nur für Forschungszwecke
3-Methyladenine (3-MA) Autophagy/PI3K-Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S2767
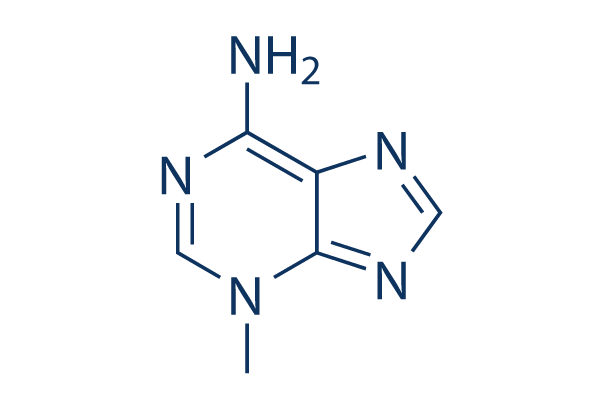
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 149.15
Qualitätskontrolle
Produkte, die oft zusammen verwendet werden mit 3-Methyladenine (3-MA)
| Verwandte Ziele | Akt mTOR GSK-3 ATM/ATR DNA-PK AMPK PDPK1 PTEN PP2A PDK |
|---|---|
| Weitere PI3K Inhibitoren | GDC-0077 (Inavolisib) SAR405 Quercetin (Sophoretin) LY294002 XL147 analogue Tersolisib (STX-478) Buparlisib (BKM120) 740 Y-P (PDGFR 740Y-P) GO-203 TFA Eganelisib (IPI-549) |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K562 | Function Assay | 10mM | 1h | decreases the expression of LC3-II and the formation of autophagosomes | 21864037 | |
| Jurkat | Function Assay | 10mM | 1h | decreases the expression of LC3-II and the formation of autophagosomes | 21864037 | |
| HeLa | Cytotoxicity Assay | 2mM | 24h | inhibites the cytotoxicity of silibinin to HeLa cells. | 21875385 | |
| PC12/TetOn | Function Assay | 0.1/1mM | 18h | leads to α-syn(WT) accumulation, toxicity, and oligomer formation | 21906659 | |
| RMPI8226 | Function Assay | 5mM | 1h | suppresses the level of autophagy under nutrient depletion | 21915620 | |
| MCF-7 | Function Assay | 10mM | 48h | blocks autophagy induced by bortezomib | 21931937 | |
| HBx | Apoptosis Assay | 10mM | 48h | DMSO | increases cell death | 22020078 |
| Marc-145 | Function Assay | 5mM | 12/24/36h | reduces the PRRSV titers and the protein expression | 22119900 | |
| U937 | Function Assay | 2mM | 12h | decreases the autophagy ratio | 22155150 | |
| BGC-823 | Function Assay | 5mM | 2h | inhibits the rate of autophagic cells | 22322152 | |
| A549 | Function Assay | 0.1mM | 24h | suppresses SU11274-induced cell death | 22466960 | |
| pDCs | Function Assay | 10mM | 0.5h | reduces the induction of IFN-α by ssRNA40 | 22396599 | |
| HeLa | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 24h | induces caspase-dependent cell death | 22545128 | |
| U251 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 24h | increases S1-induced cell death | 22579788 | |
| MCF-7 | Apoptosis Assay | 0.1mM | 6h | enhances sirtinol-induced apoptosis | 22751989 | |
| PC-3 | Apoptosis Assay | 2mM | 2h | increases ORI-induced cell death | 22745580 | |
| HCT116 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 24h | DMSO | enhances apigenin-induced cell death | 24626522 |
| U2OS | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10mM | 24h | intensifies the growth inhibition induced by Dox | 24639013 | |
| A2780cp | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5mM | 1h | ddH2O | enhances cisplatin-induced cell death | 24817946 |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 5mM | 4h | increases cellular levels of HL | 24713587 | |
| Microglia | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 24h | decreases hypoxia-induced cell death | 24818601 | |
| MDA-MB 231 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 0.5h | modulates Tocomin® induced apoptosis | 24830781 | |
| PANC-1 | Apoptosis Assay | 1mM | 48h | DMSO | enhances bortezomib-induced cell viability loss | 24842158 |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 2mM | 48h | promotes TM-induced cell death | 24970676 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 2mM | 24h | inhibits autophagy induced by TM | 24970676 | |
| MCF-7 | Function Assay | 2mM | 48h | promotes TM-induced cell death | 24970676 | |
| MCF-7 | Function Assay | 2mM | 24h | inhibits autophagy induced by TM | 24970676 | |
| HepG2 | Apoptosis Assay | 3mM | 5h | reduces cell apoptosis induced by QDs | 22836595 | |
| HeLa | Apoptosis Assay | 10mM | 2h | decreases cell viability co-treatment with PEI | 23000135 | |
