nur für Forschungszwecke
Quisinostat (JNJ-26481585) Dihydrochloride HDAC Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1096
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 467.39
Qualitätskontrolle
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A549 cells | Cell viability assay | 24, 48, or 72 h | the IC50 values of cells for 48 and 72 h of quisinostat treatment were 82.4 and 42.0 nM, respectively. | 27423454 | ||
| RH30 cells | Function assay | 15 nM | 24 h and 30 h | GSK690 and JNJ-26481585 cooperated to induce cleavage of the initiator caspase-9 into its active p35 and p37 fragments and of the effector caspase-3 into its active p12 and p17 fragments | 28617441 | |
| RD cells | Function assay | 15 nM | 24 h and 30 h | GSK690 and JNJ-26481585 cooperated to induce cleavage of the initiator caspase-9 into its active p35 and p37 fragments and of the effector caspase-3 into its active p12 and p17 fragments | 28617441 | |
| HepG2 | Cell viability assay | 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160 and 320 nM | 24, 48, 72 h | The IC50 values of cells for quisinostat treatment at 48 and 72 h were 81.2 and 30.8 nM, respectively. | 28849080 | |
| HuT78 | Function assay | 10 nM | increases the level of acetylated lysine K10 of histone H3 | 30012418 | ||
| Sf9 | Function assay | Inhibition of full length recombinant human HDAC1 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells using RHKK-Ac as substrate by fluorescence analysis, IC50 = 0.00011 μM. | 27606546 | |||
| Sf9 | Function assay | Inhibition of full length recombinant human HDAC2 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells using RHKK-Ac as substrate by fluorescence analysis, IC50 = 0.00033 μM. | 27606546 | |||
| Sf9 | Function assay | Inhibition of full length recombinant human HDAC3/NCOR2 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells using RHKK-Ac as substrate by fluorescence analysis, IC50 = 0.00486 μM. | 27606546 | |||
| HUT78 | Function assay | 18 hrs | Pro-apoptotic activity in human HUT78 cells after 18 hrs by caspase-Glo 3/7 assay, EC50 = 0.0065 μM. | 30122227 | ||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Binding affinity to human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells by ITC method, Kd = 0.0227 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Binding affinity to Schistosoma mansoni His-tagged HDAC8 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells by ITC method, Kd = 0.0284 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.0644 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| Sf9 | Function assay | Inhibition of full length recombinant human HDAC6 expressed in baculovirus infected Sf9 cells using RHKK-Ac as substrate by fluorescence analysis, IC50 = 0.0768 μM. | 27606546 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 mL6 mutant expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.093 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 mL1/mL6 mutant expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.094 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 mL6/L179I mutant expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.169 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of human His-thioredoxin-tagged HDAC8 mL1/mL6/L179I mutant expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.217 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| BL21 (DE3) | Function assay | Inhibition of Schistosoma mansoni His-tagged HDAC8 expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) cells using Fluor de Lys (R)-HDAC8 as substrate by fluorometric method, IC50 = 0.3034 μM. | 30347148 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| fibroblast cells | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for control Hh wild type fibroblast cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| fibroblast cells | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for control Hh wild type fibroblast cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Daoy | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for Daoy cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 467.39 | Formel | C21H28Cl2N6O2 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 875320-31-3 | -- | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | CN1C=C(C2=CC=CC=C21)CNCC3CCN(CC3)C4=NC=C(C=N4)C(=O)NO.Cl.Cl | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 79 mg/mL
(169.02 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Merkmale |
An orally bioavailable, second-generation, hydroxamic acid-based HDAC inhibitor.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
HDAC1
(Cell-free assay) 0.11 nM
HDAC2
(Cell-free assay) 0.33 nM
HDAC11
(Cell-free assay) 0.37 nM
HDAC10
(Cell-free assay) 0.46 nM
HDAC4
(Cell-free assay) 0.64 nM
HDAC5
(Cell-free assay) 3.69 nM
HDAC8
(Cell-free assay) 4.26 nM
HDAC3
(Cell-free assay) 4.86 nM
|
| In vitro |
JNJ-26481585 zeigt ein breites Spektrum antiproliferativer Aktivität in soliden und hämatologischen Krebszelllinien, wie allen Lungen-, Brust-, Darm-, Prostata-, Gehirn- und Eierstocktumorzelllinien, mit IC50-Werten im Bereich von 3,1-246 nM, was potenter ist als R306465, CRA-24781 oder Mocetinostat in verschiedenen getesteten menschlichen Krebszelllinien. Eine aktuelle Studie zeigt, dass JNJ-26481585 den Tod von Myelomzellen bei niedrigen nanomolaren Konzentrationen fördert, indem es zu einer Mcl-1-Depletion und Hsp72-Induktion führt. |
| Kinase-Assay |
HDAC-Aktivitätsassays
|
|
In allen Fällen werden Full-Length-HDAC-Proteine mittels Baculovirus-infizierter Sf9-Zellen exprimiert. Zusätzlich wird HDAC3 als Komplex mit humanem NCOR2 koexprimiert. Zur Beurteilung der Aktivität von HDAC1-enthaltenden Zellkomplexen werden immunpräzipitierte HDAC1-Komplexe mit einem [3H]acetyl-markierten Fragment des Histon H4-Peptids [Biotin-(6-Aminohexansäure)Gly-Ala-(acetyl[3H])Lys-Arg-His-Arg-Lys-Val-NH2] in einem Gesamtvolumen von 50 μL Enzymassaypuffer (25 mM HEPES (pH 7,4), 1 M Saccharose, 0,1 mg/mL BSA und 0,01 % (v/v) Triton X-100) inkubiert. Die Inkubation erfolgt für 45 Minuten bei 37 °C (Immunpräzipitate) oder 30 Minuten bei Raumtemperatur. Vor Zugabe des Substrats werden HDAC-Inhibitoren in steigenden Konzentrationen hinzugefügt und 10 Minuten bei Raumtemperatur vorinkubiert. Nach der Inkubation wird die Reaktion mit 35 μL Stopppuffer (1 M HCl und 0,4 M Essigsäure) abgebrochen. Freigesetzte [3H]Essigsäure wird mit 800 μL Ethylacetat extrahiert und durch Szintillationszählung quantifiziert. Gleiche Mengen an HDAC1 werden, wie durch Western-Blot-Analyse angezeigt, immunpräzipitiert. Die Ergebnisse der HDAC1-Aktivität werden als Mittelwert ± SD von drei unabhängigen Experimenten an einem einzigen Lysat dargestellt.
