nur für Forschungszwecke
Perifosine Akt Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1037
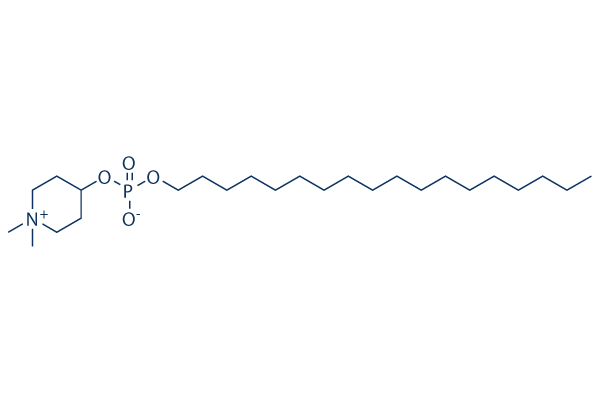
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 461.66
Qualitätskontrolle
- Zitiert in Nature Medicine für seine erstklassige Qualität
- COA
- NMR
-
Warum Mikroanalyse?
- Datenblatt
- SDS
- Zitiert in Nature Medicine für seine erstklassige Qualität
- COA
- NMR
- Datenblatt
- SDS
- Zitiert in Nature Medicine für seine erstklassige Qualität
- COA
- NMR
- Datenblatt
- SDS
- Zitiert in Nature Medicine für seine erstklassige Qualität
- COA
- NMR
- Datenblatt
- SDS
- Zitiert in Nature Medicine für seine erstklassige Qualität
- COA
- NMR
- Datenblatt
- SDS
| Verwandte Ziele | PI3K mTOR GSK-3 ATM/ATR DNA-PK AMPK PDPK1 PTEN PP2A PDK |
|---|---|
| Weitere Akt Inhibitoren | SC79 AZD5363 (Capivasertib) MK-2206 Dihydrochloride Ipatasertib (GDC-0068) GSK690693 Triciribine (API-2) Afuresertib (GSK2110183) CCT128930 A-674563 HCl Akti-1/2 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HL-60 | Apoptosis Asssay | 10 μM | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis time-dependently | 20130960 | |
| MOLM | Apoptosis Asssay | 10 μM | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis time-dependently | 20130960 | |
| OCI | Apoptosis Asssay | 10 μM | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis time-dependently | 20130960 | |
| BJAB | Apoptosis Asssay | 10 μM | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis time-dependently | 20130960 | |
| MAVER | Apoptosis Asssay | 10 μM | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis time-dependently | 20130960 | |
| SKW6.4 | Apoptosis Asssay | 10 μM | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis time-dependently | 20130960 | |
| HL-60 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 2-10 μM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 20130960 | |
| MOLM | Growth Inhibition Assay | 2-10 μM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 20130960 | |
| OCI | Growth Inhibition Assay | 2-10 μM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 20130960 | |
| BJAB | Growth Inhibition Assay | 2-10 μM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 20130960 | |
| MAVER | Growth Inhibition Assay | 2-10 μM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 20130960 | |
| SKW6.4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 2-10 μM | 48 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 20130960 | |
| A2780cis | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 48/72 h | IC50 = 6 μm | 20405296 | |
| A2780 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 48/72 h | IC50 = 3 μm | 20405296 | |
| SKOV3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-40 μM | 72 h | IC50~30 μM, inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 20405296 | |
| PA-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-40 μM | 72 h | IC50~25 μM, inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 20405296 | |
| OAW-42 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-40 μM | 72 h | IC50~10 μM, inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 20405296 | |
| Bel-7402 | Apoptosis Asssay | 5/10/20 μM | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis at the long-time exposure | 20842425 | |
| HepG2 | Apoptosis Asssay | 5/10/20 μM | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis at the long-time exposure | 20842425 | |
| Bel-7402 | Function Assay | 5/10/20 μM | 24 h | results in the accumulation of cell number in the G2/M phase | 20842425 | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 5/10/20 μM | 24 h | results in the accumulation of cell number in the G2/M phase | 20842425 | |
| Bel-7402 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5/10/20/40 μM | 24/48/72 h | inhibits cell growth in both time and dose dependent manner | 20842425 | |
| HepG2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5/10/20/40 μM | 24/48/72 h | inhibits cell growth in both time and dose dependent manner | 20842425 | |
| CWR22RV1 | Function Assay | 5 μM | 24 h | reduced phosphorylation of Akt significantly | 21496273 | |
| CWR22RV1 | Apoptosis Asssay | 10 μM | 24 h | enhances radiation induced apoptosis | 21496273 | |
| CWR22RV1 | Cell Viability Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | increases sensitivity of human CWR22RV1 cells to radiation | 21496273 | |
| A498 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 21644050 | |
