nur für Forschungszwecke
KU-55933 ATM Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1092
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 395.49
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | HDAC PARP DNA-PK WRN DNA/RNA Synthesis Topoisomerase PPAR Sirtuin Casein Kinase eIF |
|---|---|
| Weitere ATM/ATR Inhibitoren | Ceralasertib (AZD6738) AZD1390 Berzosertib (VE-822) Lartesertib (M4076) Camonsertib (RP-3500) KU-60019 VE-821 AZ20 AZD0156 Mirin |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DU-145 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3.27352 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuO-3N1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.17142 μM | SANGER | |||
| LAMA-84 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.58465 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-72 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.48084 μM | SANGER | |||
| LoVo | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.93239 μM | SANGER | |||
| HH | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.27671 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8.28575 μM | SANGER | |||
| KM12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.21142 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1437 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.8097 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1838 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.1865 μM | SANGER | |||
| J-RT3-T3-5 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.2417 μM | SANGER | |||
| GOTO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.6996 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2241-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.7186 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.788 μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.6354 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-12T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.617 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-684 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.1569 μM | SANGER | |||
| DOK | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.3329 μM | SANGER | |||
| Hs-578-T | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.4182 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-423MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.5236 μM | SANGER | |||
| DBTRG-05MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.6111 μM | SANGER | |||
| VM-CUB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=15.9849 μM | SANGER | |||
| KG-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.0996 μM | SANGER | |||
| 8305C | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.1889 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuH-7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.2674 μM | SANGER | |||
| LXF-289 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.2747 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1793 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.4712 μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.6568 μM | SANGER | |||
| GCIY | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.7905 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-28 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.0475 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-SNU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.1269 μM | SANGER | |||
| CTB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.2259 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.4573 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2998 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.6733 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2030 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.1997 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuP-T3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.5888 μM | SANGER | |||
| 697 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.0201 μM | SANGER | |||
| MLMA | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.0557 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC70 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.489 μM | SANGER | |||
| A704 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19.8305 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-283MED | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.5339 μM | SANGER | |||
| U031 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.1489 μM | SANGER | |||
| HSC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.1835 μM | SANGER | |||
| JVM-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.506 μM | SANGER | |||
| Mewo | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.5073 μM | SANGER | |||
| YH-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.5123 μM | SANGER | |||
| LB1047-RCC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.5879 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2157 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.8054 μM | SANGER | |||
