nur für Forschungszwecke
Cabazitaxel Microtubule Associated Hemmer
Kat.-Nr.S3022
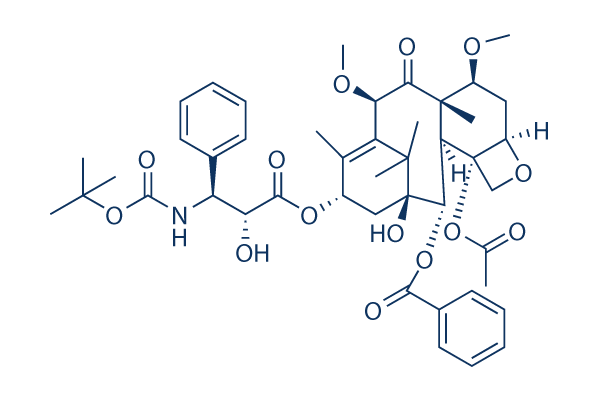
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 835.93
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | Akt Wnt/beta-catenin PKC HSP ROCK Integrin Bcr-Abl Actin FAK Kinesin |
|---|---|
| Weitere Microtubule Associated Inhibitoren | Nocodazole MMAF Patupilone (Epothilone B) Lexibulin (CYT997) CW069 Combretastatin A4 Epothilone A ABT-751 (E7010) TAI-1 Cucurbitacin B |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGC7901 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human SGC7901 cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.0003553μM | 24405702 | |||
| U937 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human U937 cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.0005391μM | 24405702 | |||
| MCF7 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human MCF7 cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.001187μM | 24405702 | |||
| PANC1 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human PANC1 cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.001283μM | 24405702 | |||
| HT1080 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human HT1080 cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.001406μM | 24405702 | |||
| DU145 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human DU145 cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.001429μM | 24405702 | |||
| A549 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human A549 cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.001483μM | 24405702 | |||
| A431 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human A431 cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.001483μM | 24405702 | |||
| HeLa | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human HeLa cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.001799μM | 24405702 | |||
| K562 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human K562 cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.004186μM | 24405702 | |||
| HL60 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human HL60 cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.004736μM | 24405702 | |||
| BGC823 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human BGC823 cells by MTT assay, GI50=0.4672μM | 24405702 | |||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells, IC50=0.00148μM | 28850227 | |||
| MES-SA/Dx5 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 hrs | Growth inhibition of human MES-SA/Dx5 cells after 72 hrs by SRB assay, IC50=0.015μM | 29251920 | ||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NCI-H524 | Cytotoxicity assay | 2 hrs | Cytotoxicity in human NCI-H524 cells pre-incubated for 2 hrs followed by compound wash out and subsequently incubated for 70 hrs by Cell Titer Glo assay, IC50=0.00026μM | 30735385 | ||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 835.93 | Formel | C45H57NO14 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 183133-96-2 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | XRP6258, RPR-116258A, TXD 258, Taxoid XRP6258 | Smiles | CC1=C2C(C(=O)C3(C(CC4C(C3C(C(C2(C)C)(CC1OC(=O)C(C(C5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)OC(C)(C)C)O)O)OC(=O)C6=CC=CC=C6)(CO4)OC(=O)C)OC)C)OC | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 167 mg/mL
(199.77 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Merkmale |
A semi-synthetic derivative of a natural taxoid.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Microtubule
(Cell-free assay) |
| In vitro |
Cabazitaxel erhöht die CYP3A-Enzymaktivitäten in Rattenhepatozyten. Die mittlere ex-vivo-Plasmaproteinbindung dieser Verbindung beim Menschen beträgt 91,6 %. Es wird schnell und umfassend zu zahlreichen Metaboliten metabolisiert. Diese Verbindung zeigt Aktivität in mehreren murinen und humanen resistenten Zelllinien. Bei einer 4-tägigen Exposition mit dieser Chemikalie wird bei relativ niedrigen Cabazitaxel-Konzentrationen eine Zytotoxizität festgestellt. Es zeigt eine hohe Antitumoraktivität in 3 humanen kolorektalen Zelllinien (HCT-116, HCT-8 und HT-29). |
| In vivo |
In begleitenden Modellen wird festgestellt, dass Cabazitaxel eine signifikante Antitumoraktivität aufweist. In murinen Tumorxenografts (Colon C38 und Pankreas P03) führt diese Verbindung zu vollständigen Tumorregressionen. Unter Verwendung der humanen Glioblastom-Zelllinien SF-295 und U251 werden sowohl orthotope als auch subkutane murine Xenografts erzeugt. Diese chemische Behandlung führt zu einer vollständigen Regression bei der Mehrheit der subkutan implantierten Tumoren. Darüber hinaus führt sie in orthotopen Modellen zu einer vollständigen Tumorregression bei 4 von 10 U251-Tumoren. |
Literatur |
|
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04622761 | Not yet recruiting | Prostate Cancer |
The Clatterbridge Cancer Centre NHS Foundation Trust|University of Liverpool |
January 15 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04495179 | Completed | Progressive Metastatic Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer |
AstraZeneca|Parexel |
August 4 2020 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03257891 | Unknown status | Adrenocortical Carcinoma |
Azienda Socio Sanitaria Territoriale degli Spedali Civili di Brescia|San Luigi Gonzaga Hospital |
January 25 2018 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03043989 | Terminated | Prostate Cancer |
Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins|Maryland Technology Development Corporation |
March 21 2017 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
What is the elimination half-life of this compound?
Antwort:
According to the paper report, its elimination half-life is 95h.
