nur für Forschungszwecke
Amiloride HCl Sodium Channel Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1811
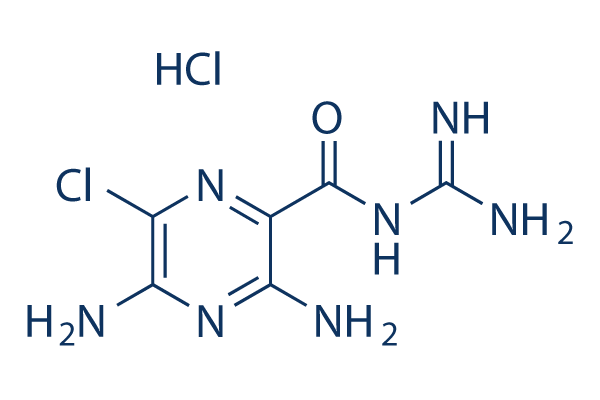
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 266.09
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | CFTR CRM1 CD markers AChR Calcium Channel Potassium Channel GABA Receptor TRP Channel ATPase GluR |
|---|---|
| Weitere Sodium Channel Inhibitoren | Camostat Mesilate A-803467 cariporide Tolperisone HCl Vinpocetine Veratramine Bulleyaconi cine A Ambroxol HCl Benzocaine Nefopam HCl |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D17 | Cell viability assay | 72 h | IC50=110.66 μM | 30556178 | ||
| Abrams | Cell viability assay | 72 h | IC50=121.61 μM | 30556178 | ||
| Dharma | Cell viability assay | 72 h | IC50=148.37 μM | 30556178 | ||
| YD-10B | Function assay | 4 mM | 4 h | amiloride strongly blocked the meridianin C‐induced accumulation of vacuoles in YD-10B cells | 30246484 | |
| NS20Y | Function assay | Amiloride dose dependently inhibits the ASIC current in NS20Y cells with an IC50 of 11.04 μM | 27342076 | |||
| COS-7 | Function assay | Binding affinity for HA-tagged mutant human Adenosine A2A receptor (H250N) using [3H]-CGS-21,680 as radioligand expressed in COS-7 cells, Ki=3.28μM | 9258366 | |||
| COS-7 | Function assay | Binding affinity for HA-tagged mutant human Adenosine A2A receptor (V84L), using [3H]CGS-21680 as radioligand expressed in COS-7 cells, Ki=11.6μM | 9258366 | |||
| COS-7 | Function assay | Binding affinity for HA-tagged wild type human Adenosine A2A receptor (WT) using [3H]CGS-21680 as radioligand expressed in COS-7 cells, Ki=12μM | 9258366 | |||
| MDCK | Function assay | TP_TRANSPORTER: inhibition of TEA uptake in OCT2-expressing MDCK cells, Ki=4.7μM | 11758759 | |||
| MDCK | Function assay | TP_TRANSPORTER: inhibition of TEA uptake in OCT1-expressing MDCK cells, Ki=6.9μM | 11758759 | |||
| AP1 | Function assay | Inhibition of Amphiuma tridactylum NHE1 mutant containing TM10-12 domain of Pleuronectes americanus expressed in chinese hamster AP1 cells assessed as intracellular pHi recovery by ammonium chloride prepulse protocol, IC50=38μM | 17493937 | |||
| AP1 | Function assay | Inhibition of Pleuronectes americanus NHE1 C-terminal mutant containing TM7 domain of Amphiuma tridactylum expressed in chinese hamster AP1 cells assessed as intracellular pHi recovery by ammonium chloride prepulse protocol | 17493937 | |||
| AP1 | Function assay | Inhibition of Pleuronectes americanus NHE1 TM4 mutant containing TFFLF sequence of Amphiuma tridactylum expressed in chinese hamster AP1 cells assessed as intracellular pHi recovery by ammonium chloride prepulse protocol | 17493937 | |||
| HBE | Function assay | Inhibition of human ENaC in HBE cells by short-circuit current technique, IC50=0.22μM | 22197144 | |||
| FRT | Function assay | Inhibition of guinea pig ENaCbeta1/gamma1 expressed in FRT cells by short-circuit current technique, IC50=0.54μM | 22197144 | |||
| HBE | Function assay | Blockade of human ENaC expressed in HBE cells by short-circuit current assay, IC50=0.22μM | 22425452 | |||