| SNU-449 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.8748 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ramos-2G6-4C10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.96 μM | SANGER | |||
| CHL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.7292 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-30 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.4662 μM | SANGER | |||
| PANC-08-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.0938 μM | SANGER | |||
| QIMR-WIL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.1858 μM | SANGER | |||
| BFTC-905 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.5944 μM | SANGER | |||
| GI-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.7055 μM | SANGER | |||
| MDA-MB-415 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=26.5033 μM | SANGER | |||
| GT3TKB | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=26.5342 μM | SANGER | |||
| DEL | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=26.8356 μM | SANGER | |||
| KOSC-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=26.9075 μM | SANGER | |||
| RVH-421 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.2921 μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-13 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.4308 μM | SANGER | |||
| 639-V | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.5119 μM | SANGER | |||
| A2780 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.641 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW982 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.9052 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW1710 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.0981 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1569 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.4897 μM | SANGER | |||
| MV-4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.5735 μM | SANGER | |||
| BHT-101 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.6572 μM | SANGER | |||
| Ca9-22 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.714 μM | SANGER | |||
| HAL-01 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.7615 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-263MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.344 μM | SANGER | |||
| NEC8 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29.5548 μM | SANGER | |||
| EKVX | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.5847 μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.6304 μM | SANGER | |||
| MFM-223 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31.8098 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-PN-DW | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.1406 μM | SANGER | |||
| HuO9 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.5282 μM | SANGER | |||
| MHH-PREB-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.6234 μM | SANGER | |||
| OVCAR-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.8363 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1648 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.8651 μM | SANGER | |||
| MKN1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34.1101 μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-450 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34.6444 μM | SANGER | |||
| ES8 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34.8975 μM | SANGER | |||
| MS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34.9554 μM | SANGER | |||
| HOP-92 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=35.9277 μM | SANGER | |||
| SKG-IIIa | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.2561 μM | SANGER | |||
| TE-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36.5243 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-NEP-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.6744 μM | SANGER | |||
| DB | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=37.9185 μM | SANGER | |||
| IA-LM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.0239 μM | SANGER | |||
| COLO-829 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.4159 μM | SANGER | |||
| TGBC11TKB | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=39.1408 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-51 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.0612 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2228 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.3662 μM | SANGER | |||
| C32 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.4024 μM | SANGER | |||
| KU-19-19 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.7683 μM | SANGER | |||
| KNS-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=40.8381 μM | SANGER | |||
| FADU | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=41.2502 μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-33 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.6749 μM | SANGER | |||
