B-raf plays crucial roles in MAPK signaling pathway, ErbB signaling pathway, Insulin signaling pathway and mTOR signaling pathway which have effect on cell survival, growth and differentiation. RAF can be regulated by RAS and PKC. [show the full text]
Raf Inhibitoren (Raf Inhibitors)
Isoformspezifische Produkte
| Kat.-Nr. | Produktname | Informationen | Publikationen | Validierung |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2807 | Dabrafenib (GSK2118436) | Dabrafenib ist ein spezifischer Inhibitor der mutierten BRAFV600E mit einer IC50 von 0,7 nM in zellfreien Assays, mit 7- und 9-fach geringerer Wirksamkeit gegen B-Raf(wt) bzw. c-Raf. |
|

|
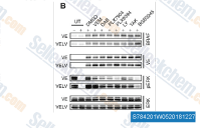
| S7842 | LY3009120 | LY3009120 (DP-4978) ist ein potenter Pan-Raf-Inhibitor mit einer IC50 von 44 nM, 31-47 nM und 42 nM für A-Raf, B-Raf und C-Raf in A375-Zellen. Diese Verbindung induziert Autophagy. Phase 1. |
|
|
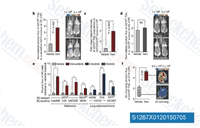
| S1267 | PLX4032 (Vemurafenib) | Vemurafenib (PLX4032, RG7204, RO5185426) ist ein neuartiger und potenter Inhibitor von B-RafV600E mit einer IC50 von 31 nM im zellfreien Assay. 10-fach selektiv für B-RafV600E gegenüber Wildtyp-B-Raf in enzymatischen Assays, und die zelluläre Selektivität kann das 100-fache übersteigen. Vemurafenib (PLX4032, RG7204) induziert Autophagy. |
|
|
| E1649 | Exarafenib (KIN-2787) | Exarafenib (KIN-002787, KIN-2787, RAF/KIN_2787) ist ein oral verfügbarer, selektiver Inhibitor von pan-RAF. Exarafenib ist wirksam bei RAF-abhängigen Krebserkrankungen, einschließlich aller Klassen von BRAF-Veränderungen. Exarafenib unterdrückt die MAPK-Signalgebung in RAF-abhängigen Melanomzelllinien. KIN-2787 zeigt eine niedrige nanomolare bis picomolare Potenz gegen RAF1, BRAF und ARAF mit einem IC50 von 0,06-3,46 nM bei minimaler Aktivität gegenüber Nicht-RAF-Kinasen. | ||
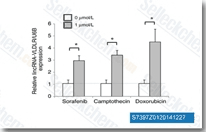
| S7397 | Sorafenib (BAY 43-9006) | Sorafenib ist ein Multikinase-Inhibitor von Raf-1 und B-Raf mit einer IC50 von 6 nM bzw. 22 nM in zellfreien Assays. Sorafenib hemmt VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, PDGFR-β, Flt-3 und c-KIT mit einer IC50 von 90 nM, 20 nM, 57 nM, 59 nM bzw. 68 nM. Sorafenib induziert Autophagy und Apoptosis und aktiviert Ferroptosis mit Antitumoraktivität. |
|
|
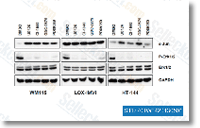
| S1104 | GDC-0879 | GDC-0879 (AR-00341677) ist ein neuartiger, potenter und selektiver B-Raf-Inhibitor mit einem IC50-Wert von 0,13 nM in A375- und Colo205-Zellen mit Aktivität auch gegen c-Raf; keine Hemmung anderer Proteinkinasen bekannt. |
|
|
| S7170 | Avutometinib (Ro5126766, CH5126766) | Avutometinib(RO5126766,CH5126766,VS 6766, CKI-27, R-7304, RG-7304) ist ein dualer RAF/MEK-Inhibitor mit IC50 von 8,2 nM, 19 nM, 56 nM und 160 nM für BRAF V600E, BRAF, CRAF bzw. MEK1. Phase 1. |
|
|
| S1040 | Sorafenib Tosylate (BAY 43-9006) | Sorafenib Tosylate ist ein Multikinase-Inhibitor von Raf-1 und B-Raf mit einem IC50 von 6 nM bzw. 22 nM in zellfreien Assays. Sorafenib Tosylate hemmt VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, PDGFR-β, Flt-3 und c-KIT mit IC50-Werten von 90 nM, 20 nM, 57 nM, 59 nM bzw. 68 nM. Sorafenib Tosylate induziert autophagy und apoptosis und aktiviert ferroptosis mit Antitumoraktivität. |