| 769-P | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 21644050 | |
| CAKI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 21644050 | |
| 786-O | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 21644050 | |
| 786-0 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-40 μM | 72 h | IC50~5 μM | 21644050 | |
| 769-P | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-40 μM | 72 h | IC50~5-10 μM | 21644050 | |
| CAKI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-40 μM | 72 h | IC50~10 μM | 21644050 | |
| A498 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-40 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 21644050 | |
| HT-29 | Cytotoxicity Assay | 5 μM | 48 h | enhances paclitaxel induced ovarian cancer cell death | 21775054 | |
| A2780 | Cytotoxicity Assay | 5 μM | 48 h | enhances paclitaxel induced ovarian cancer cell death | 21775054 | |
| SKOV3 | Cytotoxicity Assay | 5 μM | 48 h | enhances paclitaxel induced ovarian cancer cell death | 21775054 | |
| CaOV3 | Cell Viability Assay | 1/5/10 μM | 48 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner cotreated with paclitaxel | 21775054 | |
| OCUT1 | Function Assay | 3 μm | 24 h | causes a dramatic increase in G2/M phase | 22090271 | |
| K1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1-3 μM | 5 d | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 22090271 | |
| OCUT1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1-3 μM | 5 d | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 22090271 | |
| K562 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 48 h | induces autophagy | 22407228 | |
| HL-60 | Function Assay | 2.5/5/10 μM | 24 h | induces the phosphorylation of JNK1/2 in a dose dependent manner | 22407228 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Function Assay | 2.5/5/10 μM | 24 h | induces the phosphorylation of JNK1/2 in a dose dependent manner | 22407228 | |
| HL-60 | Function Assay | 2.5/5/10 μM | 24 h | decreases Akt and p-Akt levels dose-dependently | 22407228 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Function Assay | 2.5/5/10 μM | 24 h | decreases Akt and p-Akt levels dose-dependently | 22407228 | |
| HL-60 | Apoptosis Asssay | 10 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 22407228 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Apoptosis Asssay | 10 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 22407228 | |
| HL-60 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-20 μM | 24/48 h | decreases cell viability in both dose and time dependent manner | 22407228 | |
| Kasumi-1 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-20 μM | 24/48 h | decreases cell viability in both dose and time dependent manner | 22407228 | |
| BON1 | Function Assay | 7.5/10 μM | 8 h | decreases the expression of the anti-apoptotic proteins BCL2 and Bcl-XL | 22499437 | |
| BON1 | Apoptosis Asssay | 0-10 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis dose dependently | 22499437 | |
| BON1 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-100 μM | 24/72 h | decreases cell viability in both dose and time dependent manner | 22499437 | |
| GOT1 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-100 μM | 24/72 h | decreases cell viability in both dose and time dependent manner | 22499437 | |
| NCI-H727 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-100 μM | 24/72 h | decreases cell viability in both dose and time dependent manner | 22499437 | |
| MCAS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.5 μM | 23877012 | |||
| A2780S | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.5 μM | 23877012 | |||
| OVCAR5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.7 μM | 23877012 | |||
| A2780CP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.6 μM | 23877012 | |||
| HeyA8 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.3 μM | 23877012 | |||
| OVCAR8 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.1 μM | 23877012 | |||
| M41R | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.8 μM | 23877012 | |||
| M41 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.7 μM | 23877012 | |||
| TykNuR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.5 μM | 23877012 | |||
| TykNu | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.5 μM | 23877012 | |||
| MGC803 | Function Assay | 0.75/10 μM | 48 h | decreases p-Akt (Ser 473), p-GSK3β (Ser 9), and C-MYC levels | 23912246 | |
| SGC7901 | Function Assay | 0.75/10 μM | 48 h | decreases p-Akt (Ser 473), p-GSK3β (Ser 9), and C-MYC levels | 23912246 | |