| SK-HEP-1 | Apoptosis Assay | 10mM | 1h | protects against autophagy and induces apoptosis in bufalin-treated cells | 22858649 | |
| MDA-MB231 | Function Assay | 5mM | 1h | increases resveratrol-mediated caspase activation and cell death | 23088850 | |
| PaCa44 | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5mM | 1h | reduces genipin-mediated apoptosis | 23124112 | |
| T-47D | Function Assay | 10mM | 2h | inhibits autophagy process and increases rapamycin induced apoptosis | 23300026 | |
| GTL-16 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 24h | reduces cell viability as compared to cells treated with MET inhibitors | 23313490 | |
| U251MG | Function Assay | 3mM | 1h | suppresses LC3-II protein expression | 23338618 | |
| T24 | Function Assay | 10mM | 1h | reduces the cleavage of LC3 after baicalin treatment | 23354080 | |
| HUVECs | Function Assay | 3mM | 24h | blocks the protective effect of resveratrol by inhibiting autophagy | 23358928 | |
| MCF-7 | Function Assay | 5mM | 24h | inhibits starvation-induced autophagy | 23395679 | |
| Hela | Function Assay | 5mM | 24h | inhibits starvation-induced autophagy | 23395679 | |
| OR6 | Function Assay | 10mM | 72h | suppresses HCV replication and formation of autophagosomes | 23395875 | |
| HT-29 | Function Assay | 1mM | 48/96h | inhibits AMPK induces autophagic cell death | 23508272 | |
| SH-SY5Y | Cytotoxicity Assay | 5mM | 24h | increases PCN toxicity | 23525265 | |
| Saos-2 | Apoptosis Assay | 1mM | 96h | increases cell death induced by PCX | 23563171 | |
| 1321N1 | Cytotoxicity Assay | 5mM | 24h | protects cell against PCN-induced toxicity | 23525265 | |
| A2780 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 24h | converts FTY720 with CDDP into an additive effect towards killing ovarian cancer cells | 23592281 | |
| OV2008 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 24h | converts FTY720 with CDDP into an additive effect towards killing ovarian cancer cells | 23592281 | |
| PC12 | Function Assay | 10mM | 24h | water | inhibits chymotrypsin-like proteasomal activity. | 23603979 |
| SH-SY5Y | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 1h | abolishes celastrol neuroprotective effect | 23619395 | |
| SH-SY5Y | Function Assay | 1mM | 24h | inhibits the autophagy induced by TOCP | 23743148 | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 10mM | 24h | inhibits siTIGAR- and HBSS-induced autophagy | 23817040 | |
| HeLa | Function Assay | 10mM | 2h | suppresses LC3 II expressison | 23864738 | |
| HONE-1 | Function Assay | 5mM | 1h | represses 6r-mediated ROS production | 23892358 | |
| MCF7 | Function Assay | 5mM | 24h | increases CuO induced cell death | 23962629 | |
| HO8910 | Apoptosis Assay | 10mM | 12h | enhances B19-induced apoptosi | 23983610 | |
| SMMC-7721 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 24h | attenuates TNF-α protection against serum starvation-mediated apoptosis | 24066693 | |
| Hep3B | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 24h | attenuates TNF-α protection against serum starvation-mediated apoptosis | 24066693 | |
| H460 | Function Assay | 10mM | 4h | increases cisplatin-induced cell death | 24173208 | |
| A549 | Function Assay | 10mM | 4h | inhibits autophagy induced by irradiation | 24142735 | |
| H1299 | Function Assay | 10mM | 4h | increases cisplatin-induced cell death | 24173208 | |
| WiDr | Function Assay | 10mM | 1h | inhibits PCBL-induced LC3 II expression | 24190489 | |
| LoVo | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 48h | enhances DCA-induced apoptosis. | 24201812 | |
| HepG2 E47 | Function Assay | 2.5mM | 48h | increases the toxicity of AA, BSO, and CCl4 | 24273738 | |
| RKO | Function Assay | 2mM | 1h | DMSO | enhances cell death by geldanamycin | 24291777 |
