nur für Forschungszwecke
KU-0063794 mTOR Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1226
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 465.54
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | PI3K Akt GSK-3 ATM/ATR DNA-PK AMPK PDPK1 PTEN PP2A PDK |
|---|---|
| Weitere mTOR Inhibitoren | Torin 1 Torin 2 AZD8055 Ridaforolimus (Deforolimus, MK-8669) Sapanisertib (MLN0128, INK-128) Torkinib (PP242) MHY1485 Vistusertib (AZD2014) OSI-027 WYE-354 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HepG2 | Cell Viability Assay | 0.1–50 μM | 72 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 26278819 | |
| HepG2 | Colony Formation Assay | 1–50 μM | 10 d | decreases the number of viable HepG2 colonies significantly | 26278819 | |
| HepG2 | Apoptosis Assay | 0.1–50 μM | 48 h | induces apoptosis in a dose dependent manner | 26278819 | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 5/10 μM | 24 h | dramatically inhibits phosphorylation of AKT at Ser-473 | 26278819 | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 5/10 μM | 24 h | downregulates the levels HIF1α and cyclin D1 | 26278819 | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 0.1–50 μM | 24 h | induces p62 downregulation, Beclin-1 expression and LC3B-I to LC3B-II conversion in a dose dependent manner | 26278819 | |
| HepG3 | Function Assay | 0.1–50 μM | 48 h | induces cell autophagy in a dose dependent manner | 26278819 | |
| AGS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.0 ± 2.91 μM | 24597478 | |||
| HGC27 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.0 ± 4.82 μM | 24597478 | |||
| MKN45 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=0.82 ± 0.01 μM | 24597478 | |||
| NUGC4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2.93 ± 0.31 μM | 24597478 | |||
| PC9 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=10.15±0.62 nM | 23874880 | ||
| PC9GR | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=6.21±1.30 nM | 23874880 | ||
| H1650 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=7.61±0.62 nM | 23874880 | ||
| H1975 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=11.15±0.93 nM | 23874880 | ||
| PC9 | Function Assay | 10.15 nM | 72 h | inhibits mTOR phosphorylation status | 23874880 | |
| PC9GR | Function Assay | 6.21 nM | 72 h | inhibits mTOR phosphorylation status | 23874880 | |
| H1650 | Function Assay | 7.61 nM | 72 h | inhibits mTOR phosphorylation status | 23874880 | |
| H1975 | Function Assay | 11.15 nM | 72 h | inhibits mTOR phosphorylation status | 23874880 | |
| PC9 | Function Assay | 10.15 nM | 72 h | inhibits phosphorylation of p70S6K | 23874880 | |
| PC9GR | Function Assay | 6.21 nM | 72 h | inhibits phosphorylation of p70S6K | 23874880 | |
| H1650 | Function Assay | 7.61 nM | 72 h | inhibits phosphorylation of p70S6K | 23874880 | |
| H1975 | Function Assay | 11.15 nM | 72 h | inhibits phosphorylation of p70S6K | 23874880 | |
| LNCaP | Cell Viability Assay | 0-10 μM | 24 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 23840605 | |
| PC-3 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-10 μM | 24 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 23840605 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-10 μM | 24 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 23840605 | |
| LNCaP | Function Assay | 200–800 nM | 24 h | decreases the phosphorylation level of p70S6K in a dose dependent manner | 23840605 | |
| PC-3 | Function Assay | 200–800 nM | 24 h | decreases the phosphorylation level of p70S6K in a dose dependent manner | 23840605 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Function Assay | 200–800 nM | 24 h | decreases the phosphorylation level of p70S6K in a dose dependent manner | 23840605 | |
| Caki-1 | Function Assay | 100-2000 nM | 10-180 min | DMSO | inhibits both mTORC1 and mTORC2 as indicated by the decrease in phosphorylation of downstream effectors | 23349989 |
