nur für Forschungszwecke
L-NAME HCl NOS Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S2877
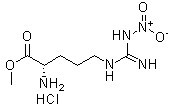
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 269.69
Qualitätskontrolle
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mouse BV2 cells | Function assay | 24 h | Inhibition of Nitric oxide synthase activity in mouse BV2 cells assessed as LPS-induced NO production after 24 hrs by Griess reaction, IC50=18.9 μM | 21377368 | ||
| mouse RAW264.7 cells | Function assay | 17-20 h | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of IFN-gamma/LPS-stimulated nitric oxide production after 17 to 20 hrs by Griess assay, IC50=27.13 μM | 19359068 | ||
| HUVEC | Function assay | Ability to inhibit conversion of [3H]L-Arg to [3H]L-citrulline catalyzed by endothelial NOS (e NOS) from HUVEC cells, IC50=2.7μM | 11327580 | |||
| DLD-1 | Function assay | Ability to inhibit conversion of [3H]L-Arg to [3H]L-citrulline catalyzed by inducible NOS (i NOS) from human DLD-1 cells, IC50=14μM | 11327580 | |||
| BV2 | Function assay | Inhibition of NOS-dependent nitric oxide production in mouse BV2 cells, IC50=36μM | 17046255 | |||
| BV2 | Function assay | Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase in mouse BV2 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced NO production, IC50=20.1μM | 18161942 | |||
| BV2 | Function assay | Inhibition of iNOS-mediated NO production in LPS-induced mouse BV2 cells, IC50=25.8μM | 18926710 | |||
| BV2 | Antiinflammatory assay | 24 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse BV2 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced iNOS-dependent nitrite production after 24 hrs by Griess method, IC50=25.8μM | 21028898 | ||
| BV2 | Function assay | Inhibition of iNOS in mouse BV2 microglial cells assessed as NO production, IC50=25.8μM | 21115251 | |||
| RAW264.7 | Function assay | 1 hr | Inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide production in mouse RAW264.7 cells preincubated with compound for 1 hr before exposure to LPS measured after 24 hrs by Griess reaction method, IC50=48.5μM | 21435874 | ||
| Sf9 | Function assay | 45 mins | Inhibition of human recombinant eNOS expressed in Sf9 cells assessed as inhibition of conversion of [3H]-L-arginine to [3H]-L-citrulline after 45 mins by liquid scintillation counting, IC50=0.68μM | 21923116 | ||
| Sf9 | Function assay | 45 mins | Inhibition of human recombinant nNOS expressed in Sf9 cells assessed as inhibition of conversion of [3H]-L-arginine to [3H]-L-citrulline after 45 mins by liquid scintillation counting, IC50=0.69μM | 21923116 | ||
| Sf9 | Function assay | 45 mins | Inhibition of human recombinant iNOS expressed in Sf9 cells assessed as inhibition of conversion of [3H]-L-arginine to [3H]-L-citrulline after 45 mins by liquid scintillation counting, IC50=0.83μM | 21923116 | ||
| BV2 | Function assay | 24 hrs | Inhibition of iNOS-mediated nitric oxide production in LPS-stimulated mouse BV2 cells measured after 24 hrs of post-stimulation by Griess reaction method, IC50=13.35μM | 22115618 | ||
| BV2 | Function assay | 1 hr | Inhibition of LPS-induced NO production in mouse BV2 cells preincubated for 1 hr followed by LPS addition measured after 24 hrs by Griess assay, IC50=24.7μM | 27588326 | ||
| RAW264.7 | Antiinflammatory assay | 2 hrs | Antiinflammatory activity in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide production preincubated for 2 hrs followed by LPS stimulation measured after 18 hrs by Griess assay, IC50=30.6μM | 28099011 | ||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RAW264.7 | Anti-inflammatory assay | 17 to 20 hr | Anti-inflammatory activity in Mus musculus (mouse) RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of IFN-gamma/LPS-induced NO production after 17 to 20 hr by Griess assay, IC50=23.21μM | ChEMBL | ||
| RAW264.7 | Anti-inflammatory assay | 17 to 20 hr | Anti-inflammatory activity in Mus musculus (mouse) RAW264.7 cells assessed as inhibition of IFN-gamma/LPS-induced nitric oxide production after 17 to 20 hr by Griess assay, IC50=26.21μM | ChEMBL | ||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 269.69 | Formel | C7H15N5O4.HCl |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 51298-62-5 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | NG-Nitroarginine methyl ester, N-Nitro-L-arginine methylester | Smiles | COC(=O)C(CCCN=C(N)N[N+](=O)[O-])N.Cl | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
Water : 54 mg/mL
DMSO
: Insoluble
Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
nNOS
(Cell-free assay) 15 nM(Ki)
eNOS
(Cell-free assay) 39 nM(Ki)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
NG-nitro-L-argininmethylester (L-NAME; bei 0,1-100 mM) bewirkt eine konzentrationsabhängige Hemmung der Ca2(+)-abhängigen endothelialen NO-Synthase aus Schweineaorten. Diese Verbindung verursacht eine Endothel-abhängige Kontraktion und eine Hemmung der Endothel-abhängigen Relaxation, die durch Acetylcholin (ACh) in Aortenringen induziert wird. In einer anderen Untersuchung ist die Viabilität von rMC-1-Zellen oder BREC in 25 mM Glukose signifikant geringer als bei 5 mM Glukose, und dieser Zelltod wird durch diese Chemikalie in beiden Zelltypen gehemmt.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
Enzymtest
|
|
Die Oxidation von L-NAME HCl (Nω-nitro-L-argininmethylesterhydrochlorid) wird durch die Umwandlung von [3H]- oder [14C]-Arginin zu L-Citrullin überwacht, wobei L-Citrullin von L-Arginin durch Dowex 50x8-200 (Na)-Chromatographie getrennt wird. Typische Reaktionsgemische (100 pL) enthalten 50 mM HEPES, pH 7,0, 8 pM Tetrahydrobiopterin, 1 mM CaC12, 0,01 mg/mL Calmodulin, 0,5 mM EDTA, 0,450 pM [14C]-Arginin (30000 cpm) und 100-200 pM NADPH. Die cNOS-katalysierte Oxidation von NADPH zu NADP+ wird durch die Abnahme der Absorption bei 340 nm mit einem Kontron 860 Spektrophotometer in einem Volumen von 300 pL überwacht. Alle Reaktionen erfolgen bei 30 ℃, sofern nicht anders angegeben.
|
|
| In vivo |
L-NAME HCl (0,03-300 mg kg-1, i.v.) induziert einen dosisabhängigen Anstieg des mittleren systemischen arteriellen Blutdrucks, begleitet von Bradykardie. Diese Verbindung (100 mg kg-1, i.v.) hemmt signifikant die hypotensiven Reaktionen auf ACh und Bradykinin. Der durch diese Chemikalie hervorgerufene Anstieg des Blutdrucks und der Bradykardie wird durch L-Arginin (30-100 mg kg-1, i.v.) dosisabhängig umgekehrt.
|
Literatur |
|
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