|
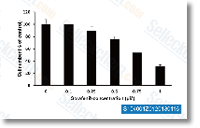
|
| S1152 | PLX-4720 | PLX4720 ist ein potenter und selektiver Inhibitor von B-RafV600E mit einer IC50 von 13 nM in einem zellfreien Assay, ebenso potent wie c-Raf-1 (Y340D- und Y341D-Mutationen), 10-fache Selektivität für B-RafV600E gegenüber Wildtyp-B-Raf. |
|
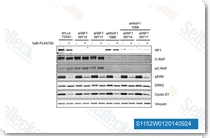
|
| S5069 | Dabrafenib Mesylate | Dabrafenib Mesylate (GSK2118436) ist die Mesylatsalzform von Dabrafenib, einem oral bioverfügbaren Inhibitor des B-raf (BRAF)-Proteins mit IC50-Werten von 0,8 nM, 3,2 nM und 5 nM für B-Raf (V600E), B-Raf (WT) bzw. C-Raf. |
|
|
RAF kinase signaling is highlighted in the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK signal transduction cascade. Activated RAS kinase signaling results in the activation of RAF proteins. Following these events, MEK1 and MEK2 dual specificity protein kinases become phosphorylated and activated. It should be noted that RAF kinases display restricted substrate specificity for these MEK enzymes. The RAF family of protein-serine/threonine kinases comprise of A-RAF, B-RAF, and C-RAF oncogenes originally discovered in the early 1980s. RAF family proteins function as six dimeric members, either in homo- and heterodimer formation. Since there are four RAS members, the total number of RAS-RAF interactions is equivalent to twenty-four. And downstream, with two MEK members available the total number of interactions between RAF-MEK constituents is twelve.[1]
All RAF kinases share three conserved regions (CR): CR1, CR2, and CR3. CR1 consists of cysteine-rich domain (binds to two zinc ions) and a RAS-binding domain. These properties facilitate CR1 interaction with RAS and phospholipids in the membrane. CR2, is a serine/threonine rich domain that facilitates the binding of regulatory protein 14-3-3 upon phosphorylation – this result in inactivation. At the C-terminus is the protein kinase domain, CR3, which contains a downstream stimulatory 14-3-3 binding site. Regulating RAF kinase activity are a number of protein-protein interactions, phosphorylation, dephosphorylation and conformational changes. In their inactivated state, most RAF proteins are found in the cytosol.[1]
It was not until 2002, that B-RAF mutations were noted in cancer cells lines. Most notably, B-RAF has been associated with melanomas and papillary thyroid, ovarian, and colorectal tumors. And to a lesser degree cancers of the lung, pancreas, and bladder have also been found to have aberrant B-RAF activity. Consequently, since B-RAF mutations are involved in several different cancer types it is believed that B-RAF functions as an oncogene driver. In clinical trials, the first RAF inhibitor was Bayer’s Sorafenib (Nexavar). The compound was found to be effective in restricting tumor activity in renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular cancers and is currently in use for these indications. Recently, PLX4032 was discovered to be a highly selective RAF inhibitor (Roche) and is currently in advanced clinical trials for testing against melanomas.[2]
