nur für Forschungszwecke
Abexinostat (PCI-24781) HDAC Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1090
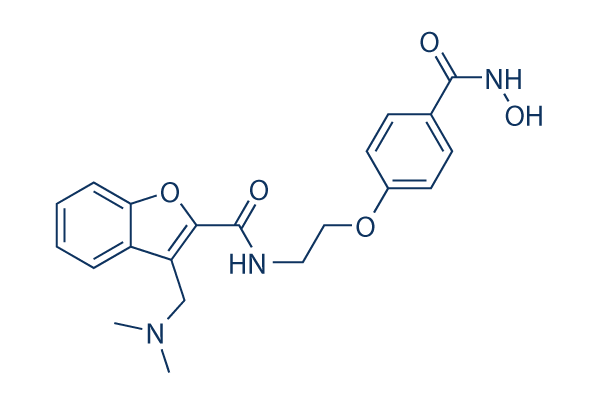
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 397.42
Qualitätskontrolle
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa | Function assay | 2 hrs | Inhibition of dye-labeled tracer binding to HDAC10 (unknown origin) transfected in human HeLa cells measured after 2 hrs by nano-luciferase reporter gene-based BRET assay, IC50=0.007943μM | 30964290 | ||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 397.42 | Formel | C21H23N3O5 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 783355-60-2 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | CRA-024781 | Smiles | CN(C)CC1=C(OC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)NCCOC3=CC=C(C=C3)C(=O)NO | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 80 mg/mL
(201.29 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
HDAC1
(Cell-free assay) 7 nM(Ki)
HDAC3/SMRT
8.2 nM(Ki)
HDAC6
17 nM(Ki)
HDAC2
(Cell-free assay) 19 nM(Ki)
HDAC10
24 nM
HDAC8
280 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Abexinostat (PCI-24781) zeigt eine potente Antitumoraktivität gegen eine Vielzahl von Tumorzelllinien mit GI50-Werten im Bereich von 0,15 μM bis 3,09 μM und hat auch einen antiproliferativen Effekt auf HUVEC-Endothelzellen mit einem GI50 von 0,43 μM. Die Behandlung mit dieser Verbindung führt zu einer dosisabhängigen Akkumulation von acetylierten Histonen und acetyliertem Tubulin in HCT116- oder DLD-1-Zellen, induziert die Expression von p21 und führt zu PARP-Spaltung und Akkumulation von γH2AX. Die Hemmung von HDAC-Enzymen durch PCI-24781 führt zu einer signifikanten Reduktion der Transkription von Genen, die spezifisch mit HR assoziiert sind, einschließlich RAD51. Konsistent mit der Hemmung von HR führt dies zu einer verringerten Fähigkeit, die homologe Reparatur von I-SceI-induzierten Chromosomenbrüchen in transfizierten CHO-Zellen durchzuführen. Es induziert S-Phasen-Depletion, G2-Zellzyklusarrest und Apoptose in Weichgewebesarkom (STS)-Zellen und verursacht auch eine Rad51-Transkriptionsrepression in STS-Zellen, möglicherweise vermittelt durch eine verstärkte E2F1-Bindung an den proximalen Rad51-Promotor. Zusätzlich induziert diese Verbindung Caspase- und reaktive Sauerstoffspezies-abhängige Apoptose durch NF-κB-Mechanismen in Hodgkin-Lymphom- und Non-Hodgkin-Lymphom-Zelllinien.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
HDAC Aktivität
|
|
Die HDAC-Aktivität wird unter Verwendung eines kontinuierlichen Trypsin-gekoppelten Assays gemessen. Für die Inhibitorkarakterisierung werden Messungen in einem Reaktionsvolumen von 100 μL unter Verwendung von 96-Well-Assay-Platten durchgeführt. Für jedes Isoenzym wird das HDAC-Protein in Reaktionspuffer [50 mM HEPES, 100 mM KCl, 0,001% Tween 20, 5% DMSO (pH 7,4), ergänzt mit Rinderserumalbumin in Konzentrationen von 0% (HDAC1), 0,01% (HDAC2, 3, 8 und 10) oder 0,05% (HDAC6)] mit Abexinostat (PCI-24781) in verschiedenen Konzentrationen gemischt und 15 Minuten inkubiert. Trypsin wird zu einer Endkonzentration von 50 nM hinzugefügt, und Acetyl-Gly-Ala-(N-acetyl-Lys)-AMC wird zu einer Endkonzentration von 25 μM (HDAC1, 3 und 6), 50 μM (HDAC2 und 10) oder 100 μM (HDAC8) hinzugefügt, um die Reaktion zu initiieren. Negativkontrollreaktionen werden in Abwesenheit dieser Verbindung in acht Replikaten durchgeführt. Die Reaktionen werden in einem Fluoreszenz-Plattenlesegerät überwacht. Nach einer 30-minütigen Verzögerungszeit wird die Fluoreszenz über einen Zeitraum von 30 Minuten unter Verwendung einer Anregungswellenlänge von 355 nm und einer Detektionswellenlänge von 460 nm gemessen. Die Zunahme der Fluoreszenz mit der Zeit wird als Maß für die Reaktionsrate verwendet. Hemmkonstanten Ki(app) werden mit dem Programm BatchKi erhalten.
|
|
| In vivo |
Abexinostat (PCI-24781) wurde mit 200 mg/kg einmal täglich jeden zweiten Tag (q.o.d.) verabreicht, was das Wachstum von HCT116- und DLD-1-Xenografts in Mäusen signifikant um 69 % bzw. 59 % hemmte. Im HCT116-Modell verursachte die Verabreichung dieser Verbindung in Dosen von 20 mg/kg, 40 mg/kg, 80 mg/kg oder 160 mg/kg einmal täglich an 4 aufeinanderfolgenden Tagen, gefolgt von 3 behandlungsfreien Tagen pro Woche (q.d. × 4 pro Woche), eine Hemmung des Tumorwachstums um 48 %, 57 %, 82,2 % bzw. 80,0 %.
|
Literatur |
|
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05698524 | Recruiting | Recurrent High Grade Glioma|Anaplastic Astrocytoma|Anaplastic Oligodendroglioma|Glioblastoma|Gliosarcoma |
University of Nebraska|Xynomic Pharmaceuticals Inc. |
June 26 2023 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03934567 | Recruiting | Lymphoma Follicular |
Xynomic Pharmaceuticals Inc. |
April 22 2020 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03939182 | Active not recruiting | Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma|Mantle Cell Lymphoma |
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center|Janssen Scientific Affairs LLC|Xynomic Pharmaceuticals Inc. |
May 29 2019 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03600441 | Active not recruiting | Follicular Lymphoma |
Xynomic Pharmaceuticals Inc. |
August 27 2018 | Phase 2 |
| NCT01543763 | Active not recruiting | Metastatic Solid Tumors |
Pamela Munster|Pharmacyclics LLC.|Novartis|Xynomic Pharmaceuticals Inc.|GlaxoSmithKline Research and Education Foundation for Cardiovascular Disease|University of California San Francisco |
June 25 2012 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
