nur für Forschungszwecke
Patupilone (Epothilone B) Microtubule Associated Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1364
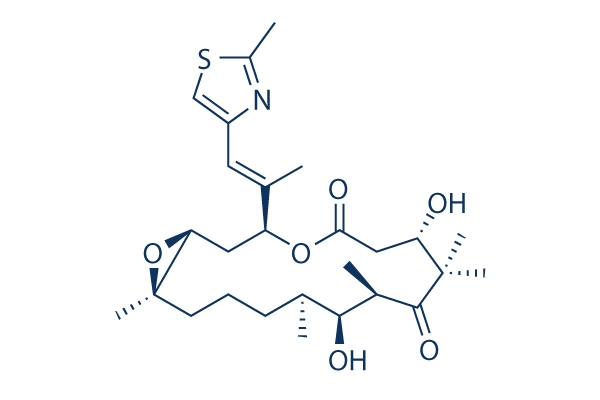
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 507.68
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | Akt Wnt/beta-catenin PKC HSP ROCK Integrin Bcr-Abl Actin FAK Kinesin |
|---|---|
| Weitere Microtubule Associated Inhibitoren | Nocodazole MMAF Lexibulin (CYT997) CW069 Combretastatin A4 Epothilone A ABT-751 (E7010) TAI-1 Cucurbitacin B INH1 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| human LC-2-ad cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LC-2-ad cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=3.77e-06 μM | ||||
| human A431 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A431 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=9.86e-06 μM | ||||
| human SW1710 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1710 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.14e-05 μM | ||||
| human Daoy cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human Daoy cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.73e-05 μM | ||||
| human BFTC-905 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BFTC-905 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=4.99e-05 μM | ||||
| human A375 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A375 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=5e-05 μM | ||||
| human RKO cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RKO cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=6.47e-05 μM | ||||
| human KYSE-510 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-510 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=7.38e-05 μM | ||||
| human HLE cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HLE cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=8.26e-05 μM | ||||
| human MCF7 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MCF7 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=8.66e-05 μM | ||||
| human 786-0 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human 786-0 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.11 nM | ||||
| human TE-8 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human TE-8 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.111 nM | ||||
| ovarian carcinoma 1A9 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibitory concentration against ovarian carcinoma 1A9 cell growth | ||||
| human PANC-03-27 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human PANC-03-27 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.132 μM | ||||
| human VMRC-RCZ cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human VMRC-RCZ cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.136 μM | ||||
| human IGROV-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human IGROV-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.156 μM | ||||
| human MG-63 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MG-63 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.165 μM | ||||
| human SIG-M5 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SIG-M5 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.169 μM | ||||
| human NCI-H650 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H650 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.17 μM | ||||
| human PSN1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human PSN1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.173 μM | ||||
| human PA-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human PA-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.174 μM | ||||
| KB-8511 cells | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | Concentration required to inhibit the growth of human epidermoid carcinoma cells KB-8511 by 50 percent (72 hr exposure), IC50=0.18 μM | |||
| KB-31 cells | Growth inhibition assay | 72 h | Concentration required to inhibit the growth of human epidermoid carcinoma cells KB-31 by 50 percent (72 hr exposure) | |||
| human BHY cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BHY cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.195 nM | ||||
| human BB30-HNC cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BB30-HNC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.201 μM | ||||
| human HOS cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HOS cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.215 μM | ||||
| human 639-V cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human 639-V cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.218 μM | ||||
| human ES1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ES1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.221 μM | ||||
| human TE-15 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human TE-15 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.225 μM | ||||
| human LXF-289 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LXF-289 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.277 μM | ||||
| human CAL-12T cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-12T cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.239 μM | ||||
| human T84 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human T84 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.24 μM | ||||
| human KYSE-450 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-450 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.267 μM | ||||
| human LCLC-103H cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LCLC-103H cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.31 nM | ||||
| human NCI-H810 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H810 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.322 μM | ||||
| human HUTU-80 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HUTU-80 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.328 μM | ||||
| human NCI-H460 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H460 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.333 μM | ||||
| human HGC-27 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HGC-27 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.338 μM | ||||
| human HSC-2 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HSC-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.363 nM | ||||
| human IA-LM cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human IA-LM cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.393 μM | ||||
| human HMV-II cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HMV-II cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.394 μM | ||||
| human COLO-679 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human COLO-679 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.394 μM | ||||
| human NCI-H2122 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H2122 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.41 μM | ||||