| Hep3B | Apoptosis Assay | 2mM | 12h | DMSO | inhibits AZD8055-induced cell death | 24297300 |
| ACHN-5968 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 3h | enhances paclitaxel-mediated apoptosis | 24305604 | |
| Huh7 | Apoptosis Assay | 2mM | 12h | DMSO | inhibits AZD8055-induced cell death | 24297300 |
| UOK257 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 3h | enhances paclitaxel-mediated apoptosis | 24305604 | |
| ECSCs | Apoptosis Assay | 10mM | 4h | decreases rapamycin-treated apoptosis | 24319109 | |
| MCF-7 | Function Assay | 10mM | 24h | inhibits the autophagy induced by chemotherapy drugs | 24315578 | |
| SGC-7901 | Apoptosis Assay | 2mM | 1h | increases CA-4 induced apoptosis | 24321340 | |
| SMMC-7721 | Apoptosis Assay | 2mM | 1h | increases CA-4 induced apoptosis | 24321340 | |
| T24 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 1.5h | potentiates celecoxib-induced apoptosis | 24349176 | |
| NTUB1 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 1.5h | potentiates celecoxib-induced apoptosis | 24349176 | |
| MG-63 | Apoptosis Assay | 10mM | 12h | enhances DP-induced apoptosis | 24358301 | |
| MG-63 | Apoptosis Assay | 0.5/1mM | 32h | enhances salinomycin-induced cell apoptosis | 24358342 | |
| MG-63 | Function Assay | 0.5/1mM | 48h | induces salinomycin-induced cell viability loss | 24358342 | |
| U2OS | Function Assay | 0.5/1mM | 48h | induces salinomycin-induced cell viability loss | 24358342 | |
| HGC-27 | Function Assay | 10mM | 1h | inhibits the cell viability loss by RAD001 or MK-2206 | 24416349 | |
| HCT116 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 24h | enhances the apoptosis induced by apigenin | 24626522 | |
| A549 | Apoptosis Assay | 10mM | 48h | accelerates the reduction of cell viability induced by PTX | 24626722 | |
| Saos-2 | Apoptosis Assay | 10mM | 24h | intensifies the growth inhibition of the U2OS cells induced by Dox | 24639013 | |
| U2OS | Apoptosis Assay | 10mM | 24h | intensifies the growth inhibition of the U2OS cells induced by Dox | 24639013 | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 5mM | 4h | increases HL release | 24713587 | |
| A549 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 48h | decreases the percentage of cell death and expression levels of caspase-3, Beclin-1 and LC3-II | 24706303 | |
| A2780cp | Apoptosis Assay | 2.5mM | 1h | ddH2O | enhances cisplatin-induced cell death | 24817946 |
| Microglia | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 24h | decreases hypoxia-induced cell death | 24818601 | |
| HT-29 | Apoptosis Assay | 1mM | 48h | DMSO | enhances bortezomib-induced cell viability loss | 24842158 |
| MDR | Apoptosis Assay | 10mM | 6h | strengthens the power of anticancer drugs | 25019701 | |
| H157 | Function Assay | 5mM | 2h | suppresses SPC induced accumulation of LC3-II | 25285628 | |
| A549 | Function Assay | 5mM | 2h | suppresses SPC induced accumulation of LC3-II | 25285628 | |
| A2780cp | Growth Inhibition Assay | 1mM | 1h | increases cisplatin-induced cell death | 25322694 | |
| NBL-W-S | Apoptosis Assay | 1mM | 6h | increases cell apoptosis induced by GANT-61 | 25323222 | |
| NBL-W-S | Growth Inhibition Assay | 1mM | 6h | enhances GANT-61 toxicity | 25323222 | |
| A549 | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 2h | DMSO | inhibits BDMC-induced apoptotic cell death | 25716561 |
| 95D | Apoptosis Assay | 5mM | 2h | DMSO | inhibits BDMC-induced apoptotic cell death | 25716561 |
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 3mM | 2h | DMSO | reduces growth inhibitory effect of BDMC | 25716561 |
| 95D | Growth Inhibition Assay | 3mM | 2h | DMSO | reduces growth inhibitory effect of BDMC | 25716561 |
