nur für Forschungszwecke
PLX-4720 B-Raf-Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1152
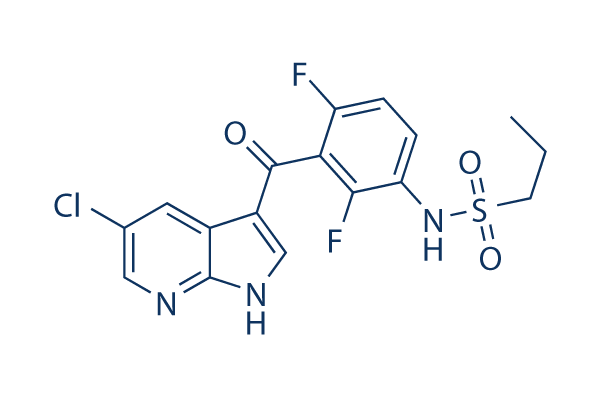
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 413.83
Qualitätskontrolle
Produkte, die oft zusammen verwendet werden mit PLX-4720
| Verwandte Ziele | ERK p38 MAPK JNK MEK Ras KRas S6 Kinase MAP4K TAK1 Mixed Lineage Kinase |
|---|---|
| Weitere Raf Inhibitoren | LY3009120 Exarafenib (KIN-2787) GDC-0879 Avutometinib (Ro5126766, CH5126766) AZ 628 SB590885 TAK-632 GW5074 RAF265 (CHIR-265) PLX8394 (Plixorafenib, FORE8394) |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DU-4475 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.07457 μM | SANGER | |||
| EoL-1-cell | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.14166 μM | SANGER | |||
| C32 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.15131 μM | SANGER | |||
| M14 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.21757 μM | SANGER | |||
| CP50-MEL-B | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.29784 μM | SANGER | |||
| A101D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.32589 μM | SANGER | |||
| G-361 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.34637 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-144 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.36329 μM | SANGER | |||
| ACN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.38477 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-829 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.38968 μM | SANGER | |||
| MEL-HO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.41179 μM | SANGER | |||
| SH-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.41422 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.51568 μM | SANGER | |||
| A375 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.67359 μM | SANGER | |||
| MMAC-SF | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.68614 μM | SANGER | |||
| BHT-101 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.70702 μM | SANGER | |||
| K5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.76148 μM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.79644 μM | SANGER | |||
| RVH-421 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.86796 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2218 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.87844 μM | SANGER | |||
| WM-115 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.88692 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-28 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.04569 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-679 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.10464 μM | SANGER | |||
| MZ7-mel | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.14963 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-30 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.33386 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H209 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.6086 μM | SANGER | |||
| HTC-C3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1.66294 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-45 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.04978 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.11969 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.30787 μM | SANGER | |||
| PA-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.72673 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuO-3N1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.87946 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H358 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.92232 μM | SANGER | |||
| CTB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.40176 μM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.55266 μM | SANGER | |||
| CP66-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.15927 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.49179 μM | SANGER | |||
| DBTRG-05MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.53325 μM | SANGER | |||
| A2058 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.72164 μM | SANGER | |||
| KG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.73908 μM | SANGER | |||
| 8305C | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.1873 μM | SANGER | |||
| RPMI-7951 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.80283 μM | SANGER | |||
| CHL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.97603 μM | SANGER | |||
| TI-73 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.00902 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1080 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.10946 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.14924 μM | SANGER | |||
| 8-MG-BA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.18129 μM | SANGER | |||
| NB7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.21373 μM | SANGER | |||
| H4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.22493 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-72 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.45423 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.81931 μM | SANGER | |||
| BCPAP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.21764 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2241-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.36907 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-741 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.01679 μM | SANGER | |||
| HSC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.07068 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW982 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.41516 μM | SANGER | |||
| GCT | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.75314 μM | SANGER | |||
| KY821 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.05178 μM | SANGER | |||
| JVM-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.56999 μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.6048 μM | SANGER | |||
| VA-ES-BJ | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.0149 μM | SANGER | |||
| A431 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.4212 μM | SANGER | |||
| LXF-289 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.458 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.8274 μM | SANGER | |||
| NOS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.8472 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.2404 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-HEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.3527 μM | SANGER | |||
| A3-KAW | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.7178 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-LU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.2655 μM | SANGER | |||