| CHP-134 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.8496 μM | SANGER | |||
| HDLM-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=42.9084 μM | SANGER | |||
| NBsusSR | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.0725 μM | SANGER | |||
| SW954 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.1053 μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.411 μM | SANGER | |||
| VMRC-RCZ | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.4586 μM | SANGER | |||
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.931 μM | SANGER | |||
| NKM-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43.9558 μM | SANGER | |||
| DMS-273 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44.7567 μM | SANGER | |||
| TYK-nu | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.1234 μM | SANGER | |||
| KALS-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.146 μM | SANGER | |||
| A101D | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.4456 μM | SANGER | |||
| G-361 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.2138 μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-299 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.3516 μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.542 μM | SANGER | |||
| HT-1376 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.7426 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-N-AS | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.7822 μM | SANGER | |||
| MG-63 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.9036 μM | SANGER | |||
| EPLC-272H | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=46.9503 μM | SANGER | |||
| BALL-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=47.832 μM | SANGER | |||
| LCLC-97TM1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.202 μM | SANGER | |||
| HO-1-N-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=48.9676 μM | SANGER | |||
| MFE-280 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.4617 μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H526 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.8163 μM | SANGER | |||
| D-566MG | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.9096 μM | SANGER | |||
| BB30-HNC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.9498 μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-N-DZ | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=50.0481 μM | SANGER | |||
| HepG2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | blocks SC-III3-induced S phase arrest | 25527123 | |
| HepG2 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | suppresses the phosphorylations of ATM on Ser1981, Chk1 on Ser345, Chk2 on Thr68, and Cdk2 on Tyr15 induced by SC-III3 | 25527123 | |
| KATO III | Growth Inhibition Assay | 2.5/5/7.5 μM | DMSO | enhances the toxicity of olaparib | 24841718 | |
| hTCEpi | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | DMSO | prevents the cytopathic effect of HSV-1 | 24370835 | |
| MCF10A | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | DMSO | potentiates the cytotoxicity of GA | 24150595 |
| HL-60 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 0.5 h | DMSO | reduces phosphorylation of Chk2 | 23934411 |
| MCF-7 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 1-100μM | 24 h | FBS | inhibits the cell proliferation | 23185347 |
| HeLa | Growth Inhibition Assay | 1-100μM | 24 h | FBS | inhibits the cell proliferation | 23185347 |
| SH-SY5Y | Function Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | inhibits clioquinol-induced phosphorylation of p53 | 22627294 | |
| IMR-32 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | inhibits clioquinol-induced phosphorylation of p53 | 22627294 | |
| A549 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 1 h | suppresses Nano-Co-induced p53 accumulation | 22559321 | |
| T47D | Function Assay | 20 mM | 24 h | DMSO | prevents IR-induced degradation of IκBα | 21144805 |
| A29 MEF | Function Assay | 10 μM | 1h | blocks the phosphorylation of Akt at Ser473 | 20053781 | |
| MDA-MB-453 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5-40 μM | 72 h | IC50 of 10 μM | 20053781 | |
| PC-3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 5-40 μM | 72 h | IC50 of 10 μM | 20053781 | |
| U2OS | Function assay | Inhibition of ATM in human U2OS cells assessed as inhibition of p53 phosphorylation at Ser15 residue, IC50 = 0.25 μM. | 26632965 | |||
| MCF7 | Function assay | 1 hr | Inhibition of ATM kinase in human MCF7 cells after 1 hr by immunofluorescence assay, IC50 = 0.3 μM. | 26632965 | ||
| BJ | Function assay | 10 uM | 10 days | Suppression of senescence in human BJ cells assessed as increase in cell number at 10 uM after 10 days by senescence reversal assay | 16767085 | |
| BJ | Function assay | 10 uM | 10 days | Inhibition of ataxia telangiectasia-mutated in human BJ cells assessed as increase in cell number at 10 uM after 10 days by senescence reversal assay | 16767085 | |