| Nara-H | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5mM | 48h | enhances temsirolimusmediated suppression of Nara-H cell proliferation | 21805033 | |
| HUVECs | Function Assay | 10mM | 0.5h | decreases the AGE-BSAinduced autophagy leve | 21468592 | |
| HepG2 | Apoptosis Assay | 2mM | 1h | enhances radiation-induced cell death | 21453691 | |
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 149.15 | Formel | C6H7N5 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | 3 years -20°C powder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 5142-23-4 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen | Lösungen sind instabil. Frisch zubereiten oder kleine, vorverpackte Größen kaufen. Nach Erhalt umpacken. | |
| Synonyme | NSC 66389 | Smiles | CN1C=NC(=N)C2=C1N=CN2 | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 10 mg/mL
(67.04 mM)
Mit 50°C Wasserbad erwärmt;
Ultraschallbehandelt;
Ethanol : 10 mg/mL Water : 4 mg/mL |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Autophagy
Vps34
(HeLa cells) 25 μM
PI3Kγ
(HeLa cells) 60 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Die leichte Präferenz für die Vps34-Prävention durch 3-Methyladenine (3-MA) resultiert wahrscheinlich aus einem hydrophoben Ring, der spezifisch für Vps34 ist und die 3-Methylgruppe dieser Verbindung umschließt. Es wurde berichtet, dass es unter normalen und Hungerbedingungen den Tod von Krebszellen verursacht und auch die Zellmigration und Invasion unabhängig von seiner Fähigkeit, Autophagy zu hemmen, unterdrücken könnte, was impliziert, dass es andere Funktionen als die Autophagy-Unterdrückung besitzt. Diese Verbindung löst einen Caspase-abhängigen Zelltod aus, der unabhängig von der Autophagy-Hemmung ist. Die Behandlung mit 5 mM davon reduziert den Prozentsatz der Glukose-gehungerten HeLa-Zellen, die GFP-LC3-Punktate zeigen, auf 23%. Die LC3-I-Spiegel nehmen zu und die LC3-II-Spiegel nehmen zwischen 12 und 48 Stunden in Zellen ab, die mit 3-MA behandelt werden. Die Umwandlung von LC3-I zu LC3-II wird durch die Verbindung unterdrückt. Die Behandlung von HeLa-Zellen damit bei 2,5 mM oder 5 mM für einen Tag beeinflusst die Zellviabilität nicht, während die Behandlung mit 10 mM für einen Tag eine Abnahme der Zellviabilität um 25,0% verursacht. Die Behandlung von Zellen mit 2,5, 5 oder 10 mM für zwei Tage verursacht eine Abnahme der Viabilität um 11,5%, 38,0% bzw. 79,4%. Es verringert die Zellviabilität in einer zeit- und dosisabhängigen Weise und verkürzt die Dauer des Nocodazol-induzierten Prometaphase-Arrests erheblich. Die Unterdrückung der Autophagy durch 3-MA hemmt den SU11274-induzierten Zelltod. Eine verlängerte Behandlung damit (bis zu 9 Stunden) induziert eine signifikante LC3 I zu II Umwandlung in Wildtyp-MEFs. Eine verlängerte Behandlung mit 3-MA, aber nicht mit Wortmannin, erhöht die GFP-LC3-Punktation/-Aggregation deutlich. Die induzierte LC3-Umwandlung und die freie GFP-Freisetzung sind ATG7-abhängig. Die Behandlung damit führt zu einem evidenten Anstieg des p62-Proteinspiegels. Die Verbindung erhöht den p62-Spiegel sogar in Atg5−/− MEFs sowie in Zellen mit DOX-vermittelter Deletion von ATG5. Es hemmt Klasse I und Klasse III PI3K in verschiedenen zeitlichen Mustern. Die induzierte LC3 I zu LC3 II Umwandlung ist in Tsc2−/− Zellen im Vergleich zu Wildtyp-Zellen dramatisch beeinträchtigt. Diese Verbindung stört die anti-autophagische Funktion des mTOR-Komplexes 1. |
| Kinase-Assay |
Proteinabbau-Assay
|
|
HeLa-Zellen werden 24 Stunden lang mit 0,05 mCi/mL l-[U- 14C]Valin radioaktiv markiert. Am Ende der Markierungsperiode werden die Zellen dreimal mit PBS gespült. Die Zellen werden für die angegebenen Zeiten entweder in vollem Medium oder in EBSS mit oder ohne 10 mM 3-Methyladenine (3-MA) inkubiert.