| TYK-nu | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.3932 μM | SANGER | |||
| NMC-G1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.6062 μM | SANGER | |||
| BB65-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.7169 μM | SANGER | |||
| QIMR-WIL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.8833 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-566MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.9576 μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-140 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.0753 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCC-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.3359 μM | SANGER | |||
| U251 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.8492 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-542MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.9222 μM | SANGER | |||
| LAMA-84 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.9932 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H720 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.2684 μM | SANGER | |||
| DEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4293 μM | SANGER | |||
| SBC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4305 μM | SANGER | |||
| ECC10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4458 μM | SANGER | |||
| Daoy | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.7616 μM | SANGER | |||
| SCH | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.7835 μM | SANGER | |||
| MZ2-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.0646 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-12T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.4862 μM | SANGER | |||
| KE-37 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.8107 μM | SANGER | |||
| LS-411N | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.118 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2228 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.3071 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.4965 μM | SANGER | |||
| HN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.7248 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1648 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.818 μM | SANGER | |||
| IA-LM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.3172 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5708 μM | SANGER | |||
| YKG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.5711 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-81-FD | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.5858 μM | SANGER | |||
| 23132-87 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.7642 μM | SANGER | |||
| NUGC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.9887 μM | SANGER | |||
| 5637 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.0478 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1755 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.4764 μM | SANGER | |||
| RH-18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.5748 μM | SANGER | |||
| RXF393 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.6756 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-134-A | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.7056 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.7201 μM | SANGER | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.1915 μM | SANGER | |||
| IGR-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.3796 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-92 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.4987 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MES-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.7381 μM | SANGER | |||
| LU-65 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.8624 μM | SANGER | |||
| MS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.1203 μM | SANGER | |||
| LoVo | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.244 μM | SANGER | |||
| A704 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.5155 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1376 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.6059 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-MEL1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.6751 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos-2G6-4C10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.7366 μM | SANGER | |||
| T47D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.7979 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1197 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.0817 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2518-MEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.6412 μM | SANGER | |||
| J-RT3-T3-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.7595 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-NEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.8744 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H526 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.0023 μM | SANGER | |||
| IST-SL1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.2751 μM | SANGER | |||
| HH | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.3192 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.938 μM | SANGER | |||
| SNU-449 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2018 μM | SANGER | |||
| COR-L23 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2813 μM | SANGER | |||
| LOXIMVI | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.368 μM | SANGER | |||
| GR-ST | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.6706 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.944 μM | SANGER | |||
| ALL-PO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.1604 μM | SANGER | |||
| ML-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.2814 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.713 μM | SANGER | |||
| EGI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.8845 μM | SANGER | |||
| TCCSUP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.9272 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB996-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.5682 μM | SANGER | |||
| LCLC-97TM1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.1964 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1304 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.3301 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.5973 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1770 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.1648 μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.6504 μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.7236 μM | SANGER | |||
| ACHN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8385 μM | SANGER | |||