| MCF7 | Function assay | 10 uM | 10 mins | Sensitization of infrared-induced DNA damage in human MCF7 cells assessed as reduction in colony formation at 10 uM pretreated for 10 mins followed by irradiation for 4 hrs measured after 10 days by crystal violet staining analysis | 26632965 | |
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 395.49 | Formel | C21H17NO3S2 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 587871-26-9 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | ATM Kinase Inhibitor | Smiles | C1COCCN1C2=CC(=O)C=C(O2)C3=C4C(=CC=C3)SC5=CC=CC=C5S4 | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 39 mg/mL
(98.61 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
ATM
(Cell-free assay) 12.9 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
KU-55933 hemmt DNA-PK und PI3K mit einer IC50 von 2,5 μM bzw. 16,6 μM. Außerdem verhindert diese Verbindung auch die Aktivität von mTOR mit einer IC50 von 9,3 μM. Sie ist auf zellulärer Ebene aktiv, indem sie ein gut charakterisiertes ATM-abhängiges Phosphorylierungsereignis ablatiert. Diese Chemikalie hat einen dosisabhängigen Effekt bei der Hemmung dieses ATM-abhängigen Phosphorylierungsereignisses mit einer IC50 von 300 nM. KU-58050 verhindert die ATM-abhängige Phosphorylierung von p53 Serin 15 erst ab einer Dosis von 30 μM. Die Zugabe dieser Verbindung hat keine nennenswerten Auswirkungen auf die UV-induzierte Phosphorylierung von H2AX an Serin 139, NBS1 an Serin 343, CHK1 an Serin 345 und SMC1 an Serin 966. Im starken Gegensatz zu den UV-Reaktionen eliminiert sie die ionisierende strahlungsinduzierte Phosphorylierung dieser ATM-Substrate. Diese Chemikalie sensibilisiert HeLa-Zellen für eine Reihe von ionisierenden Strahlungsdosen. Sie hemmt die durch Wachstumsfaktoren induzierte Phosphorylierung von Akt in Krebszellen. Diese Verbindung unterdrückt die Proliferation von Krebszellen. Darüber hinaus verbessert die Unterdrückung von ATM durch diese Chemikalie das Überleben, wahrscheinlich durch die Verhinderung der nachgeschalteten Aktivierung von TAp63α.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
Gereinigte Enzymassays
|
|
ATM zur Verwendung im In-vitro-Assay wird aus HeLa-Kernextrakt durch Immunpräzipitation mit Kaninchen-polyklonalem Antiserum gewonnen, das gegen die COOH-terminalen 400 Aminosäuren von ATM in Puffer mit 25 mM HEPES (pH 7,4), 2 mM MgCl2, 250 mM KCl, 500 μM EDTA, 100 μM Na3VO4, 10% v/v Glycerin und 0,1% v/v Igepal hergestellt wurde. ATM-Antikörperkomplexe werden aus dem Kernextrakt isoliert, indem sie 1 Stunde lang mit Protein A-Sepharose-Kügelchen inkubiert und anschließend zentrifugiert werden, um die Kügelchen zurückzugewinnen. In der Vertiefung einer 96-Well-Platte werden ATM-haltige Sepharose-Kügelchen mit 1 μg des Substrats Glutathion-S-Transferase–p53N66 (NH2-terminale 66 Aminosäuren von p53, fusioniert mit Glutathion-S-Transferase) in ATM-Assay-Puffer [25 mM HEPES (pH 7,4), 75 mM NaCl, 3 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, 50 μM Na3VO4, 500 μM DTT und 5% v/v Glycerin] bei 37 °C in An- oder Abwesenheit dieser Verbindung inkubiert. Nach 10 Minuten unter leichtem Schütteln wird ATP zu einer Endkonzentration von 50 μM hinzugefügt und die Reaktion weitere 1 Stunde bei 37 °C fortgesetzt. Die Platte wird bei 250 × g für 10 Minuten (4 °C) zentrifugiert, um die ATM-haltigen Kügelchen zu entfernen, und der Überstand wird entnommen und in eine weiße, undurchsichtige 96-Well-Platte überführt und bei Raumtemperatur 1,5 Stunden lang inkubiert, um die Bindung von Glutathion-S-Transferase-p53N66 zu ermöglichen. Diese Platte wird dann mit PBS gewaschen, trocken getupft und mittels einer Standard-ELISA-Technik mit einem Phospho-Serin 15 p53-Antikörper analysiert. Der Nachweis des phosphorylierten Glutathion-S-Transferase-p53N66-Substrats erfolgt in Kombination mit einem Ziegen-Anti-Maus-Meerrettichperoxidase-konjugierten Sekundärantikörper. Zur Signalgenerierung wird eine verbesserte Chemilumineszenzlösung verwendet und die Chemilumineszenzdetektion durchgeführt.
|
|
| In vivo |
Die Unterdrückung der ATM-abhängigen STAT3-Aktivierung durch KU-55933 verstärkt die TRAIL-vermittelte Apoptose durch Hochregulation der DR5-Oberflächenexpression, während die Unterdrückung von STAT3 und NF-κB an der Herunterregulierung von cFLIP beteiligt zu sein scheint, begleitet von einer zusätzlichen Zunahme der apoptotischen Spiegel. Diese Verbindung beeinflusst die TRAIL-vermittelte Apoptose stärker als der JAK2-Inhibitor, AG490, oder die Überexpression von STAT3β.
|
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
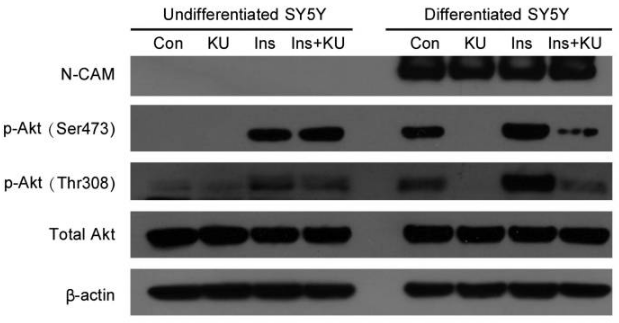
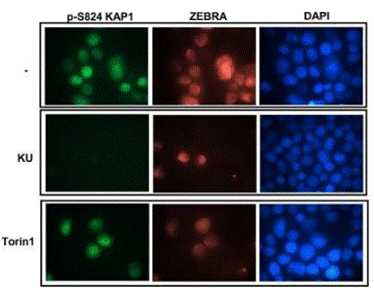
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-AKT(Ser473) / p-AKT(Thr308) PARP / Cleaved PARP / Caspase-3 / Cleaved caspase-3 ATM-S1981 / ATM / p-p53(S15) / p53 p21 / p27 / p53 |
|
22739265 |
| Immunofluorescence | p-S824 KAP1 / ZEBRA |
|
28249048 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
