nur für Forschungszwecke
Monastrol Kinesin Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S8439
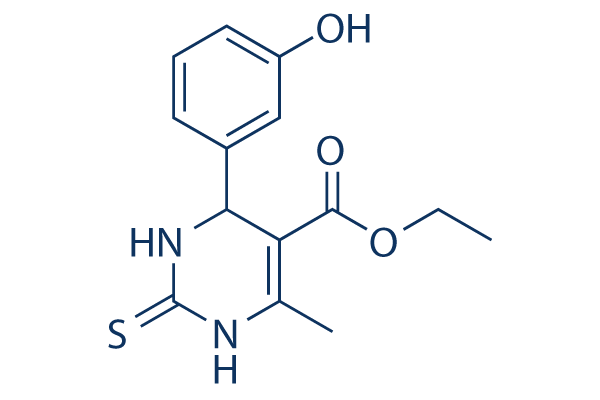
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 292.35
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | Akt Wnt/beta-catenin PKC HSP ROCK Microtubule Associated Integrin Bcr-Abl Actin FAK |
|---|---|
| Weitere Kinesin Inhibitoren | GSK923295 Ispinesib (SB-715992) SB743921 HCl ARQ 621 K 858 BTB-1 VLS-1488(KIF18A-IN-6 ) H-Cys(Trt)-OH Filanesib hydrochloride GW406108X |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HeLa | Function assay | 12 hrs | Inhibition of Eg5 ATPase activity expressed in HeLa cells after 12 hrs, IC50=6.1μM | 17587586 | ||
| HCT116 | Cell cycle assay | Effect on cell cycle progression in human HCT116 cells assessed as mitotic arrest measured by doubling DNA content by fluorescence microscopy, EC50=1.2μM | 18793847 | |||
| HCT116 | Cell cycle assay | Effect on cell cycle progression in human HCT116 cells assessed as increase in phospho-histone H3 by fluorescence microscopy, EC50=1.5μM | 18793847 | |||
| KBV1/KB3-1 | Function assay | Drug resistant ratio of EC50 for human KBV1 cells overexpressing MDR1 to EC50 for KB3-1 cells, EC50=0.0012μM | 20597485 | |||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT116 cells after 72 hrs by Alamar blue assay, EC50=24.155μM | 20597485 | ||
| hTERT-HME1 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human hTERT-HME1 cells after 72 hrs by Alamar blue assay, EC50=45.082μM | 20597485 | ||
| KBV1 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human KBV1 cells overexpressing MDR1 after 72 hrs by Alamar blue assay in presence of zosuquidar, EC50=45.394μM | 20597485 | ||
| HL-60(TB) | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human HL-60(TB) cells, GI50=25.1μM | 21855351 | |||
| M14 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human M14 cells, GI50=25.1μM | 21855351 | |||
| CCRF-CEM | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human CCRF-CEM cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| K562 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human K562 cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| MOLT4 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human MOLT4 cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| SR | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human SR cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| NCI-H522 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human NCI-H522 cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| COLO205 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human COLO205 cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| HCT116 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human HCT116 cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| KM12 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human KM12 cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| SF295 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human SF295 cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| U251 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human U251 cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| SK-MEL-2 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human SK-MEL-2 cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| RPMI8266 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human RPMI8266 cells, GI50=31.6μM | 21855351 | |||
