nur für Forschungszwecke
NSC 23766 Trihydrochloride Rac GTPase-Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S8031
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 530.97
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | CDK HSP PD-1/PD-L1 ROCK Wee1 DNA/RNA Synthesis Microtubule Associated Ras KRas Aurora Kinase |
|---|---|
| Weitere Rho Inhibitoren | EHop-016 CCG-1423 ML141 (CID-2950007) EHT 1864 2HCl ZCL278 MBQ-167 CCG-203971 Rhosin hydrochloride CID44216842 1A-116 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RA4 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24 h | inhibits Matrigel invasion | 17622308 | |
| RA3 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24 h | inhibits Matrigel invasion | 17622308 | |
| RA2 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24 h | inhibits Matrigel invasion | 17622308 | |
| RA1 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24 h | inhibits Matrigel invasion | 17622308 | |
| RA-FLS (RA2) | Growth Inhibition Assay | 25/50 μM | 1-9 d | inhibits cell growth in both dose and time dependent manner | 17622308 | |
| IEC-6 | Function Assay | 120 µM | 4/6/8 h | prevents the increased activation of FAK at 6 and 8 h | 20448461 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | induces a dose-dependent decrease in phosphorylation of p65 subunit | 20515940 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 48 h | induces a dose-dependent decrease in phosphorylation of p65 subunit | 20515940 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 24 h | increases phosphorylation of JNK in a dose dependent manner | 20515940 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Function Assay | 50/100 μM | 24 h | increases phosphorylation of JNK in a dose dependent manner | 20515940 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 24 h | inhibits caspase-3 activation | 20515940 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Apoptosis Assay | 50/100 μM | 24 h | induces apoptosis | 20515940 | |
| T47D | Function Assay | 100 μM | 48 h | increases the cell number in G1 phase and decreases the cell number in S and G2-M phases | 20515940 | |
| MCF7 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 48 h | increases the cell number in G1 phase and decreases the cell number in S and G2-M phases | 20515940 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 48 h | increases the cell number in G1 phase and decreases the cell number in S and G2-M phases | 20515940 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 0-100 μM | 24 h | selectively inhibits Rac1 activation without interfering with the activity of the closely related small GTPase Cdc42 | 20515940 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Cytotoxicity Assay | 0-100 μM | 48 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 20515940 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Cytotoxicity Assay | 0-100 μM | 48 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 20515940 | |
| T47D | Cytotoxicity Assay | 0-100 μM | 48 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 20515940 | |
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity Assay | 0-100 μM | 48 h | decreases cell viability in a dose dependent manner | 20515940 | |
| SKBR3-pMKO.1 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24 h | inhibits Rac1 activation | 21943825 | |
| SKBR3 | Function Assay | 50 μM | 24 h | inhibits Rac1 activation | 21943825 | |
| NCI-H1703 | Function Assay | 0-500 μM | 24 h | diminishes basal NF-κB activity dose dependently | 22549160 | |
| NCI-H1703 | Function Assay | 100 μg/ml | 24 h | slows progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle | 22549160 | |
| NCI-H1703 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-500 μM | 24 h | inhibits cell growth in a dose dependent manner | 22549160 | |
| T98MG | Function Assay | 50 mM | 24 h | DMSO | enhances the antimigratory effect of erlotinib | 23832120 |
| A172MG | Function Assay | 50 mM | 24 h | DMSO | enhances the antimigratory effect of erlotinib | 23832120 |