| 786-O | Function Assay | 100-2000 nM | 10-180 min | DMSO | inhibits both mTORC1 and mTORC2 as indicated by the decrease in phosphorylation of downstream effectors | 23349989 |
| Caki-1 | Cell Viability Assay | 300-4000 nM | 24-96 h | DMSO | suppresses the cell viability in both time and dose dependent manner | 23349989 |
| 786-O | Cell Viability Assay | 300-4000 nM | 24-96 h | DMSO | suppresses the cell viability in both time and dose dependent manner | 23349989 |
| Caki-1 | Function Assay | 2 µM | 72 h | DMSO | induces G1 cell cycle arrest and autophagy | 23349989 |
| 786-O | Function Assay | 2 µM | 72 h | DMSO | induces G1 cell cycle arrest and autophagy | 23349989 |
| HEK293 | Function assay | 2 hrs | Inhibition of recombinant FLAG-tagged mTOR expressed in HEK293 cells using biotinylated p70S6K substrate after 2 hrs by alphascreen competition assay, IC50=0.003μM | 19762236 | ||
| HBCx-10 | Function assay | 5 mg/kg | Potentiation of irinotecan-induced tumor regression against human HBCx-10 cells xenografted in immunocompromised mouse at 5 mg/kg, po qd administered on days 1 to 3 of weekly cycle | 19762236 | ||
| U87MG | Function assay | 2 hrs | Inhibition of mTORC1 in human U87MG cells assessed as phosphorylated S6 ribosomal protein (Ser235/236) level after 2 hrs by Western blotting, IC50=0.1μM | 19762236 | ||
| U87MG | Function assay | 2 hrs | Inhibition of mTORC2 in human U87MG cells assessed as phosphorylated AKT (Ser473) level after 2 hrs by Western blotting, IC50=0.15μM | 19762236 | ||
| T47D | Antiproliferative assay | 120 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human T47D cells after 120 hrs by SRB assay, GI50=0.35μM | 19762236 | ||
| HEK293 | Function assay | Inhibition of recombinant FLAG-tagged mTOR (1362 to 2549) (unknown origin) expressed in HEK293 cells, IC50=0.0025μM | 23375793 | |||
| MDA-MB-468 | Function assay | 2 hrs | Inhibition of mTORC2 in human MDA-MB-468 cells assessed as reduction of AKT phosphorylation at Ser473 after 2 hrs, IC50=0.24μM | 23375793 | ||
| MDA-MB-468 | Function assay | 2 hrs | Inhibition of mTORC1 in human MDA-MB-468 cells assessed as reduction of pS6 phosphorylation at Ser235/236 after 2 hrs, IC50=0.66μM | 23375793 | ||
| HEK293 | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of mTORC1 in HEK293 cells using GST-tagged S6K1 or Akt1 as substrate after 30 mins by immunoblotting assay, IC50=0.01μM | 29211480 | ||
| PC3 | Function assay | 100 mg/kg | Inhibition of Akt phosphorylation at Ser473 in PTEN-deficient human PC3 cells xenograft mouse model at 100 mg/kg, po single dose measured up to 8 hrs | 29211480 | ||
| PC3 | Antitumor assay | 30 mg/kg | Antitumor activity against human PC3 cells xenograft mouse model assessed as inhibition of tumor growth at 30 mg/kg, po bid in presence of 1-aminobenzotriazole | 29211480 | ||
| PC3 | Antitumor assay | 60 mg/kg | Antitumor activity against human PC3 cells xenograft mouse model assessed as inhibition of tumor growth at 60 mg/kg, po bid in presence of 1-aminobenzotriazole | 29211480 | ||
| HEK293 | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of mTORC2 in HEK293 cells using GST-tagged S6K1 or Akt1 as substrate after 30 mins by immunoblotting assay, IC50=0.01μM | 29211480 | ||
| SW620 | Function assay | 20 mg/kg | Potentiation of irinotecan-induced tumor regression against human SW620 cells xenografted in immunocompromised mouse at 20 mg/kg, po qd administered on days 2 to 4 of weekly cycle | 29211480 | ||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 465.54 | Formel | C25H31N5O4 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 938440-64-3 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | CC1CN(CC(O1)C)C2=NC3=C(C=CC(=N3)C4=CC(=C(C=C4)OC)CO)C(=N2)N5CCOCC5 | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 16 mg/mL
(34.36 mM)
Ethanol : 5 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
mTORC1
(Cell-free assay) ~10 nM