| human CAL-39 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-39 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.411 μM | ||||
| human SW954 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW954 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.436 μM | ||||
| human LCLC-97TM1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LCLC-97TM1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.444 μM | ||||
| human KYSE-270 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-270 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.445 μM | ||||
| human NB13 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB13 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.447 μM | ||||
| human SK-LMS-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-LMS-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.646 μM | ||||
| human SW620 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW620 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.648 μM | ||||
| human HCT-15 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HCT-15 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.717 μM | ||||
| human DU-145 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DU-145 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.721 μM | ||||
| human ST486 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ST486 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.721 μM | ||||
| human A427 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A427 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.828 μM | ||||
| human HT-1080 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HT-1080 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.842 μM | ||||
| human NCI-H2009 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H2009 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.862 μM | ||||
| human SK-LU-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-LU-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.866 μM | ||||
| human SCC-4 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SCC-4 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.877 μM | ||||
| human NCI-H1299 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1299 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.88 μM | ||||
| human NH-12 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NH-12 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.891 μM | ||||
| human SK-UT-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-UT-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.892 μM | ||||
| human Bel7402 | Proliferation assay | 72 h | Antiproliferative activity against human Bel7402 after 72 hrs by CellTiter Glo assay, IC50=0.9 μM | |||
| human A388 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A388 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.94 μM | ||||
| human SW982 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW982 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.999 μM | ||||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 507.68 | Formel | C27H41NO6S |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 152044-54-7 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | EPO906 | Smiles | CC1CCCC2(C(O2)CC(OC(=O)CC(C(C(=O)C(C1O)C)(C)C)O)C(=CC3=CSC(=N3)C)C)C | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 102 mg/mL
(200.91 mM)
Ethanol : 102 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Tubulin
(Cell-free assay) 1.8 μM(EC0.01)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Patupilone (Epothilone B) zeigt eine bessere Aktivität als Epothilon A, mit einem EC0.01 von 1,8 μM. Es hemmt die Zellproliferation in HCT116-Zellen potent mit einer IC50 von 0,8 nM. Diese Verbindung induziert einen Mitosearrest und zeigt Zytotoxizität in KB3-1-, KBV-1-, Hela- und Hs578T-Zellen, mit einer IC50 von 3 nM bis 92 nM. Es konkurriert mit Taxol bei der Bindung an Mikrotubuli, mit einer IC50 von 3,3 μM. In MCF-7-Zellen, die GFP-α-Tubulin überexprimieren, blockiert es (3,5 nM) effizient die Mikrotubuli-Dynamik. Gleichzeitig induziert es einen Mitosearrest mit einer IC50 von 3,5 nM. In Multiples-Myelom (MM)-Zellen, einschließlich RPMI 8226, U266, MM.1S, LR5 und MR20, unterdrückt es direkt die Proliferation mit einer IC50 von 1 nM bis 10 nM. Ähnlich induziert es (10 nM) auch einen Zellzyklusarrest und Apoptose. Eine aktuelle Studie zeigt, dass es in Ovarialkarzinom-Hey-Zellen (5 nM–100 nM) das Epithelialzell-Adhäsionsantigen (EpCAM) auf der Oberfläche verstärkt, ohne die Transkription oder das gesamte zelluläre Niveau von EpCAM zu beeinflussen. |
| Kinase-Assay |
Tubulinpolymerisationsassay
|
|
Kälberhirn-Mikrotubulusproteine (MTP) werden gereinigt, wobei sie ca. 15%–20% Mikrotubulus-assoziierte Proteine enthalten. Der für die Epothilon B-Mikrotubulus-Studien verwendete Puffer (MES-Puffer) enthält 0,1 M 2-Morpholinoethansulfonsäure (MES), 1 mM EGTA und 0,5 mM MgCl2 bei pH 6,6. Proben für die Elektronenmikroskopie werden auf Kohlenstoff-über-Parlodion-beschichtete Gitter (300 mesh) gelegt und negativ mit 2% Uranylacetat gefärbt. Die Mikrotubulus-Assemblierung in An- oder Abwesenheit von Patupilone (Epothilone B) wird spektrophotometrisch mittels eines Spektrophotometers überwacht, das mit einem thermostatisch geregelten Flüssigkeitszirkulator ausgestattet ist. Die Temperatur wird bei 35 °C gehalten und Änderungen der Trübung (repräsentativ für die Polymermasse) werden bei 350 nm überwacht. Die effektive Konzentration (EC0.01), definiert als die interpolierte Konzentration, die eine anfängliche Steigung von 0,01 OD/min induzieren kann, wird unter Verwendung der Formel EC0.01 = Konzentration/Steigung berechnet und als Mittelwert mit Standardabweichung aus drei verschiedenen Konzentrationen ausgedrückt.
|
|
| In vivo |
In einem Maus-Xenograft-Modell von RPMI 8226-Zellen verlängert Patupilone (Epothilone B) (2,5 mg/kg–4 mg/kg) das Überleben und unterdrückt das Tumorwachstum. Ähnlich hemmt diese Verbindung in der gleichen Dosis auch das Tumorwachstum in Maus-Xenograft-Modellen von Prostatakrebszellen, einschließlich DU145 und PC3. |
Literatur |
|
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00496600 | Completed | Refractory Malignancy |
University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey|Novartis Pharmaceuticals|National Cancer Institute (NCI)|Rutgers The State University of New Jersey |
July 2007 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00442741 | Withdrawn | Solid Tumors |
Novartis Pharmaceuticals|Novartis |
July 2007 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00468260 | Terminated | Advanced Malignancies |
Novartis Pharmaceuticals|Novartis |
May 2007 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00448396 | Completed | Advanced Malignancies |
Novartis Pharmaceuticals|Novartis |
March 2007 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00426140 | Completed | Advanced Malignancies|Solid Tumors |
Novartis Pharmaceuticals|Novartis |
August 2006 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