| NCI-H322M | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human NCI-H322M cells, GI50=39.8μM | 21855351 | |||
| HCC2998 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human HCC2998 cells, GI50=39.8μM | 21855351 | |||
| HCT15 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human HCT15 cells, GI50=39.8μM | 21855351 | |||
| SW620 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human SW620 cells, GI50=39.8μM | 21855351 | |||
| SNB75 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human SNB75 cells, GI50=39.8μM | 21855351 | |||
| SK-MEL-5 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human SK-MEL-5 cells, GI50=39.8μM | 21855351 | |||
| UACC62 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human UACC62 cells, GI50=39.8μM | 21855351 | |||
| SN12C | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of human SN12C cells, GI50=39.8μM | 21855351 | |||
| HL-60(TB) | Growth inhibition assay | 24 hrs | Growth inhibition of human HL-60(TB) cells incubated for 24 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.147μM | 28667871 | ||
| MOLT4 | Growth inhibition assay | 24 hrs | Growth inhibition of human MOLT4 cells incubated for 24 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.215μM | 28667871 | ||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| McCoy | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against mouse McCoy cells assessed as decrease in cell viability after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=26.8μM | 29908443 | ||
| MM1S | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human MM1S cells incubated for 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=8.7μM | ChEMBL | ||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT116 cells incubated for 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=9μM | ChEMBL | ||
| C6 | Antiproliferative assay | 100 uM | 24 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against rat C6 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability at 100 uM after 24 hrs by MTS assay relative to control | ChEMBL | |
| C6 | Cell cycle assay | 100 uM | 24 hrs | Cell cycle arrest in rat C6 cells assessed as accumulation at G2/M phase at 100 uM after 24 hrs by propidium iodide staining based flow cytometry | ChEMBL | |
| U138MG | Apoptosis assay | 200 uM | 48 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in human U138MG cells at 200 uM after 48 hrs by Annexin V/propidium iodide staining based flow cytometry | ChEMBL | |
| U138MG | Necrosis assay | 200 uM | 48 hrs | Induction of necrosis in human U138MG cells at 200 uM after 48 hrs by Annexin V/propidium iodide staining based flow cytometry | ChEMBL | |
| C6 | Apoptosis assay | 100 uM | 48 hrs | Induction of apoptosis in rat C6 cells at 100 uM after 48 hrs by Annexin V/propidium iodide staining based flow cytometry | ChEMBL | |
| U138MG | Function assay | 200 uM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of EG5 in human U138MG cells assessed as monopolar spindle formation at 200 uM after 24 hrs by Hoechst staining based immunofluorescence microscopic method | ChEMBL | |
| C6 | Function assay | 100 uM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of EG5 in rat C6 cells assessed as monopolar spindle formation at 100 uM after 24 hrs by Hoechst staining based immunofluorescence microscopic method | ChEMBL | |
| C6 | Antiproliferative assay | 5 to 50 uM | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against rat C6 cells at 5 to 50 uM after 48 hrs by Neubauer chamber method | ChEMBL | |