| U87MG | Cell Viability Assay | 0-25 μM | 24-96 h | decreases cell viability in both dose and time dependent manner | 24065522 | |
| AsPC-1 | Function Assay | 0.5 μM | 24 h | inhibits Akt, S6K1, and Erk1/2 phosphorylation | 24519751 | |
| MIA | Function Assay | 0.5 μM | 24 h | inhibits Akt, S6K1, and Erk1/2 phosphorylation | 24519751 | |
| PANC-1 | Function Assay | 0.5 μM | 24 h | inhibits Akt, S6K1, and Erk1/2 phosphorylation | 24519751 | |
| AsPC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-25 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24519751 | |
| MIA | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-25 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24519751 | |
| PANC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-25 μM | 72 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24519751 | |
| Ema | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1–100 μM | 48 h | IC50=58.7 μM | 24881508 | |
| UL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1–100 μM | 48 h | IC50=7.01 μM | 24881508 | |
| CLBL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1–100 μM | 48 h | IC50=33.0 μM | 24881508 | |
| GL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.1–100 μM | 48 h | IC50=9.91 μM | 24881508 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-10 μM | 48 h | EC50=1.13 ± 0.07 μM | 25293576 | |
| HCC1806 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-10 μM | 48 h | EC50=2.84 ± 0.07 μM | 25293576 | |
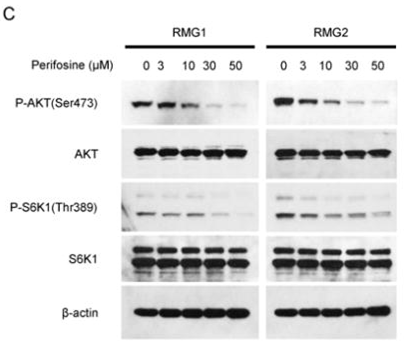
| RMG2 | Apoptosis Asssay | 30 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 25519148 | |
| RMG1 | Apoptosis Asssay | 30 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 25519148 | |
| A2780 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-30 μM | 48 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 25519148 | |
| SKOV3 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-30 μM | 48 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 25519148 | |
| OVISE | Cell Viability Assay | 1-30 μM | 48 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 25519148 | |
| RMG2 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-30 μM | 48 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 25519148 | |
| HAC2 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-30 μM | 72 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 25519148 | |
| KOC7C | Cell Viability Assay | 1-30 μM | 72 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 25519148 | |
| RMG2 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-30 μM | 72 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 25519148 | |
| RMG1 | Cell Viability Assay | 1-30 μM | 72 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 25519148 | |
| H460 | Function Assay | 3 μM | 8 h | blocks mTORC1, and ERK-MAPK activation combined with MEK-162 | 25697899 | |
| A549 | Function Assay | 3 μM | 8 h | blocks mTORC1, and ERK-MAPK activation combined with MEK-162 | 25697899 | |
| H460 | Function Assay | 3 μM | 8 h | blocks AKT activation | 25697899 | |
| A549 | Function Assay | 3 μM | 8 h | blocks AKT activation | 25697899 | |
| H460 | Apoptosis Asssay | 1/3 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis | 25697899 | |
| A549 | Apoptosis Asssay | 1/3 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis | 25697899 | |
| H460 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.3-10 μM | 24/72 h | inhibits cell growth in both time and dose dependent manner | 25697899 | |
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0.3-10 μM | 24/72 h | inhibits cell growth in both time and dose dependent manner | 25697899 | |
| U-87 MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | 20/40 μM | 24/48 h | inhibits cell growth in both time and dose dependent manner | 25934232 | |
| HepG2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 20/40 μM | 24/48 h | inhibits cell growth in both time and dose dependent manner | 25934232 | |
| U-87 MG | Function Assay | 20 μM | 6/24 h | increases the autophagic flux at 6 h while inhibits this flux at 24h | 25934232 | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 6/24 h | decreases LC3-II degradation from 6 h | 25934232 | |
| U-87 MG | Function Assay | 20 μM | 6/24 h | increases the levels of LC3-II cotreated with CQ | 25934232 | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 6/24 h | increases the levels of LC3-II cotreated with CQ | 25934232 | |
