nur für Forschungszwecke
DMOG (Dimethyloxallyl Glycine) HIF-PH Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S7483
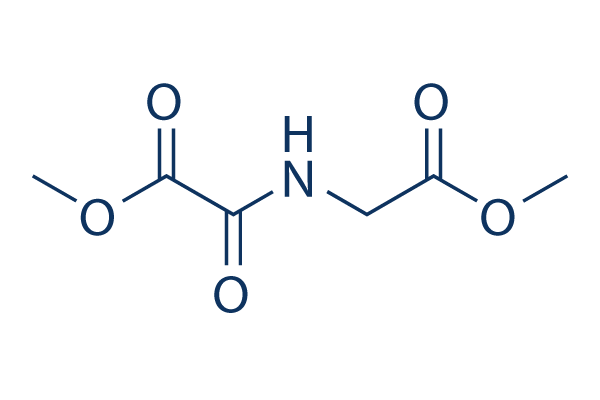
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 175.14
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | Dehydrogenase HSP Transferase P450 (e.g. CYP17) PDE phosphatase PPAR Vitamin Carbohydrate Metabolism Mitochondrial Metabolism |
|---|---|
| Weitere Hydroxylase Inhibitoren | Ro 61-8048 Meldonium 4-Chloro-DL-phenylalanine Nepicastat (SYN-117) HCl 2-Thiouracil (R)-Nepicastat HCl H-Tyr(3-I)-OH |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| human SR cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SR cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=4.57946 μM | SANGER | |||
| human LB996-RCC cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LB996-RCC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=5.6877 μM | SANGER | |||
| human LOUCY cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LOUCY cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=10.3493 μM | SANGER | |||
| human KS-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KS-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=11.2557 μM | SANGER | |||
| human U-698-M cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human U-698-M cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=13.3306 μM | SANGER | |||
| human A3-KAW cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A3-KAW cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=15.8174 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BL-70 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BL-70 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=15.9423 μM | SANGER | |||
| human DMS-273 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DMS-273 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=15.965 μM | SANGER | |||
| human CAL-39 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-39 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=19.3277 μM | SANGER | |||
| human KYSE-410 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-410 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=20.8197 μM | SANGER | |||
| human YT cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human YT cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.3984 μM | SANGER | |||
| human LC-2-ad cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LC-2-ad cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=24.5573 μM | SANGER | |||
| human COR-L105 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human COR-L105 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=26.4436 μM | SANGER | |||
| human CAL-12T cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-12T cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=26.5502 μM | SANGER | |||
| human KU812 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KU812 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=28.4579 μM | SANGER | |||
| human OPM-2 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human OPM-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=28.8227 μM | SANGER | |||
| human SW982 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW982 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=33.7007 μM | SANGER | |||
| human HH cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HH cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=34.0235 μM | SANGER | |||
| human RS4-11 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RS4-11 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=34.1806 μM | SANGER | |||
| human BEN cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BEN cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=36.8187 μM | SANGER | |||
| human CCRF-CEM cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CCRF-CEM cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.7729 μM | SANGER | |||
| human EW-13 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human EW-13 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=39.0481 μM | SANGER | |||
| human NCI-H2228 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H2228 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=42.818 μM | SANGER | |||
| human KE-37 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KE-37 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=43.2915 μM | SANGER | |||
| human A4-Fuk cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A4-Fuk cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=45.0364 μM | SANGER | |||
| human MZ1-PC cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MZ1-PC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=45.9888 μM | SANGER | |||
| human MLMA cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MLMA cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=46.3292 μM | SANGER | |||
| human EB-3 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human EB-3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=49.5792 μM | SANGER | |||
| human 293T cells | Function assay | 2.5 mM | Inhibition of JMJD2-mediated H3K36 demethylation in human 293T cells at 2.5 mM | 19359167 | ||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 175.14 | Formel | C6H9NO5 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | 3 years -20°C powder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 89464-63-1 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen | Lösungen sind instabil. Frisch zubereiten oder kleine, vorverpackte Größen kaufen. Nach Erhalt umpacken. | |
| Synonyme | Dimethyloxalylglycine | Smiles | COC(=O)CNC(=O)C(=O)OC | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 35 mg/mL
(199.84 mM)
Water : 35 mg/mL Ethanol : 35 mg/mL |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
HIF prolyl hydroxylase
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
DMOG zeigt im mikrosomalen System nur eine schwache Aktivität, unterdrückt aber effizient die Hydroxyprolin-Synthese in intakten Zellen. Diese Verbindung reduziert die FGF-2-induzierte Proliferation und Cyclin-A-Expression durch Hemmung der Prolylhydroxylase-Aktivität in HPASMC. |
| In vivo |
DMOG hemmt die endogene HIF-Inaktivierung und induziert die Angiogenese in ischämischen Skelettmuskeln von Mäusen. Die Hochregulierung von Hypoxie-induzierbarem Faktor-1α durch diese Verbindung verstärkt die kardioprotektiven Effekte des ischämischen Postconditionings bei hyperlipidämischen Ratten. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
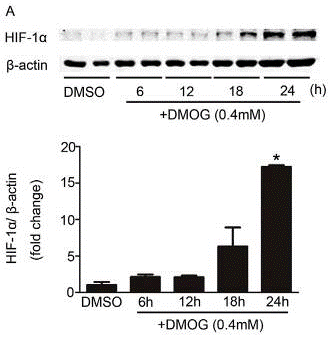
| Western blot | HIF-1α p-CHK1 / CHK1 / p-p53 / p53 / p-CHK2 / CHK2 / p-ATM / ATM WNT11 / HIF-2α |
|
29555474 |
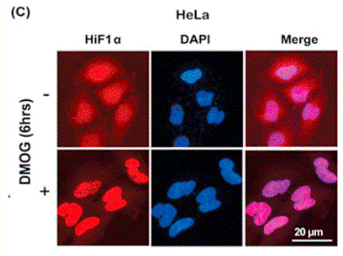
| Immunofluorescence | HIF1α |
|
28955984 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