|
|
| In vivo |
In einem HDAC1-sensitiven A2780-Ovarialtumor-Screeningmodell führt die Dosierung von JNJ-26481585 in seiner maximal tolerierten Dosis (10 mg/kg i.p. und 40 mg/kg p.o.) über 3 Tage zu einer HDAC1-regulierten Fluoreszenz, die die Tumorzellwachstumshemmung vorhersagt. Darüber hinaus zeigt JNJ-26481585 auch potentere Hemmeffekte auf das Wachstum von C170HM2 kolorektalen Lebermetastasen. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
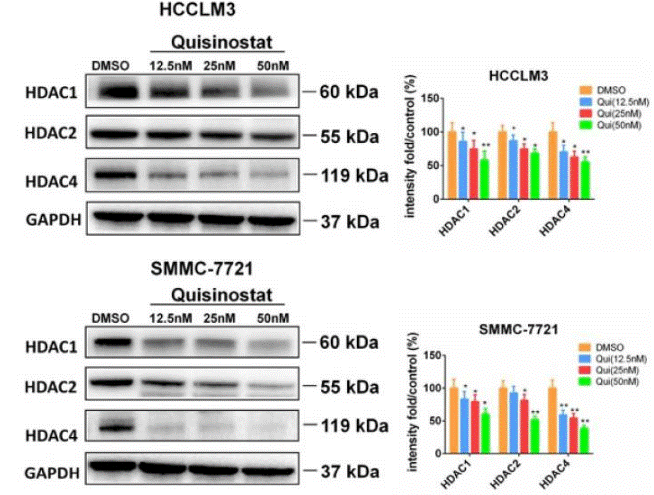
| Western blot | HDAC1 / HDAC2 / HDAC4 p21 / CDK2 / CDK4 / CDK6 / Cyclin D1 / Cyclin E1 / Cyclin A2 Caspase-3/ Cleaved caspase-3 / caspase-9 / Cleaved caspase-9 / PARP / Cleaved PARP / Bcl-xl / Bcl2 / Bax / Survivin PI3K-p110 / PI3K-p85 / p-AKT / JNK / p-JNK / p-c-Jun |
|
30443188 |
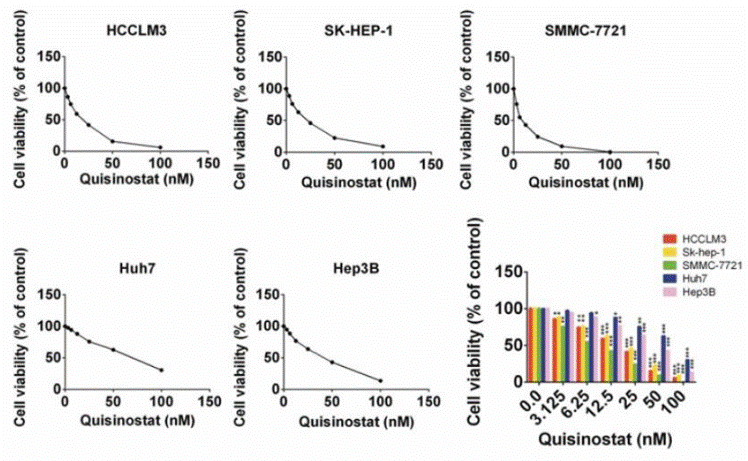
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
30443188 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02948075 | Completed | Ovarian Cancer |
NewVac LLC|Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. Belgium |
September 2015 | Phase 2 |
| NCT01464112 | Completed | Multiple Myeloma |
Janssen Research & Development LLC |
September 16 2011 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00676728 | Terminated | Advanced or Refractory Leukemia|Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development L.L.C. |
December 2008 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00677105 | Completed | Lymphoma|Neoplasms |
Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development L.L.C.|Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. Belgium |
August 2007 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
I was thinking of resuspending it in 10% hydroxy-propyl-β-cyclodextrin, 25mg/ml mannitol, in sterile water (final pH 8.7). Is this a good vehicle to use? What is the solubility of this compound in such a vehicle?
Antwort:
This vehicle can be used for in vivo studies. The following papers also used this vehicle: 1. http://www.nature.com/leu/journal/v23/n10/full/leu2009121a.html; 2. http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/69/13/5307.long (The solvent contains 10% hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, 0.8% HCl (0.1 N), 0.9 % NaOH (0.1 N), 3.4% mannitol and pyrogen-free water). Its solubility is 2mg/ml.
