nur für Forschungszwecke
1400W 2HCl NOS Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S8337
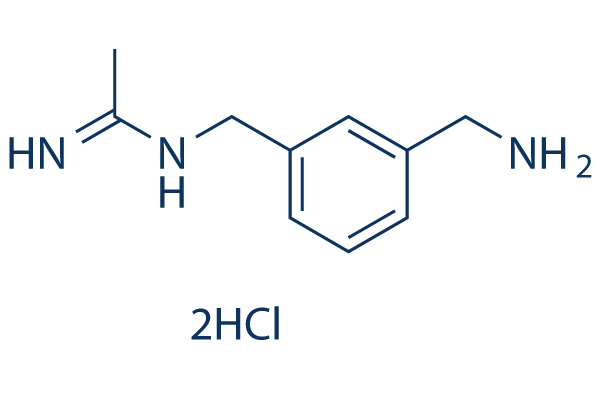
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 250.17
Qualitätskontrolle
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 24 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide production after 24 hrs by Griess assay, IC50=0.2μM | 23232148 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 20 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity against LPS-stimulated mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as nitrite accumulation after 20 hrs by fluorimetry, IC50=0.3μM | 11678654 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | Inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide generation in mouse RAW264.7 cells pretreated 1 hr before LPS challenge by Griess method, IC50=1.5μM | 19278854 | |||
| N9 | Function assay | Inhibitory effect of compound on the accumulation of NO2 in the culture media of N9 cells in response to LPS/IFN-gamma, IC50=2.2μM | 15013012 | |||
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | Antiinflammatory activity in LPS-stimulated mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of nitric oxide production pretreated 1 hr before LPS challenge, IC50=2.3μM | 12662101 | |||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | Inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide accumulation in mouse RAW264.7 cells, IC50=2.7μM | 19699097 | |||
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 24 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity against mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced nitrite accumulation after 24 hrs, IC50=2.9μM | 15568764 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 24 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in LPS-stimulated mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as effect on NO production pretreated 1 hr before LPS challenge measured after 24 hrs, IC50=3.1μM | 11908984 | ||
| N9 | Antiinflammatory assay | Antiinflammatory activity in LPS/IFN-gamma-stimulated mouse N9 cells assessed as inhibition of nitric oxide production pretreated 1 hr before LPS/IFNgamma challenge, IC50=3.6μM | 12662101 | |||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | Inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide production in mouse RAW264.7 cells, IC50=3.78μM | 17988874 | |||
| RAW 264 | Function assay | 24 hrs | Inhibition of 1ug/ml LPS-stimulated nitirc oxide accumulation in RAW 264 cells after 24 hrs, IC50=5.2μM | 17320246 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | Inhibitory effect of compound on the accumulation of NO2 in the culture media of RAW 264.7 cells in response to LPS, IC50=6.1μM | 15013012 | |||
| N9 | Antiinflammatory assay | 24 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity against mouse N9 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS/IFN-gamma-induced nitrite accumulation after 24 hrs, IC50=6.3μM | 15568764 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as cell viability after 24 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=47.47μM | 23232148 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 50 uM | 24 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced nitrite production at 50 uM treated 30 mins before LPS challenge measured after 24 hrs by Griess method | 20447741 | |
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 0.5 to 2 uM | 2 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced COX-2 expression at 0.5 to 2 uM incubated for 2 hrs prior to LPS challenge measured after 24 hrs by Western blot analysis | 23232148 | |
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 2 uM | 2 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as downregulation of LPS-induced iNOS mRNA expression at 2 uM incubated for 2 hrs prior to LPS challenge measured after 9 hrs by RT-PCR analysis | 23232148 | |
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 0.5 to 2 uM | 2 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced iNOS expression at 0.5 to 2 uM incubated for 2 hrs prior to LPS challenge measured after 24 hrs by Western blot analysis | 23232148 | |
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | 4 uM | Inhibition iNOS mRNA expression levels in LPS-induced mouse RAW264.7 cells at 4 uM by RT-PCR analysis | 27542306 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | 4 uM | Inhibition iNOS protein expression levels in LPS-induced mouse RAW264.7 cells at 4 uM by Western blot analysis | 27542306 | ||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 250.17 | Formel | C10H15N3.2HCl |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 214358-33-5 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N-(3-(Aminomethyl)benzyl)acetamidine | Smiles | CC(=NCC1=CC=CC(=C1)CN)N.Cl.Cl | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 35 mg/mL
(139.9 mM)
Water : 35 mg/mL Ethanol : 35 mg/mL |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
iNOS
(Cell-free assay) <7 nM(Kd)
nNOS
(Cell-free assay) 2 μM(Ki)
eNOS
(Cell-free assay) 50 μM(Ki)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
1400W ist entweder ein irreversibler Inhibitor oder ein extrem langsam reversibler Inhibitor der humanen iNOS. Die Hemmung der humanen iNOS durch 1400W ist zeitabhängig. 1400W ist kompetitiv mit L-Arginin. 1400W ist kein Substrat für iNOS.
|
| In vivo |
1400W verhindert selektiv Mikrovaskulaturverletzungen bei Ratten. 1400W ist in einem Rattenmodell für Endotoxin-induzierte Gefäßverletzungen mehr als 50-mal potenter gegen iNOS als gegen eNOS. Darüber hinaus reduziert 1400W dosisabhängig die LPS-induzierte Gefäßleckage, die mit der iNOS-Induktion im Dickdarm, in der Lunge, Leber, Niere und im Herzen verbunden ist. Der maximale Schutz liegt bei nahezu 100 % für alle Organe außer der Niere (Niere: 54 %). 1400W hat eine mildernde Wirkung auf sowohl oxidativen als auch nitrosativen Stress in den Nieren gegen renale I/R-Verletzungen bei Ratten. Die Behandlung mit 1400W kann die Wachstumsrate solider Tumoren bei Mäusen reduzieren.
|
Literatur |
|
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00845169 | Completed | Endothelial Dysfunction |
University of Edinburgh|NHS Lothian|Umeå University |
April 2012 | Not Applicable |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
