay) 18.7 nM(Ki)
PAK3
(Cell-free assay) 99 nM
PAK2
(Cell-free assay) 190 nM
|
| In vitro |
PF-3758309 ist ein potenter (Kd = 2,7 nM), ATP-kompetitiver Inhibitor von PAK4 mit einem Ki von 18,7 nM. In Zellen hemmt diese Verbindung die Phosphorylierung des PAK4-Substrats GEF-H1 (IC50 = 1,3 nM) und das Verankerungs-unabhängige Wachstum einer Reihe von Tumorzelllinien (IC50 = 4,7 nM). Es hemmt auch die endogene pGEF-H1-Akkumulation in HCT116-Zellen. Diese Chemikalie hemmt potent die zelluläre Proliferation (IC50 = 20 nM) und das Verankerungs-unabhängige Wachstum (IC50 = 27 nM) von A549-Zellen. |
| Kinase-Assay |
Phospho-GEF-H1 Zellulärer Assay
|
|
TR-293-KDG-Zellen werden aus HEK293-Zellen konstruiert, die stabil mit Tetracyclin-induzierbarer PAK4-Kinase-Domäne (Aminosäuren 291-591) und konstitutiv exprimiertem HA-markiertem GEFH1ΔDH (Aminosäuren 210-921) transfiziert wurden. TR-293-KDG-Zellen werden 3 Stunden lang mit PF-3758309 inkubiert, auf einer Anti-HA-Antikörper-beschichteten Platte eingefangen, mit einem Anti-Phospho-S810-GEF-H1-Antikörper nachgewiesen und mit einem Meerrettichperoxidase-Ziegen-Anti-Kaninchen-Antikörper-Konjugat quantifiziert.
|
|
| In vivo |
PF-3758309 blockiert das Wachstum mehrerer menschlicher Tumoren-Xenotransplantate, mit einem Plasma-EC50-Wert von 0,4 nM im empfindlichsten Modell. Diese Verbindung ist antiproliferativ und induziert Apoptose in einem HCT116-Tumormodell. |
Literatur |
Anwendungen
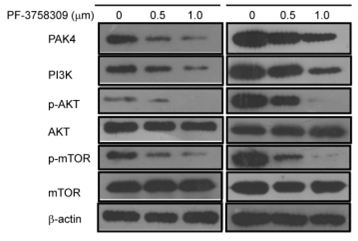
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | PAK4 / PI3K / p-AKT / AKT / p-mTOR / mTOR |
|
28407679 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
If this compound crosses the blood brain barrier?
Antwort:
We're sorry we don't have any data on whether it can cross BBB or not, the following reference indicate that this compound can not: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3490962/.
