MEK is a member of kinases in MAPK signal pathway which can activates p38 MAPK and JNK when MEK is ACTIVATED by TNF-alpha, GPCR and so on. MEK could be regulated by MEKKs or RAF. The Raf / MEK / ERK signal transduction is involved in cell growth, cell proliferation and cell survival. [show the full text]
MEK Inhibitoren (MEK Inhibitors)
| Kat.-Nr. | Produktname | Informationen | Publikationen | Validierung |
|---|---|---|---|---|
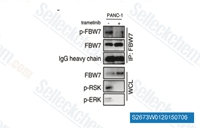
| S2673 | Trametinib (GSK1120212) | Trametinib (GSK1120212, JTP-74057) ist ein hochspezifischer und potenter MEK1/2-Inhibitor mit einer IC50 von 0,92 nM/1,8 nM in zellfreien Assays, und es hemmt die Kinaseaktivitäten von c-Raf, B-Raf, ERK1/2 nicht. Diese Verbindung aktiviert die Autophagy und induziert Apoptosis. |
|
|
| S1036 | PD0325901 (Mirdametinib) | Mirdametinib (PD0325901) ist ein selektiver und nicht-ATP-kompetitiver MEK-Inhibitor mit einer IC50 von 0,33 nM in zellfreien Assays, etwa 500-fach potenter als CI-1040 bei der Phosphorylierung von ERK1 und ERK2. Phase 2. |
|

|
| S1008 | AZD6244 (Selumetinib) | Selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) ist ein potenter, hochselektiver MEK-Inhibitor mit einem IC50 von 14 nM für MEK1 und einem Kd-Wert von 530 nM für MEK2. Es hemmt auch die ERK1/2-Phosphorylierung mit einem IC50 von 10 nM, keine Hemmung von p38α, MKK6, EGFR, ErbB2, ERK2, B-Raf, etc. Selumetinib unterdrückt die Zellproliferation, -migration und löst Apoptose aus. Phase 3. |
|

|
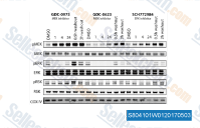
| S8041 | Cobimetinib (GDC-0973) | Cobimetinib (GDC-0973, RG7420) ist ein potenter und hochselektiver MEK1-Inhibitor mit einer IC50 von 4,2 nM, der keine signifikante Hemmung zeigt, wenn er gegen ein Panel von mehr als 100 Serin-Threonin- und Tyrosinkinasen getestet wird. Diese Verbindung induziert apoptosis. Phase 3. |
|
|
| S7170 | Avutometinib (Ro5126766, CH5126766) | Avutometinib(RO5126766,CH5126766,VS 6766, CKI-27, R-7304, RG-7304) ist ein dualer RAF/MEK-Inhibitor mit IC50 von 8,2 nM, 19 nM, 56 nM und 160 nM für BRAF V600E, BRAF, CRAF bzw. MEK1. Phase 1. |
|
|
| S1102 | U0126-EtOH | U0126-EtOH ist ein hochselektiver Inhibitor von MEK1/2 mit einer IC50 von 0,07 μM/0,06 μM in zellfreien Assays, 100-fach höhere Affinität für ΔN3-S218E/S222D MEK als PD98059. U0126 hemmt autophagy und mitophagy mit antiviraler Aktivität. |
|

|
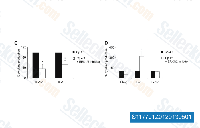
| S1177 | PD 98059 | PD98059 ist ein nicht-ATP-kompetitiver MEK-Inhibitor mit einer IC50 von 2 μM in einem zellfreien Assay, der die MEK-1-vermittelte Aktivierung von MAPK spezifisch hemmt; ERK1 oder ERK2 werden nicht direkt gehemmt. PD98059 ist ein Ligand für den Aryl-Hydrocarbon-Rezeptor (AHR) und fungiert als AHR-Antagonist. |
|
|
| S1020 | PD184352 (CI-1040) | PD184352 (CI-1040) ist ein ATP-nicht-kompetitiver MEK1/2-Inhibitor mit einer IC50 von 17 nM in zellbasierten Assays, 100-fach selektiver für MEK1/2 als für MEK5. Diese Verbindung induziert selektiv apoptosis. |
|

