nur für Forschungszwecke
Cilengitide trifluoroacetate Integrin Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S7077

Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 702.68
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | Akt Wnt/beta-catenin PKC HSP ROCK Microtubule Associated Bcr-Abl Actin FAK Kinesin |
|---|---|
| Weitere Integrin Inhibitoren | SB273005 Cilengitide (EMD 121974) RGD peptide (Arg-Gly-Asp) ATN-161 Cyclo(-RGDfK) TFA Cyclo(RGDyK) TFA Leukadherin-1 A-205804 Pyrintegrin RGD peptide (GRGDNP) |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G28 | Function Assay | 50 μg/ml | 30/60/120 min | inhibits phosphorylation of FAK, Src and Akt | 19114005 | |
| HMEC-1 | Function Assay | 20/40/60 μg/ml | inhibits FAK and Src | 19114005 | ||
| G44 | Apoptosis Assay | 1/5/50 μg/ml | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 19114005 | |
| G28 | Apoptosis Assay | 1/5/50 μg/ml | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 19114005 | |
| G44 | Proliferation Assay | 1/5/50 μg/ml | 24/48/72 h | inhibits proliferation in a dose dependent manner | 19114005 | |
| G28 | Proliferation Assay | 1/5/50 μg/ml | 24/48/72 h | inhibits proliferation in a dose dependent manner | 19114005 | |
| HMEC-1 | Apoptosis Assay | 1/5/50 μg/ml | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 19114005 | |
| HMEC-1 | Proliferation Assay | 1/5/50 μg/ml | 24/48/72 h | inhibits proliferation in a dose dependent manner | 19114005 | |
| HMEC-1 | Function Assay | 1/5/50 μg/ml | 24 h | induces a dose dependent detachment | 19114005 | |
| LNT-229 | Function Assay | 0.1/1/10 μM | 24 h | impairs the adhesion of cells to vitronectin in a dose dependent manner | 19221171 | |
| T98G | Function Assay | 0.1/1/10 μM | 24 h | impairs the adhesion of cells to vitronectin in a dose dependent manner | 19221171 | |
| LN-18 | Function Assay | 0.1/1/10 μM | 24 h | impairs the adhesion of cells to vitronectin in a dose dependent manner | 19221171 | |
| LN-308 | Function Assay | 0.1/1/10 μM | 24 h | impairs the adhesion of cells to vitronectin in a dose dependent manner | 19221171 | |
| U87MG | Function Assay | 0.1/1/10 μM | 24 h | impairs the adhesion of cells to vitronectin in a dose dependent manner | 19221171 | |
| U87 | Function Assay | 0-25 μg/mL | 12 h | induces autophagy dose dependently | 21788343 | |
| U251 | Function Assay | 0-25 μg/mL | 12 h | induces autophagy dose dependently | 21788343 | |
| U87 | Apoptosis Assay | 25 μg/mL | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis at 48 h significantly | 21788343 | |
| U251 | Apoptosis Assay | 25 μg/mL | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis at 48 h significantly | 21788343 | |
| U87 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-25 μg/mL | 0-48 h | inhibits cell growth in dose and time dependent manner | 21788343 | |
| U251 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-25 μg/mL | 0-48 h | inhibits cell growth in dose and time dependent manner | 21788343 | |
| U251MG | Apoptosis Assay | 1 µM | 48 h | induces apoptosis | 23354807 | |
| U87MG | Apoptosis Assay | 1 µM | 48 h | induces apoptosis | 23354807 | |
| U251MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-25 μM | 24/48 h | inhibits cell growth in dose and time dependent manner | 23354807 | |
| U87MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-25 μM | 24/48 h | inhibits cell growth in dose and time dependent manner | 23354807 | |
| MCF-7 | Apoptosis Assay | 0-20 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis | 24153102 | |
| T-47D | Apoptosis Assay | 0-20 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis | 24153102 | |
| MCF-7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 96 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24153102 | |
| T-47D | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-20 μM | 96 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 24153102 | |
| FaDu | Apoptosis Assay | 25 µM | 48 h | induces apoptosis | 24557056 | |
| CAL27 | Apoptosis Assay | 25 µM | 48 h | induces apoptosis | 24557056 | |
| SCC25 | Apoptosis Assay | 25 µM | 48 h | induces apoptosis | 24557056 | |
| FaDu | Growth Inhibition Assay | 6.25–200 µM | 72 h | results moderate, dose-dependent growth inhibition | 24557056 | |
| CAL27 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 6.25–200 µM | 72 h | results moderate, dose-dependent growth inhibition | 24557056 | |
| SCC25 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 6.25–200 µM | 72 h | results moderate, dose-dependent growth inhibition | 24557056 | |
| H28 | Cell Viability Assay | 1 nM-200 μM | 72 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 24595274 | |
| MM05 | Cell Viability Assay | 1 nM-200 μM | 72 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 24595274 | |
| MSTO-211H | Cell Viability Assay | 1 nM-200 μM | 72 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 24595274 | |