| U-87 MG | Function Assay | 20 μM | 24 h | increases double-membrane bound structures | 25934232 | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 20 μM | 24 h | produces an intense cytoplasmic vacuolization corresponding to a notable dilatation of the ER cisterns | 25934232 | |
| T24 BC | Apoptosis Asssay | 2.5 μM | 24 h | sensitizes BC cells to sorafenib-induced apoptotic | 26097873 | |
| T24 BC | Cell Viability Assay | 0.5/1/2.5 μM | 24 h | enhances sorafenib-induced cell viability decrease | 26097873 | |
| T24 BC | Function Assay | 0.5/1/2.5 μM | 3 h | reduces the basal CB tyrosine phosphorylation levels in a dose-dependent manner | 26097873 | |
| RBL2H3 | Function assay | Toxicity in rat RBL2H3 cells, MTD=25μM | 20153565 | |||
| PC3 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human PC3 cells by sulforhodamine B assay, GI50=0.44μM | 21543141 | |||
| NUGC3 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human NUGC3 cells by sulforhodamine B assay, GI50=0.54μM | 21543141 | |||
| HCT15 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human HCT15 cells by sulforhodamine B assay, GI50=1.25μM | 21543141 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human MDA-MB-231 cells by sulforhodamine B assay, GI50=2.86μM | 21543141 | |||
| NCI-H23 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human NCI-H23 cells by sulforhodamine B assay, GI50=4.21μM | 21543141 | |||
| ACHN | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human ACHN cells by sulforhodamine B assay, GI50=4.56μM | 21543141 | |||
| A549 | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of Akt phosphorylation in insulin-stimulated human A549 cells treated 2 hrs before insulin stimulation measured after 30 mins by ELISA, IC50=5.3μM | 22138309 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells after 24 hrs by FACS analysis, IC50=7μM | 22138309 | ||
| KATO III | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human KATO III cells after 24 hrs by FACS analysis, IC50=12.8μM | 22138309 | ||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MCF7 cells after 24 hrs by FACS analysis, IC50=13.3μM | 22138309 | ||
| PC3 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human PC3 cells by SRB assay, GI50=0.44μM | 23266181 | |||
| NUGC3 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human NUGC3 cells by SRB assay, GI50=0.54μM | 23266181 | |||
| HCT15 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human HCT15 cells by SRB assay, GI50=1.25μM | 23266181 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human MDA-MB-231 cells by SRB assay, GI50=2.86μM | 23266181 | |||
| NCI-H23 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human NCI-H23 cells by SRB assay, GI50=4.21μM | 23266181 | |||
| ACHN | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human ACHN cells by SRB assay, GI50=4.56μM | 23266181 | |||
| A549 | Function assay | 2 hrs | Inhibition of Akt phosphorylation in human insulin-stimulated A549 cells incubated for 2 hrs prior to insulin-induction measured after 30 mins by ELISA, IC50=5.3μM | 23415083 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells by flow cytometric analysis, IC50=7μM | 23415083 | |||
| KATO III | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human KATO III cells by flow cytometric analysis, IC50=12.8μM | 23415083 | |||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human MCF7 cells by flow cytometric analysis, IC50=13.3μM | 23415083 | |||
| PC3 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human PC3 cells by SRB assay, GI50=0.44μM | 23567950 | |||
| NUGC3 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human NUGC3 cells by SRB assay, GI50=0.54μM | 23567950 | |||
| HCT15 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT15 cells by SRB assay, GI50=1.25μM | 23567950 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human MDA-MB-231 cells by SRB assay, GI50=2.86μM | 23567950 | |||
| NCI-H23 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human NCI-H23 cells by SRB assay, GI50=4.21μM | 23567950 | |||
| ACHN | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human ACHN cells by SRB assay, GI50=4.56μM | 23567950 | |||
| PC3 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | Growth inhibition of human PC3 cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, GI50=0.44μM | 24095759 | ||
| NUGC3 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | Growth inhibition of human NUGC3 cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, GI50=0.54μM | 24095759 | ||