|
|
| In vivo |
3-Methyladenine (3-MA) blockiert Autophagy durch seine Wirkung auf die Klasse III Phosphatidylinositol-3-Kinase (PI3K). Die Behandlung mit dieser Verbindung verändert das Ausmaß der Hämorrhagie im Vergleich zur Subarachnoidalblutung (SAH)-Gruppe nicht. Die Vorbehandlung verschlimmert die neurologischen Symptome im Vergleich zur SAH + Vehikel-Gruppe signifikant. Autophagy nimmt ab, wenn sie angewendet wird. Umgekehrt wird gespaltenes Caspase-3 in der SAH + 3-MA-Gruppe deutlich hochreguliert. Im Einklang mit der Hochregulation der gespaltenen Caspase-3-Expression ist die Anzahl der TUNEL-positiven Zellen im rechten Kortex in der SAH + 3-MA-Gruppe im Vergleich zur SAH + Vehikel-Gruppe signifikant erhöht. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | α-SMA / TGF-β / LC-3BI / LC-3B II / Beclin-1 / NF-κB p65 caspase-3 / caspase-9 / PARP VEGF APP / BACE1 / ADAM17 / Presenilin 1 / Presenilin 2 / Nicastrin / APH-1 / Pen-2 / LC3-1 / LC3-2 |
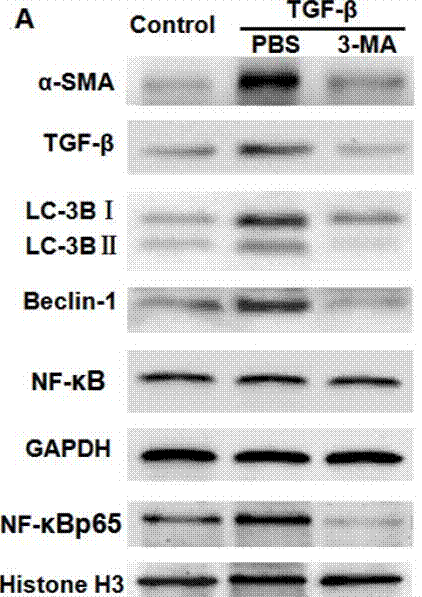
|
29296191 |
| Immunofluorescence | LC3 / Hif-α / COX2 |
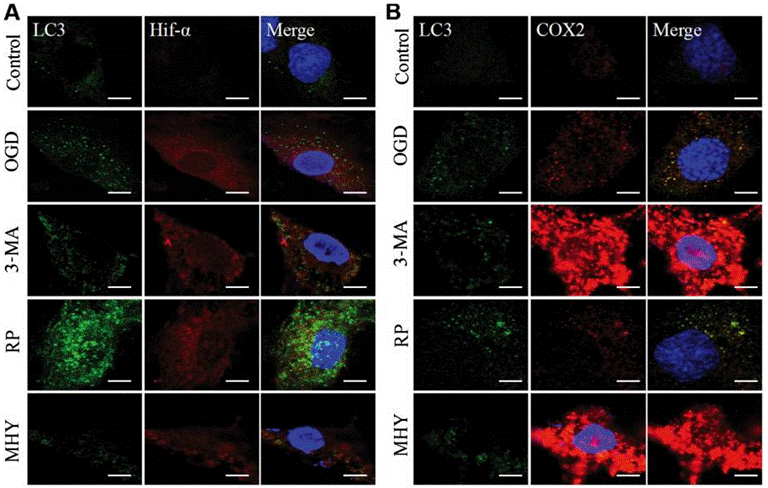
|
29039446 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
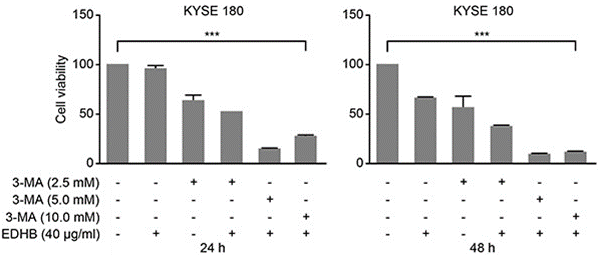
|
26934124 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
I'm also wondering whether it can be dissolved in water, or maybe something like culture medium, normal saline solution to form 10mM solution.
Antwort:
As the reference (http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal. pone.0035665), it was found to inhibit autophagy at concentrations ranging from 1 to 10 mM and was directly dissolved into the culture medium at the indicated concentrations. And we tested the solubility of S2767, and found its solubility in DMEM is 31 mg/mL at about 40°C.