| U87MG | Function Assay | 50 mM | 24 h | DMSO | enhances the antimigratory effect of erlotinib | 23832120 |
| PC40 | Cell Viability Assay | 50 mM | 144 h | DMSO | exhibits synergistic antiproliferative effects combined treatment with erlotinib | 23832120 |
| PC38 | Cell Viability Assay | 50 mM | 144 h | DMSO | exhibits synergistic antiproliferative effects combined treatment with erlotinib | 23832120 |
| T98MG | Cell Viability Assay | 50 mM | 144 h | DMSO | exhibits synergistic antiproliferative effects combined treatment with erlotinib | 23832120 |
| A172MG | Cell Viability Assay | 50 mM | 144 h | DMSO | exhibits synergistic antiproliferative effects combined treatment with erlotinib | 23832120 |
| U87MG | Cell Viability Assay | 50 mM | 144 h | DMSO | exhibits synergistic antiproliferative effects combined treatment with erlotinib | 23832120 |
| Ki-67+ CLL | Growth Inhibition Assay | 50 µM | 5 d | decreases the number of Ki-67+ CLL cells | 24501217 | |
| NIH3T3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100 μM | 24 h | has no significant impact on cell viability | 25037060 | |
| U2-OS | Function Assay | 100 μM | 24 h | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase | 25109327 |
| SW480 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 24 h | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase | 25109327 |
| A431 | Function Assay | 100 μM | 24 h | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest in the G1 phase | 25109327 |
| U2-OS | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100 μM | 24/48/72 h | inhibits cell growth in a time dependent manner | 25109327 | |
| SW480 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100 μM | 24/48/72 h | inhibits cell growth in a time dependent manner | 25109327 | |
| A431 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 100 μM | 24/48/72 h | inhibits cell growth in a time dependent manner | 25109327 | |
| RBMECs | Function Assay | 100 μM | 30 min | blockes 6Bnz-cAMP-mediated activation of Rac1 in EMAP-II-treated RBMECs | 26358039 | |
| human aortic smooth muscle cells | Function Assay | 50 uM | Inhibition of Rac1 binding to Pak1 in human aortic smooth muscle cells at 50 uM by SDS-PAGE based chemiluminescence | 19527032 | ||
| human aortic smooth muscle cells | Function Assay | 100 μM | Inhibition of Rac1 binding to Pak1 in human aortic smooth muscle cells at 100 uM by SDS-PAGE based chemiluminescence | 19527032 | ||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 530.97 | Formel | C24H35N7.3ClH |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 1177865-17-6 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | CCN(CC)CCCC(C)NC1=NC(=CC(=N1)NC2=CC3=C(C=C(N=C3C=C2)C)N)C.Cl.Cl.Cl | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 106 mg/mL
(199.63 mM)
Water : 106 mg/mL Ethanol : 5 mg/mL |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Rac GTPase
(Cell-free assay) 50 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
NSC23766 passt in eine Oberflächenfurche von Rac1, die als entscheidend für die GEF-Spezifikation bekannt ist. NSC23766 hemmt effektiv die Rac1-Bindung und -Aktivierung durch die Rac-spezifischen GEFs Trio oder Tiam1 dosisabhängig, ohne die eng verwandte Cdc42- oder RhoA-Bindung oder -Aktivierung durch ihre jeweiligen GEFs oder die Rac1-Interaktion mit BcrGAP oder dem Effektor PAK1 zu beeinträchtigen. NSC 23766 ist aktiv bei der Regulierung von Rac GTPase-Funktionen am Zytoskelett und vielen Zellfunktionen, einschließlich Cell Cycle, Zellwachstum, Adhäsion, Migration und Gentranskription. NSC 23766 (50 μM) blockiert potent Serum- oder Plättchen-Wachstumsfaktor-induzierte Rac1-Aktivierung und Lamellipodienbildung, ohne die Aktivität von endogenem Cdc42 oder RhoA in NIH 3T3-Zellen zu beeinflussen. NSC 23766 reduziert Trio- oder Tiam1-, aber nicht Vav-, Lbc-, Intersectin- oder konstitutiv aktive Rac1-Mutanten-stimuliertes NIH 3T3-Zellwachstum und unterdrückt Trio-, Tiam1- oder Ras-induzierte Zelltransformation. NSC23766 hemmt dosisabhängig die Proliferation von PC-3-Zellen und das Verankerungs-unabhängige Wachstum. 