nur für Forschungszwecke
Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester NF-κB Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S7414
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 284.31
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | HDAC Antioxidant ROS IκB/IKK Nrf2 AP-1 MALT NOD |
|---|---|
| Weitere NF-κB Inhibitoren | DCZ0415 Omaveloxolone (RTA-408) BAY 11-7082 (BAY 11-7821) JSH-23 QNZ (EVP4593) SC75741 DHA (Dihydroartemisinin) Withaferin A (WFA) Andrographolide Evodiamine |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mouse RAW264.7 cells | Function assay | 24 h | Inhibition of LPS-induced nitric oxide production in mouse RAW264.7 cells assessed as nitrite accumulation administered 1 hr before LPS challenge and measured after 24 hrs by Griess reagent assay, EC50=0.193 μM | |||
| mouse 26-L5 cells | Proliferation assay | 72 h | Antiproliferative activity against mouse 26-L5 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, EC50=0.3 μM | |||
| human HeLa cells | Proliferation assay | 72 h | Antiproliferative activity against human HeLa cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, EC50=2.36 μM | |||
| human Bewo cells | Function assay | Antitumor activity against human Bewo cells assessed as inhibition of cell growth by MTT assay, IC50=2.96 μM | ||||
| mouse J774.1 cells | Function assay | 24 h | Inhibition of LPS-induced NO production in mouse J774.1 cells after 24 hrs by Griess reagent assay, IC50=4.8 μM | |||
| human Bel7402 cells | Cytotoxic assay | Cytotoxicity against human Bel7402 cells by MTT assay, IC50=5.5 μM | ||||
| human LNCAP cells | Function assay | 24 h | Antiandrogenic activity in human LNCAP cells assessed as reduction in DHT-stimulated PSA release after 24 hrs by ELISA, IC50=6.2 nM | |||
| mouse BV2 cells | Function assay | 24 h | Inhibition of nitric oxide production in LPS-stimulated mouse BV2 cells treated 3 hrs before LPS addition measured after 24 hrs by Griess assay, IC50=6.4 μM | |||
| mouse B16-BL6 cells | Proliferation assay | 72 h | Antiproliferative activity against mouse B16-BL6 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, EC50=6.79 μM | |||
| HUVEC cells | Cytotoxic assay | 18 h | Cytoprotective activity against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in HUVEC cells after 18 hrs by Cell-Titer Blue assay | |||
| human HT1080 cells | Proliferation assay | 72 h | Antiproliferative activity against human HT1080 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, EC50=9.5 μM | |||
| human HL60 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human HL60 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=9.8 μM | |||
| human LS 174T cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human LS 174T cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC60=9.9 μM | |||
| human SGC7901 cells | Function assay | Antitumor activity against human SGC7901 cells assessed as inhibition of cell growth by MTT assay, IC50=14.26 μM | ||||
| human Bel7404 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human Bel7404 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=14.5 μM | |||
| human BGC823 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human BGC823 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=19.3 μM | |||
| human HO8910 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human HO8910 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=25.5 μM | |||
| human MCF7 cells | Cytotoxic assay | Cytotoxicity against human MCF7 cells by MTT assay, IC50=26.7 μM | ||||
| human A549 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=26.8 μM | |||
| human LNCAP cells | Cytotoxic assay | 24 h | Cytotoxicity against human LNCAP cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 24 hrs by WST-1 assay, IC50=33.7 μM | |||
| human HeLa cells | Function assay | Antitumor activity against human HeLa cells assessed as inhibition of cell growth by MTT assay, IC50=37.98 μM | ||||
| human HepG2 cells | Function assay | Antitumor activity against human HepG2 cells assessed as inhibition of cell growth by MTT assay, IC50=40.87 μM | ||||
| human ECA109 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human ECA109 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=42.6 μM | |||
| human BCG823 cells | Cytotoxic assay | Cytotoxicity against human BCG823 cells by MTT assay, IC50=44.6 μM | ||||
| human KB cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human KB cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=45.2 μM | |||
| human K562 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human K562 cells after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=46 μM | |||
| rat VSMC | Function assay | 5 μM | 30 mins | Decrease in intracellular ROS level in PDGF-stimulated rat VSMC at 5 uM pretreated with compound for 30 mins measured after up to 23 hrs of post stimulation using H2DCF by flow cytometric analysis | ||
| rat PC12 cells | Function assay | 2.5 μM | 3 h | Neuroprotective activity against H2O2-induced damage in rat PC12 cells assessed as cell viability at 2.5 uM preincubated for 3 hrs followed by H2O2 challenge measured after 5 hrs by MTT assay | ||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 284.31 | Formel | C17H16O4 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 104594-70-9 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | CAPE, Phenylethyl Caffeate | Smiles | C1=CC=C(C=C1)CCOC(=O)C=CC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 56 mg/mL
(196.96 mM)
Ethanol : 56 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
NF-κB
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Caffeic acid phenethyl ester blockiert die durch Phorbolester, Ceramid, Okadainsäure und Wasserstoffperoxid induzierte NF-κB-Aktivierung, indem es die Translokation der p65-Untereinheit von NF-κB in den Zellkern verhindert. In einer Reihe von Tumorzelllinien zeigt Caffeic acid phenethyl ester vielversprechende antiproliferative Aktivität mit EC50-Werten von 1,76, 3,16, 13,7 und 44,0 μM gegen murine Kolon-26-L5-, murine B16-BL6-Melanom-, menschliche HT-1080-Fibrosarkom- und menschliche Lungen-A549-Adenokarzinom-Zelllinien. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester übt als potentes Antioxidans seine anti-apoptotische Wirkung in zerebellären Körnerzellen aus, indem es die ROS-Bildung blockiert und die Caspase-Aktivität hemmt. Darüber hinaus mildert Caffeic acid phenethyl ester den proinflammatorischen Phänotyp von LPS-stimulierten HSCs und die LPS-induzierte Sensibilisierung von HSCs gegenüber fibrogenen Zytokinen durch Hemmung der NF-κB-Signalübertragung.