|
| S7007 | MEK162 (Binimetinib, ARRY-162) | Binimetinib (MEK162, ARRY-162, ARRY-438162) ist ein potenter Inhibitor von MEK1/2 mit einer IC50 von 12 nM in einem zellfreien Assay. Binimetinib induziert G1-Zellzyklusarrest und Apoptose in menschlichen NSCLC-Zelllinien und induziert Autophagy. Phase 3. |
|

|
| S1531 | BIX 02189 | BIX02189 ist ein selektiver Inhibitor von MEK5 mit einer IC50 von 1,5 nM, der auch die katalytische Aktivität von ERK5 mit einer IC50 von 59 nM in zellfreien Assays hemmt und eng verwandte Kinasen wie MEK1, MEK2, ERK2 und JNK2 nicht hemmt. |
|

|
In the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, receptor tyrosine kinase activation results in adaptor proteins phosphorylating RAS. This results in the activation of the RAF-MEK-ERK kinase signalling pathway, and consequently leads to the activation of several downstream substrates that affect a number of transcription factors. The knock-on effect is that a myriad of cellular processes such as cell proliferation, survival, transformation, translational control and cytoskeletal rearrangement. In oncology, the MAPK pathway is a key contributor to tumor progression, angiogenesis, and metastasis.
In the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway, MEK has been the target of oncology research. The MEK kinase is expressed from MEK1 and MEK2 – two genes that share ~80% structural homology – that display slightly different isoforms of MEK to produce potentially different functions. Both MEK1 and MEK2 kinases are implicated in ~30% of all human cancers where MAPK signalling pathway is involved.[1] These dual-specificity kinases phosphorylate both tyrosine and threonine residues; MEK1 and MEK2 sequentially phosphorylate ERK1 at 185Tyr and then at 183Thr. MEK exists just downstream of RAF in the classical MAPK pathway known as RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway. Phosphorylation of MEK by RAF results in the phosphorylation of ERK1 and ERK2. MEK kinases show very high specificity for ERK, in fact it is the only known substrate for MEK. Therefore, constitutive phosphorylation of MEK in the RAF-MEK-ERK kinase pathway occurs by either the overexpression or mutation of receptor tyrosine kinases, and/or mutations of RAS and RAF (A-RAF and B-RAF).[2]
The MEK enzyme itself consists of hydrophobic allosteric pockets adjacent to the ATP-binding site that facilitates the design of highly selective allosteric inhibitors. This is in contRASt to the many kinases for which there is no allosteric-binding site. Consequently, this feature is recognized by many pharmaceutical companies as a characteristic that facilitates more selective inhibitor design since the more conserved ATP-binding site is not directly targeted. MEK1 and MEK2 are positioned at the focal point of many mitogenic signaling pathways that integrates into the ERK pathway. Characteristics such as unusually restricted and unique substrate specificities, plus the integrating role of mitogenic signaling pathways demonstrates the benefits of developing a MEK inhibitor against the ERK pathway.[3]
The utility of targeting MEK inhibition is likely to be best realized among tumors where the MEK pathway is constitutively activated. Such a scenario includes activating mutations of BRAF that results in tumors that are dependent to MEK signaling, and consequently very sensitive to MEK inhibition.[4] This is likely to be the case among a sub-population of BRAF mutations observed in melanoma and thyroid cancers. Currently, MEK inhibition is likely to prove most effective when used in a combination strategy. This is because there is cross-talk involved between RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK and the PI3K-AKT pathway. As a consequence, inhibition of one pathway leads to constitutive signalling in the other. This is a reflection of the complexity of the kinase signalling pathways implicated in cancer.[2]
Aside from anti-tumor potential, MEK inhibition may play a role where inflammation is concerned. Several key protein downstream of MEK are involved in inflammatory responses including TNF, IL-1, and other cytokines. MEK signaling directly impacts both the expression of cytokines and subsequent activation pathways. Therefore, MEK inhibitors –particularly orally bioavailable compounds – may be suitable agents for the treatment of inflammatory disease. In addition, it should be noted that anaphylatoxins utilize the MEK kinase cascade to initiate disease processes such as arthritis.[2]