mTORC2
(Cell-free assay) ~10 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Verglichen mit dem mTOR-Inhibitor PP242 zeigt KU-0063794 eine höhere Spezifität für mTOR, da es inaktiv gegenüber PI3Ks oder 76 anderen Kinasen ist. In HEK-293-Zellen ist diese Verbindung bei 30 nM ausreichend, um die S6K1-Aktivität durch Blockierung der Phosphorylierung des hydrophoben Motivs (Thr389) und anschließend der Phosphorylierung des T-Loop-Rests (Thr229) schnell zu unterbinden. Bei IGF1-Stimulation von Serum-gehungerten HEK-293-Zellen sind 300 nM dieser Verbindung erforderlich, um die S6K1-Aktivität um ~90% zu hemmen. Diese Chemikalie bei 100-300 nM hemmt auch vollständig die Aminosäure-induzierte Phosphorylierung von S6K1 und S6-Protein. Ähnlich wie S6K1 hemmt sie die Phosphorylierung von mTORC1 an Ser2448 und mTORC2 an Ser2481 dosis- und zeitabhängig. In Anwesenheit von Serum oder nach IGF1-Stimulation induziert diese Verbindung eine dosisabhängige Hemmung der Aktivität und Phosphorylierung von Akt an Ser473 und unerwarteter Thr308 sowie der Phosphorylierung der Akt-Substrate PRAS40 an Thr246, GSK3α/GSK3β an Ser21/Ser9 und Foxo-1/3a an Thr24/Thr32. Diese Verbindung, aber nicht Rapamycin, hemmt die SGK1-Aktivität und die Ser422-Phosphorylierung sowie ihr physiologisches Substrat NDGR1 dosisabhängig, im gleichen Maße wie die S6K1- und Akt-Phosphorylierung, wohingegen sie die Phorbolester-induzierte ERK- oder RSK-Phosphorylierung und RSK-Aktivierung nicht hemmt. Verglichen mit Rapamycin zeigt diese Chemikalie eine signifikantere Potenz, die vollständige Dephosphorylierung von 4E-BP1 an Thr37, Thr46 und Ser65 zu induzieren. Sie hemmt das Zellwachstum sowohl von Wildtyp- als auch von mLST8-defizienten MEFs und induziert einen G1-Zellzyklusarrest, signifikanter als Rapamycin. |
| Kinase-Assay |
mTOR-Komplex-Kinase-Assays
|
|
HEK-293-Zellen werden frisch in Hepes-Lysepuffer lysiert. Lysat (1-4 mg) wird durch Inkubation mit 5-20 μL Protein G-Sepharose, konjugiert an präimmunes IgG, vorklärt. Die Lysatextrakte werden dann mit 5-20 μL Protein G-Sepharose, konjugiert an 5-20 μg entweder Anti-Rictor- oder Anti-Raptor-Antikörper, oder präimmunes IgG, inkubiert. Alle Antikörper sind kovalent an Protein G-Sepharose konjugiert. Immunpräzipitationen werden 1 Stunde lang bei 4 °C auf einer Vibrationsplattform durchgeführt. Die Immunpräzipitate werden viermal mit Hepes-Lysepuffer gewaschen, gefolgt von zwei Waschschritten mit Hepes-Kinasepuffer. Für Raptor-Immunpräzipitate, die zur Phosphorylierung von S6K1 verwendet werden, enthält der Puffer für die ersten beiden Waschschritte 0,5 M NaCl, um eine optimale Kinaseaktivität zu gewährleisten. GST-Akt1 wird aus serumdeprivierten HEK-293-Zellen isoliert, die mit PI-103 (1 μM für 1 Stunde) inkubiert wurden. GST-S6K1 wird aus serumdeprivierten HEK-293-Zellen gereinigt, die mit Rapamycin (0,1 μM für 1 Stunde) inkubiert wurden. mTOR-Reaktionen werden durch Zugabe von 0,1 mM ATP und 10 mM MgCl2 in Gegenwart verschiedener Konzentrationen von KU-0063794 und GST-Akt1 (0,5 μg) oder GST-S6K1 (0,5 μg) initiiert. Die Reaktionen werden 30 Minuten lang bei 30 °C auf einer Vibrationsplattform durchgeführt und durch Zugabe von SDS-Probenpuffer gestoppt. Reaktionsmischungen werden dann durch einen 0,22-μm-Porenfilter von Spin-X filtriert und Proben werden der Elektrophorese und Immunoblot-Analyse mit den angegebenen Antikörpern unterzogen.
|
|
| In vivo |
Ku0063794 hemmt das Tumorwachstum und die mTOR-Signalübertragung in einem präklinischen Nierenzellkarzinommodell. Diese Verbindung war jedoch in der Tierstudie nicht wirksamer. Eine mögliche Erklärung für das Fehlen einer größeren Aktivität in vivo für diese Chemikalie. |
Literatur |
|
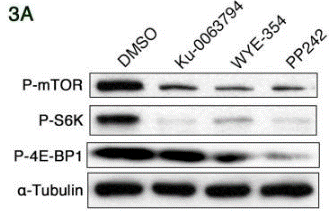
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-mTOR p-S6K / S6K / p-4E-BP1 / E7 / E6 / p53 |
|
24262658 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