| REN | Cell Viability Assay | 1 nM-200 μM | 72 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 24595274 | |
| LN-308 | Function Assay | 10 μm | 24 h | DMSO | reduces AhR protein levels and DRE reporter activity | 26500056 |
| HaCaT | Function Assay | 10 μm | 48 h | DMSO | reduces TGF-β2 mRNA expression | 26500056 |
| S-24 | Function Assay | 1/10 μm | 24 h | DMSO | reduces DRE reporter activity | 26500056 |
| ZH-161 | Function Assay | 1/10 μm | 24 h | DMSO | reduces DRE reporter activity | 26500056 |
| LN-308 | Function Assay | 1/10/100 μm | 24 h | DMSO | reduces DRE reporter activity in a concentration-dependent manner | 26500056 |
| M21 | Function assay | 1 hr | Binding affinity to integrin alphav/beta3 heterodimer in human M21 cells assessed as inhibition of integrin-mediated human M21 cell adhesion to vitronectin after 1 hr in presence of MnCl2, IC50 = 0.0004 μM. | 26753814 | ||
| HEK293T | Function assay | 2 hrs | Binding affinity to soluble truncated human recombinant Fc-tagged alphaVbeta3 and integrins were expressed in HEK293T cells after 2 hrs by competition ELISA-like assay, IC50 = 0.00051 μM. | 24095096 | ||
| HT-29 | Function assay | 2 hrs | Antagonist activity at integrin alphaVbeta5 (unknown origin) expressed in HT-29 cells assessed as reduction in cell adhesion to vitronectin after 2 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 0.12 μM. | 28351594 | ||
| HEK293 | Function assay | 2 hrs | Antagonist activity at integrin alphaVbeta3 (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells assessed as reduction in cell adhesion to fibrinogen after 2 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 0.22 μM. | 28351594 | ||
| SKOV3 | Function assay | 2 hrs | Antagonist activity at integrin alphaVbeta3alphaVbeta5 (unknown origin) expressed in SKOV3 cells assessed as reduction in cell adhesion to fibrinogen after 2 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 0.37 μM. | 28351594 | ||
| U87MG | Function assay | 100 nM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of alphaVbeta3 integrin in human U87MG cells assessed as increase in p53 accumulation at 100 nM after 24 hrs by Western blot method | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Function assay | 100 nM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of alphaVbeta3 integrin in human U87MG cells assessed as increase in p53 accumulation at 100 nM after 24 hrs in presence of MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3 by Western blot method | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Function assay | 100 nM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of alphaVbeta3 integrin in human U87MG cells assessed as increase in p53 accumulation at 100 nM after 24 hrs in presence of MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3 and MDM4 inhibitor SJ-1722550 by Western blot method | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Function assay | 100 nM | 8 hrs | Inhibition of alphaVbeta3 integrin in human U87MG cells assessed as increase in MDM2 mRNA expression at 100 nM after 8 hrs in presence of MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3 and MDM4 inhibitor SJ-1722550 by RT-PCR method | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Function assay | 100 nM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of alphaVbeta3 integrin in human U87MG cells assessed as increase in PUMA mRNA expression at 100 nM after 24 hrs by RT-PCR method | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Function assay | 100 nM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of alphaVbeta3 integrin in human U87MG cells assessed as increase in PUMA mRNA expression at 100 nM after 24 hrs in presence of MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3 by RT-PCR method | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Function assay | 100 nM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of alphaVbeta3 integrin in human U87MG cells assessed as increase in PUMA mRNA expression at 100 nM after 24 hrs in presence of MDM4 inhibitor SJ-1722550 by RT-PCR method | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Function assay | 100 nM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of alphaVbeta3 integrin in human U87MG cells assessed as increase in PUMA mRNA expression at 100 nM after 24 hrs in presence of MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3 and MDM4 inhibitor SJ-1722550 by RT-PCR method | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Function assay | 100 nM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of alphaVbeta3 integrin in human U87MG cells assessed as increase in p21 mRNA expression at 100 nM after 24 hrs by RT-PCR method | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Antiproliferative assay | 100 nM | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human U87MG cells at 100 nM after 72 hrs in presence of MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3 by MTS assay | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Antiproliferative assay | 100 nM | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human U87MG cells at 100 nM after 72 hrs in presence of MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3 and MDM4 inhibitor SJ-1722550 by MTS assay | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Cell cycle assay | 100 nM | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in human U87MG cells assessed as accumulation at G0/G1 phase at 100 nM after 24 hrs | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Anti-invasive assay | 10 uM | 24 hrs | Anti-invasive activity in human U87MG cells at 10 uM after 24 hrs by transwell assay | 29775303 | |
| U87MG | Anti-invasive assay | 10 uM | 24 hrs | Anti-invasive activity in human U87MG cells at 10 uM after 24 hrs in presence of MDM2 inhibitor nutlin-3 and MDM4 inhibitor SJ-1722550 by transwell assay | 29775303 | |
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 702.68 | Formel | C29H41F3N8O9 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 199807-35-7 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | EMD 121974, NSC 707544 | Smiles | CC(C)C1C(=O)NC(C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(C(=O)N1C)CC2=CC=CC=C2)CC(=O)O)CCCN=C(N)N.C(=O)(C(F)(F)F)O | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 100 mg/mL
(142.31 mM)
Water : 6.25 mg/mL Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
αvβ3 receptor
(Cell-free assay) 4.1 nM
αvβ5 receptor
(Cell-free assay) 79 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Cilengitide ist ein zyklisiertes Pentapeptid-Peptidomimetikum, das entwickelt wurde, um mit der Arginin-Glycin-Asparaginsäure (RGD)-Peptidsequenz zu konkurrieren, die die Integrin-Liganden-Bindung reguliert. Cilengitide blockiert selektiv und potent die Ligation der αvβ3- und αvβ5-Integrine an provisorische Matrixproteine wie Vitronectin, Fibronektin, Fibrinogen, von-Willebrand-Faktor, Osteopontin und andere.
Cilegitide hemmt die Angiogenese in vitro. 10 μM Cilengitide hemmt die Anheftung von BAE-, BME- und HUVE-Zellen an Vitronectin und Fibronektin vollständig. Cilengitide hemmt die in vitro-Angiogenese von BAE-Zellen auf dreidimensionalen Kollagen- und Fibrin-Gelen, die mit FGF-2 (oder VEGF-A) vorbehandelt wurden, mit einer IC50 von 15 μM und 8 μM, 4 μM und 3 μM, bzw.
Cilengitide blockiert die Proliferation und induziert die Apoptose von Endothelzellen sowie die Differenzierung von humanen endothelialen Vorläuferzellen (EPCs). 50 μg/mL Cilengitide hemmt die Proliferation der humanen mikrovaskulären Endothelzelllinie HMEC-1 vollständig und führt bei ~30% der Zellen zur Apoptose. 1,0 μM Cilengitide, 9 Tage lang behandelt, hemmt die Proliferation von EPCs um fast 40%. 1 μM Cilengitide hemmt die Differenzierung von EPCs nach 14 Tagen um mehr als 80%.
Cilengitide hemmt die Adhäsion und induziert die Apoptose von Tumorzellen. 25 μg/mL Cilengitide verursacht eine Ablösung von DAOY-Zellen (Medulloblastom) und U87MG-Zellen (Glioblastom) von Vitronectin und Tenascin um mehr als 60%. 25 μg/mL Cilengitide induziert eine Apoptose-Rate von fast 50% dieser Zellen.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
Integrin-Bindungswettbewerbsassay
|
|
Rekombinante lösliche Integrine werden immobilisiert, und Peptide, die in Tris-gepufferter Salzlösung (TBS++) (0,1 % (w/v) BSA, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM CaCl2, 1 mM MgCl2, 10 μM MnCl2, 20 mM Tris-HCl; pH 7,4) seriell verdünnt werden, werden parallel mit biotinyliertem Vitronectin (auf 1 μg/mL) hinzugefügt. Nach einer 3-stündigen Inkubation bei 37 °C und Waschen mit Tris-gepufferter Salzlösung wird der gebundene Ligand durch Inkubation mit einem mit Anti-Biotin-Alkalische-Phosphatase konjugierten Antikörper (BioRad) und anschließender Entwicklung mit p-Nitrophenylphosphat-Substrat nachgewiesen. Die Reaktion wird durch Zugabe von NaOH gestoppt und die Farbintensität bei 405 nm abgelesen.
|
|
| In vivo |
Cilengitide wirkt als Einzelwirkstoff gegen Tumorwachstum und Angiogenese. 100 μg Cilengitide induziert eine signifikante Abnahme der Anzahl der CD31+-Gefäße in Tumoren (2/Gesichtsfeld bei hoher Vergrößerung) im Vergleich zu Kontrolltumoren (56/Gesichtsfeld bei hoher Vergrößerung). 100 μg Cilengitide erhöht die zelluläre Apoptose in den Hirntumoren von Tieren (2,2 % apoptotische Zellen/Gesichtsfeld bei hoher Vergrößerung) im Vergleich zu Tieren, die das inaktive Peptid erhielten (1,7 % Zellen/Gesichtsfeld bei hoher Vergrößerung). Eine Cilengitide-Behandlung führt zu einem verlängerten Überleben der Mäuse mit Melanom-Xenotransplantaten M21 im Vergleich zur Kontrollbehandlungsgruppe (36,5 vs. 17,3 Tage).