| FRT | Function assay | Blockade of guinea pig ENaC expressed in FRT cells by short-circuit current assay, IC50=0.54μM | 22425452 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| AP1 | Function assay | Inhibition of rat NHE1 expressed in chinese hamster AP1 cells assessed as inhibition of acid-induced 22Na+ influx by liquid scintillation spectroscopy, Ki=1μM | ChEMBL | |||
| AP1 | Function assay | Inhibition of full length human C-terminal HA-tagged human NHE5 expressed in chinese hamster AP1 cells assessed as inhibition of acid-induced 22NA+ influx by liquid scintillation spectroscopy, Ki=21μM | ChEMBL | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 266.09 | Formel | C6H8ClN7O.HCl |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 2016-88-8 | -- | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | MK-870 HCl | Smiles | C1(=C(N=C(C(=N1)Cl)N)N)C(=O)N=C(N)N.Cl | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 53 mg/mL
(199.18 mM)
Water : 6 mg/mL Ethanol : 5 mg/mL |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Sodium channel
T-type calcium channel
uPA
7 μM(Ki)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Amiloride ist ein relativ selektiver Inhibitor des epithelialen Natriumkanals (ENaC) mit einer IC50 (die Konzentration, die erforderlich ist, um eine 50%ige Hemmung eines Ionenkanals zu erreichen) im Konzentrationsbereich von 0,1 bis 0,5 μM. Amiloride ist ein relativ schlechter Inhibitor des Na+/H+-Austauschers (NHE) mit einer IC50 von nur 3 μM bei niedriger externer [Na+], aber bis zu 1 mM bei hoher [Na+]. Amiloride ist ein noch schwächerer Inhibitor des Na+/Ca2+-Austauschers (NCX) mit einer IC50 von 1 mM. Amiloride (1 μM) und submikromolare Dosen von Benzamil (30 nM), Dosen, von denen bekannt ist, dass sie den ENaC hemmen, hemmen die myogene Vasokonstriktionsreaktion auf steigenden Perfusionsdruck durch Blockierung der Aktivität von ENaC-Proteinen. Amiloride hemmt den Na+-Einstrom vollständig in Dosen, die als relativ spezifisch für ENaC (1,5 μM) in vaskulären glatten Muskelzellen (VSMC) bekannt sind. |
| In vivo |
Amiloride in einer Dosis von 1 mg/kg/Tag subkutan verabreicht, kehrt die anfänglichen Zunahmen der Kollagenablagerung um und verhindert weitere Zunahmen bei der DOCA-Salz-hypertonen Ratte. Amiloride verzögert den Beginn der Proteinurie und verbessert die histologischen Werte von Gehirn und Nieren bei salztrinkenden, schlaganfallanfälligen spontan hypertensiven Ratten (SHRSP) im Vergleich zu Kontrollen. Amiloride antagonisiert oder verhindert die Wirkungen von Aldosteron in diesen Zellen sowie in kardiovaskulären und renalen Geweben von Tieren mit salzabhängigen Hypertonieformen. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-AKT / AKT / p-PP1 / PP1 |
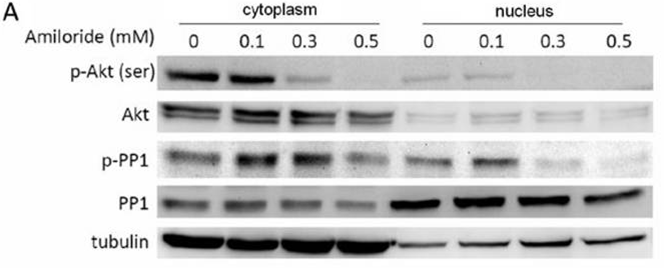
|
21694768 |
| Immunofluorescence | p53 |
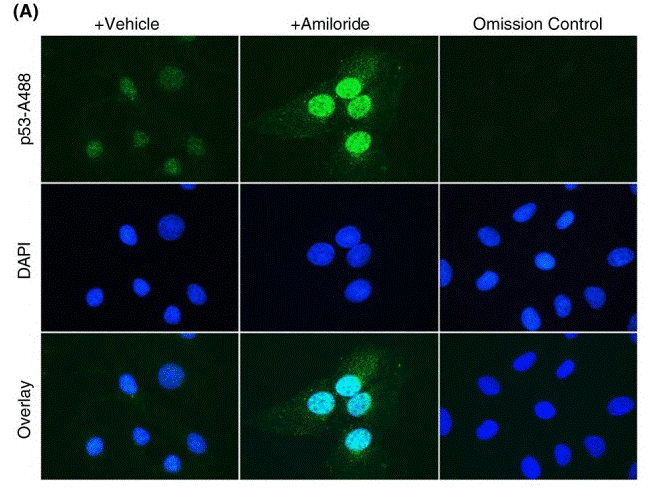
|
30556178 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05044611 | Recruiting | Bipolar Disorder |
Assistance Publique - Hôpitaux de Paris |
January 11 2023 | Phase 4 |
| NCT04181008 | Completed | Pharmacokinetics |
University of Utah|Center for Addiction and Mental Health |
September 28 2020 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT02323100 | Terminated | Cystic Fibrosis |
National Jewish Health|University of Alabama at Birmingham|Children''s Hospital of Philadelphia|Johns Hopkins University|Horizon Pharma Ireland Ltd. Dublin Ireland |
December 2 2018 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