| MN-60 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8544 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33.8971 μM | SANGER | |||
| KGN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.7292 μM | SANGER | |||
| U031 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.8132 μM | SANGER | |||
| HMV-II | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.0774 μM | SANGER | |||
| L-363 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.6455 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1155 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.0015 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1793 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1026 μM | SANGER | |||
| P30-OHK | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1332 μM | SANGER | |||
| AN3-CA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.1615 μM | SANGER | |||
| UACC-257 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.79 μM | SANGER | |||
| MCF7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=39.8629 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YN | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.4285 μM | SANGER | |||
| T98G | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.4957 μM | SANGER | |||
| HGC-27 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.274 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1092 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.2895 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-299 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.3071 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB1047-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.9959 μM | SANGER | |||
| 786-0 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.65 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2157 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.0359 μM | SANGER | |||
| NY | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.1778 μM | SANGER | |||
| EFM-19 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.7533 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-16 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.7806 μM | SANGER | |||
| UM-UC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.8059 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-29 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.8792 μM | SANGER | |||
| LN-405 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.0827 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H727 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.7726 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-502MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.9676 μM | SANGER | |||
| GMS-10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.2974 μM | SANGER | |||
| MEL-JUSO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.347 μM | SANGER | |||
| insect cells | Function assay | Inhibition of N-terminal His-tagged BRAF V600E mutant (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected insect cells co-expressing CDC37 using biotinylated-MEK as substrate by AlphaScreen assay, IC50 = 0.013 μM. | 29461827 | |||
| A375 | Function assay | Inhibition of BRAF V600E mutant in human A375 cells assessed as reduction in ERK phosphorylation by AlphaScreen assay, IC50 = 0.044 μM. | 29461827 | |||
| A375 | Function assay | Inhibition of b-Raf in human A375 cells assessed phosphorylation of ERK, IC50 = 0.046 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A375 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human A375 cells expressing B-Raf V600E mutant and wild type Ras, IC50 = 0.5 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A375 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A375 cells harboring BRAF V600E mutant after 72 hrs by CellTiter-Glo assay, IC50 = 0.5 μM. | 29461827 | ||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT116 cells expressing wild type b-Raf and KRAS mutant, IC50 = 27 μM. | 22808911 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 413.83 | Formel | C17H14ClF2N3O3S |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 918505-84-7 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | CCCS(=O)(=O)NC1=C(C(=C(C=C1)F)C(=O)C2=CNC3=C2C=C(C=N3)Cl)F | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 83 mg/mL
(200.56 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
C-Raf-1 (Y340D/Y341D)
(Cell-free assay) 6.7 nM
B-Raf (V600E)
(Cell-free assay) 13 nM
BRK
(Cell-free assay) 130 nM
B-Raf
(Cell-free assay) 160 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
PLX-4720 zeigt eine über 10-mal höhere Selektivität gegenüber Wildtyp-B-Raf und eine über 100-mal höhere Selektivität gegenüber anderen Kinasen wie Frk, Src, Fak, FGFR und Aurora A mit einer IC50 von 1,3–3,4 μM. Diese Verbindung hemmt signifikant die ERK-Phosphorylierung in Zelllinien mit B-RafV600E mit einer IC50 von 14–46 nM, jedoch nicht in Zellen mit Wildtyp-B-Raf. Sie hemmt signifikant das Wachstum von Tumorzelllinien, die das B-RafV600E-Onkogen tragen, wie COLO205, A375, WM2664 und COLO829 mit einer GI50 von 0,31 μM, 0,50 μM, 1,5 μM bzw. 1,7 μM. Darüber hinaus induziert diese chemische Behandlung bei 1 μM einen Zellzyklusarrest und Apoptose ausschließlich in den B-RafV600E-positiven 1205Lu-Zellen, nicht aber in den B-Raf-Wildtyp-C8161-Zellen. Diese Verbindung (10 μM) induziert signifikant eine >14-fache Expression von BIM in den PTEN+-Zellen im Vergleich zu den PTEN--Zelllinien (4-fach), was eine Erklärung für die Resistenz von PTEN--Zellen gegenüber dieser chemisch induzierten Apoptose liefert.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
In-vitro-Raf-Kinaseaktivitäten
|
|
Die In-vitro-Kinaseaktivitäten von Wildtyp-Raf und Mutanten werden durch Messung der Phosphorylierung von biotinyliertem MEK-Protein unter Verwendung der AlphaScreen-Technologie von Perkin-Elmer bestimmt. Für jedes Enzym (0,1 ng) werden 20-μL-Reaktionen in 20 mM Hepes (pH 7,0), 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0,01 % Tween-20, 100 nM Biotin-MEK-Protein, verschiedenen ATP-Konzentrationen und steigenden Konzentrationen von PLX-4720 bei Raumtemperatur durchgeführt. Die Reaktionen werden nach 2, 5, 8, 10, 20 und 30 Minuten mit 5 μL einer Lösung gestoppt, die 20 mM Hepes (pH 7,0), 200 mM NaCl, 80 mM EDTA und 0,3 % BSA enthält. Die Stopplösung enthält außerdem Phospho-MEK-Antikörper, Streptavidin-beschichtete Donor-Beads und Protein-A-Akzeptor-Beads aus dem AlphaScreen Protein A Detection Kit. Der Antikörper und die Beads werden in der Stopplösung im Dunkeln bei Raumtemperatur 30 Minuten lang vorinkubiert. Die Endverdünnung des Antikörpers beträgt 1/2.000, und die Endkonzentration jeder Bead beträgt 10 μg/mL. Die Assay-Platten werden eine Stunde lang bei Raumtemperatur inkubiert und dann mit einem PerkinElmer AlphaQuest-Reader abgelesen.