Cilengitide kann den therapeutischen Nutzen, der mit zytotoxischen Wirkstoffen wie Chemotherapie und Strahlentherapie in Tumormodellen verbunden ist, verstärken. Cilengitide (250 mg/Dosis) allein verändert das Tumorwachstum von Brustkrebs-Xenotransplantaten im Vergleich zu unbehandelten Mäusen nicht, aber die kombinierte Modalität RIT (CMRIT) unter Verwendung von RIT und sechs Dosen Cilengitide (250 mg/Dosis) erhöht die Wirksamkeit der Behandlung, wobei die Heilungsrate für Mäuse, die nur RIT erhielten, von 15 auf 53 % ansteigt. CMRIT erhöht die Apoptose von Tumor- und Endothelzellen nach 5 Tagen signifikant und verringert die Tumorproliferation.
|
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | GLI1 pFAK / p-AKT |
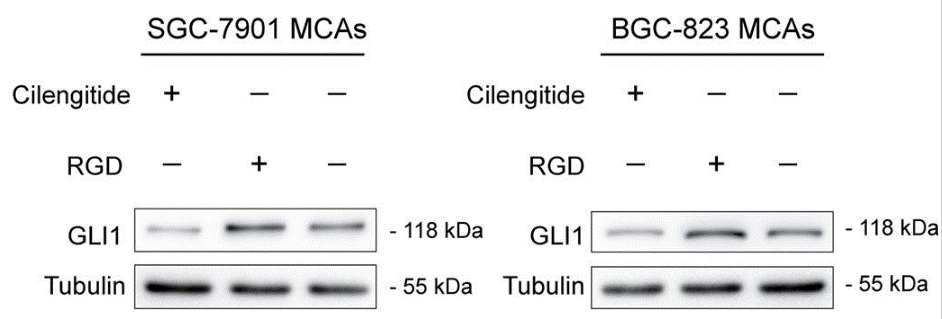
|
31366904 |
| Immunofluorescence | VE-cadherin / β3 integrin |
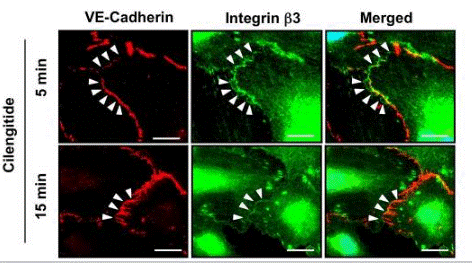
|
19212436 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell number |
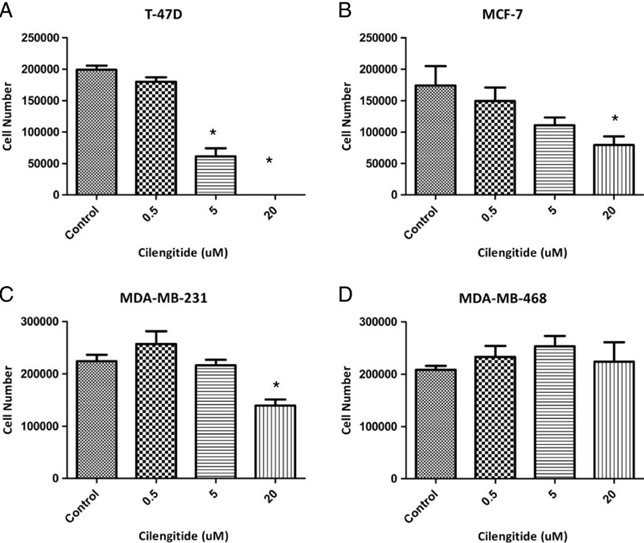
|
24153102 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01517776 | Terminated | Gliomas |
Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg|Merck KGaA Darmstadt Germany |
January 2012 | Phase 2 |
| NCT01118676 | Completed | Locally Advanced Non Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) |
Institut Claudius Regaud|Merck KGaA Darmstadt Germany |
March 2010 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
The recommended vehicle for it is 30% propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W at 30mg/ml. Can you let me know if this is a suspension or clear solution?
Antwort:
S7077 can be dissolved in 30% propylene glycol/5% Tween 80/65% D5W at 10 mg/ml as a clear solution.
Frage 2:
Is it a TFA salt?
Antwort:
S7077 is actually a TFA salt, and the ratio between it and TFA is 1:1.