|
| In vivo |
In vivo hemmt Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (10 mg/kg, i.p.) das Wachstum und die Angiogenese von Primärtumoren in C57BL/6- und BALB/c-Mäusen, die mit Lewis-Lungenkarzinom-, Kolonkarzinom- und Melanomzellen inokuliert wurden. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester (5, 10, 20 mg/kg) zeigt auch immunmodulatorische Effekte in vivo, indem es das Thymusgewicht und/oder die Zellzahl von Thymus und Milz verringert.
|
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
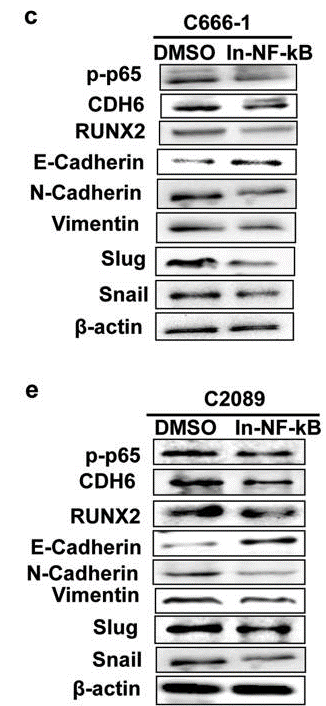
| Western blot | p-p65 / CDH6 / RUNX2 / E-cadherin / N-cadherin / Vimentin / Slug / Snail Nrf2 AKT / AKT1 / AKT2 / AKT3 / p-AKT / FOXO1 / FOXO3a / p-FOXO1 / p-FOXO3a / Skp2 / p27(Kip) / Cyclin D1 / Rb / p-Rb |
|
29284791 |
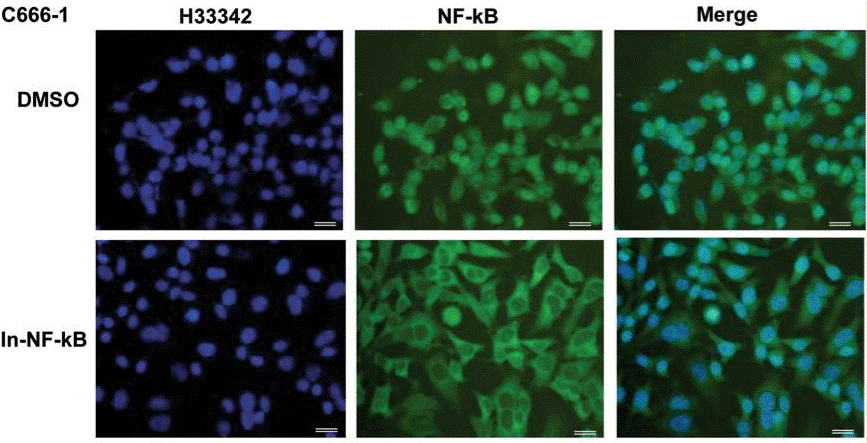
| Immunofluorescence | NF-κB |
|
29284791 |
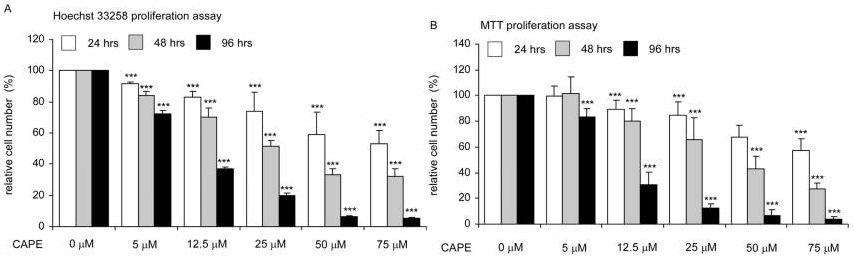
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell number |
|
23615471 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05726708 | Recruiting | Autism Spectrum Disorder |
Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois |
October 24 2023 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05934019 | Recruiting | Mental Health Issue|Transdiagnostic Mechanisms|Adolescent Psychology|Prevention|Online Intervention|Psychological Intervention|Mental Disorder in Adolescence Subclinical |
University of Bern |
June 9 2023 | Not Applicable |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