|
|
| In vivo |
Die orale Verabreichung von PLX-4720 in einer Dosis von 20 mg/kg/Tag führt zu signifikanten Tumorwachstumsverzögerungen und -regressionen in B-RafV600E-abhängigen COLO205-Tumorxenograften, ohne offensichtliche Nebenwirkungen bei Mäusen, selbst bei einer Dosis von 1 g/kg. Diese Verbindung in einer Dosis von 100 mg/kg zweimal täglich eliminiert fast vollständig die 1205Lu-Xenografts mit B-RafV600E, während sie keine Aktivität gegen C8161-Xenografts mit Wildtyp-B-Raf aufweist. Die Antitumorwirkungen dieser Verbindung korrelieren mit der Blockade des MAPK-Signalwegs in jenen Zellen, die die V600E-Mutation aufweisen. Diese chemische Behandlung in einer Dosis von 30 mg/kg/Tag hemmt signifikant das Tumorwachstum von 8505c-Xenografts um >90 % und verringert dramatisch die Fernmetastasen in der Lunge.
|
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-MEK / MEK / p-ERK / ERK / p-FAK(S910) p-EGFR 1173 / EGFR / p-Akt / Akt p27 / Cyclin D1 / pRb pAkt(Ser473) / pAkt(Thr308) |
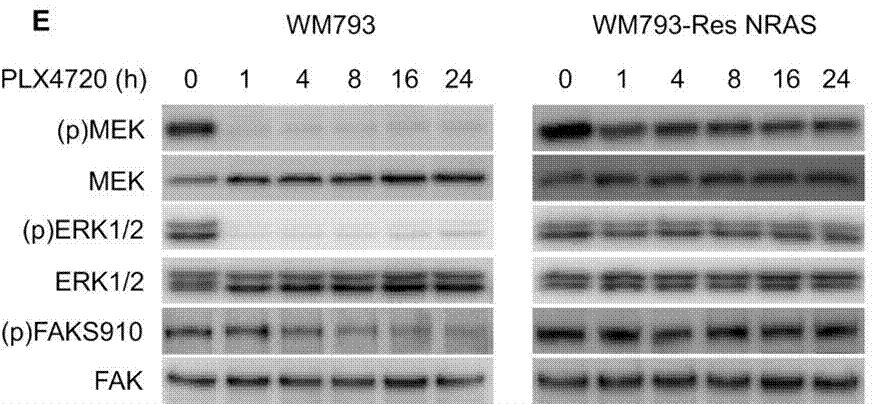
|
23076151 |
| Immunofluorescence | LAMP1 ZKSCAN3 / TFEB |
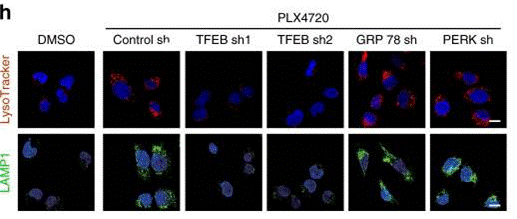
|
30979895 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |

|
27848137 |
| ELISA | mIFN-γ |
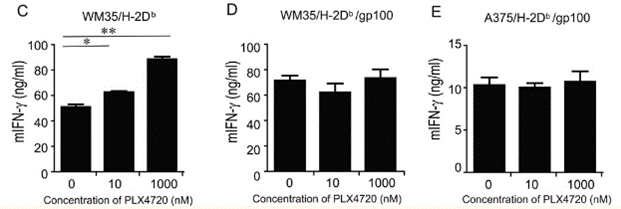
|
23204132 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
What would you recommend to make working solution for intraperitoneal injection into mice?
Antwort:
Due to its very limited solubility in aqueous solution, this compound can be administered as a not fully dissolved suspension via oral gavage. For this reason, we recommend oral gavage for its administration.