25 μM NSC23766 hemmt die Invasion von PC-3-Zellen durch Matrigel um 85 %. [1] 50 μM NSC 23766 hemmt die Thrombin-induzierte Aktivierung von Rac1 und Rac2 in menschlichen Blutplättchen sowie die Plättchenaggregation. NSC23766 verhindert die Aβ40- und Aβ42-Produktion in swAPP-HEK293-Zellen, ohne Notch und sAPPα zu beeinflussen. NSC23766 verhindert die γ-Sekretase-Aktivität in Zellen, wirkt aber nicht als direkter γ-Sekretase-Inhibitor. NSC23766 reduziert dosisabhängig die Spiegel von sezerniertem und intrazellulärem Aβ40 mit einer IC50 von 48,94 μM. 50 μM NSC 23766 hemmt die Freisetzung von Aβ42 um 57,97 %. NSC23766 reguliert die Expression der endothelialen Stickstoffmonoxid-Synthase und die endotheliale Funktion. 100 μM NSC23766 unterdrückt die eNOS-Promoteraktivität um 60 % in bovinen Aorten-ECs und um 30 % bis 35 % in bEND.3-Zellen. Die Hemmung von Rac1 mit NSC23766 destabilisiert die eNOS-mRNA und verkürzt ihre Halbwertszeit auf 17 Stunden. NSC23766 schwächt dosisabhängig die ACh-induzierte Relaxation von Aortenringen von Wildtyp-Mäusen ab. NSC23766 hemmt das Zellwachstum und induziert Apoptose. NSC23766 verringert die Lebensfähigkeit von MDA-MB-468- und MDA-MB-231-Zellen dosisabhängig mit einer IC50 von ~10 μM, was nicht mit dem Status von Östrogenrezeptor (ER), Progesteronrezeptor (PR), Her2 und p53-Mutation korreliert ist. NSC23766 hat wenig Einfluss auf das Überleben der normalen Brustepithelzellen MCF12A. Nach 24-stündiger Exposition gegenüber NSC 23766 zeigen MDA-MB-231-Zellen einen Anstieg von 41 % auf 65 % in der G1-Phase und eine gleichzeitige Abnahme in der S- und G2-M-Phase. 100 μM NSC23766 induziert einen sechsfacher Anstieg der apoptotischen MDA-MB-468. Die Hemmung von NSC23766 auf den Cell Cycle-Arrest oder die Apoptose in Brustkrebszellen wird durch die Herunterregulierung von Cyclin D1, Survivin und X-chromosomal-gebundenem Inhibitor der Proteinapoptose vermittelt. |
| Kinase-Assay |
Rho GTPase-Aktivitätstest
|
|
Zellen werden in der logarithmischen Phase in einer 10-cm-Schale gezüchtet und in einem Medium mit 0,5 % Serum oder wie anders angegeben 24 Stunden lang vor der Lyse in einem Puffer, der 20 mM Tris HCl (pH 7,6), 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 % Nonidet P-40, 10 % Glycerin und eine 1× Proteaseinhibitor-Mischung enthält, ausgehungert. Lysate werden geklärt, die Proteinkonzentrationen werden normalisiert, und das GTP-gebundene Rac1 in den Lysaten wird durch einen Effektor-Domänen-Pull-down-Assay gemessen. Für den His6-PAK1 PBD Pull-down-Assay werden Zelllysate 30 Minuten lang mit Ni2+-Agarose-immobilisiertem His6-PAK1 PBD-Domäne (~1 μg jeweils), gereinigt aus E. coli, inkubiert. Die Ni2+-Agarose-Co-Präzipitate werden zweimal im Waschpuffer gewaschen und mittels Immunoblotting mit einem Anti-Rac1-monoklonalen Antikörper analysiert.
|
|
| In vivo |
NSC23766 induziert die Mobilisierung hämatopoetischer Stammzellen/Vorläuferzellen. Die intraperitoneale Verabreichung von NSC23766 (2,5 mg/kg) an den „schlecht mobilisierenden“ C57Bl/6-Mausstamm führt zu einer zweifachen Zunahme zirkulierender hämatopoetischer Stammzellen/Vorläuferzellen 6 Stunden nach der Injektion. NSC23766 lindert Lipopolysaccharid-induzierte akute Lungenverletzungen bei Mäusen. Die Behandlung mit NSC23766 bei 1 oder 3 mg/kg reduziert nicht nur die Infiltration entzündlicher Zellen und MPO-Aktivitäten, sondern hemmt auch die mRNA-Expression proinflammatorischer Mediatoren, Tumornekrosefaktor-α und Interleukin-1β. NSC23766 reduziert auch die Akkumulation von Evans Blue und Albumin in LPS-belasteten Lungen. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | pCREB / CREB OCT4 / SOX2 / Nanog active Rac1 / Rac1 |
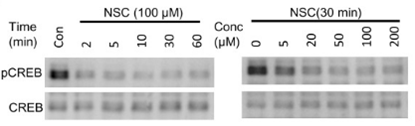
|
25319697 |
| Immunofluorescence | IP3K-A / F-actin BART / Rac1 |
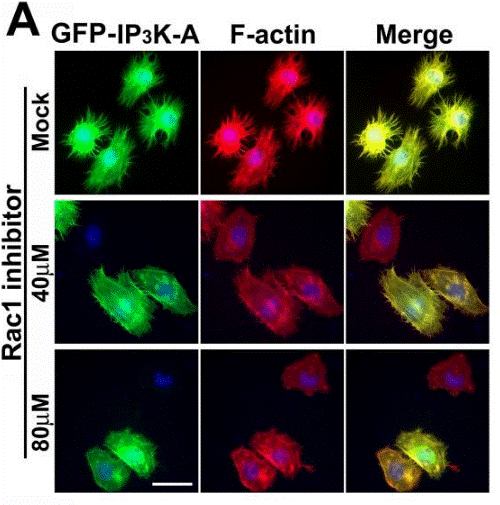
|
19890013 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