| HCT15 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | Growth inhibition of human HCT15 cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, GI50=1.25μM | 24095759 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | Growth inhibition of human MDA-MB-231 cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, GI50=2.86μM | 24095759 | ||
| NCI-H23 | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | Growth inhibition of human NCI-H23 cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, GI50=4.21μM | 24095759 | ||
| ACHN | Growth inhibition assay | 48 hrs | Growth inhibition of human ACHN cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, GI50=4.56μM | 24095759 | ||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 to 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells after 24 to 72 hrs by haemocytometry, IC50=4.17μM | 24900620 | ||
| Rosetta cells | Function assay | Inhibition of wild-type human P38alpha MAPK expressed in Escherichia coli Rosetta cells, IC50=1.2μM | 31274316 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 461.66 | Formel | C25H52NO4P |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 157716-52-4 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | KRX-0401, NSC639966, D21266 | Smiles | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCOP(=O)([O-])OC1CC[N+](CC1)(C)C | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
Water : 92 mg/mL Ethanol : 92 mg/mL
DMSO
: Insoluble
|
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Akt
(MM.1S cells) 4.7 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Perifosine entwickelt antiproliferative Eigenschaften mit einer IC50 von 0,6-8,9 M in immortalisierten Keratinozyten (HaCaT) sowie Kopf- und Hals-Plattenepithelkarzinomzellen. Diese Verbindung reduziert die Phosphorylierungsgrade von Akt und der extrazellulären signalregulierten Kinase (Erk) 1/2 stark, induziert einen Zellzyklusarrest in G1 und G2 und verursacht eine dosisabhängige Wachstumshemmung von Mäuse-Glialvorläuferzellen. Sie hemmt die Phosphorylierung von Akt in MM.1S-Zellen vollständig. Eine aktuelle Studie zeigt, dass diese Chemikalie durch Blockade der Akt-Phosphorylierung einen Zellzyklusarrest und Apoptose in humanen hepatozellulären Karzinomzelllinien induziert. |
| Kinase-Assay |
Akt-Kinase-Assay
|
|
MM.1S-Zellen werden in Gegenwart oder Abwesenheit von Perifosine (5
M, 6 Stunden) kultiviert und anschließend mit IL-6 (20 ng/mL, 10 Minuten) stimuliert. Anschließend wird ein In-vitro-Akt-Kinase-Assay unter Verwendung des Akt Kinase Assay Kits durchgeführt.
|
|
| In vivo |
Perifosine reduziert in Kombination die Tumorproliferation (eine PDGF-getriebene Gliomentstehung) in vivo. Die Ergebnisse deuten darauf hin, dass diese Verbindung ein wirksames Medikament bei Gliomen ist, bei denen die Akt- und Ras-Erk 1/2-Signalwege häufig aktiviert sind, und ein neuer Kandidat für die Gliomabehandlung in der Klinik sein könnte. Sowohl die tägliche als auch die wöchentliche orale Verabreichung dieser Chemikalie reduzieren das Wachstum menschlicher MM-Tumoren signifikant und erhöhen die Überlebensrate im Vergleich zu Kontrolltieren, die nur mit PBS-Lösung behandelt wurden. Es induziert Thrombozytose und Leukozytose und erhöht die Myelopoese in Mausknochenmark und -milz, während es Apoptose in Myelom-Xenografts verursacht. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-AKT / AKT / p-S6K1 / S6K1 PARP p-mTOR / mTOR / Raptor / Rictor / p-p70S6K / p70S6K / p-4EBP1 / 4EBP1 / c-Myc / Cyclin D1 p-PDK1 / p-GSK3α/β / p-S6R |
|
25519148 |
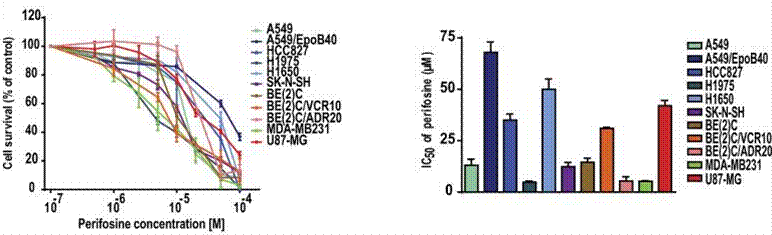
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
28332584 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01224730 | Completed | Cancer |
AEterna Zentaris |
January 24 2012 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01049841 | Completed | Pediatric Solid Tumors |
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center|University of Wisconsin Madison|Duke University|NATL COMP CA NETWORK|Pfizer|AEterna Zentaris |
January 2010 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01048580 | Completed | Colon Cancer |
AEterna Zentaris|SCRI Development Innovations LLC |
October 2009 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00776867 | Completed | Solid Tumors |
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center|University of Wisconsin Madison|Duke University|AEterna Zentaris |
October 2008 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