| MCF7 | Antiproliferative assay | 25 uM | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human MCF7 cells at 25 uM after 48 hrs by sulforhodamine B assay | ChEMBL | |
| NCI/ADR-RES | Antiproliferative assay | 25 uM | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human NCI/ADR-RES cells at 25 uM after 48 hrs by sulforhodamine B assay | ChEMBL | |
| 786-0 | Antiproliferative assay | 25 uM | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human 786-0 cells at 25 uM after 48 hrs by sulforhodamine B assay | ChEMBL | |
| HT-29 | Antiproliferative assay | 25 uM | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HT-29 cells at 25 uM after 48 hrs by sulforhodamine B assay | ChEMBL | |
| UACC62 | Antiproliferative assay | 25 uM | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human UACC62 cells at 25 uM after 48 hrs by sulforhodamine B assay | ChEMBL | |
| PC3 | Antiproliferative assay | 25 uM | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human PC3 cells at 25 uM after 48 hrs by sulforhodamine B assay | ChEMBL | |
| OVCAR3 | Antiproliferative assay | 25 uM | 48 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human OVCAR3 cells at 25 uM after 48 hrs by sulforhodamine B assay | ChEMBL | |
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 292.35 | Formel | C14H16N2O3S |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | 3 years -20°C(in the dark) powder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 329689-23-8 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | (±)-Monastrol | Smiles | CCOC(=O)C1=C(NC(=S)NC1C2=CC(=CC=C2)O)C | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 58 mg/mL
(198.39 mM)
Ethanol : 58 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
KIF11(Eg5)
(Cell-based assay) 14 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Monastrol hemmt weder den Fortschritt durch die S- und G2-Phasen des Zellzyklus noch die Zentrosomenverdopplung. Der durch diese Verbindung verursachte mitotische Arrest ist ebenfalls schnell reversibel. Es hemmt auch die Bildung bipolarer Spindeln in Xenopus-Eiextrakten. Diese Chemikalie arretiert Zellen in der Mitose mit monoastralen Spindeln, die aus einer radialen Anordnung von Mikrotubuli bestehen, umgeben von einem Chromosomenring, während sie Mikrotubuli in Interphasezellen oder die Mikrotubulipolymerisation in vitro nicht beeinflusst. Die Exposition kultivierter sympathischer Neuronen gegenüber dieser Verbindung für einige Stunden erhöht sowohl die Anzahl als auch die Wachstumsrate der Axone. Mit zusätzlicher Zeit sind die Gesamtlängen der Axone nicht von Kontrollen zu unterscheiden. Sensorische Neuronen zeigen einen ähnlichen kurzfristigen Anstieg der axonalen Wachstumsrate. Eine längere Exposition führt jedoch zu kürzeren Axonen, was darauf hindeutet, dass sensorische Neuronen empfindlicher auf toxische Wirkungen des Medikaments reagieren könnten. Dennoch ist die allgemeine Gesundheit der Kulturen immer noch weitaus robuster als Kulturen, die mit Taxol behandelt wurden, einem Medikament, das häufig zur Krebsbekämpfung eingesetzt wird. In HeLa-Zellen aktiviert diese Verbindung den Spindel-Checkpoint, was zu mitotischem Arrest und Apoptose führt. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
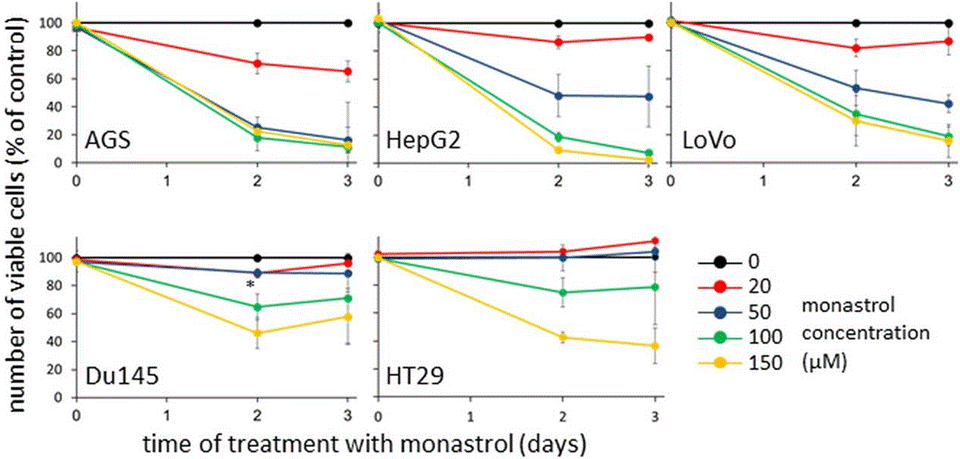
|
26035434 |
| Western blot | Cyclin B / Survivin |
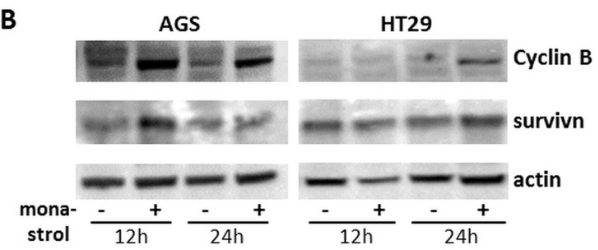
|
26035434 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
