nur für Forschungszwecke
Ganetespib (STA-9090) HSP90 Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1159
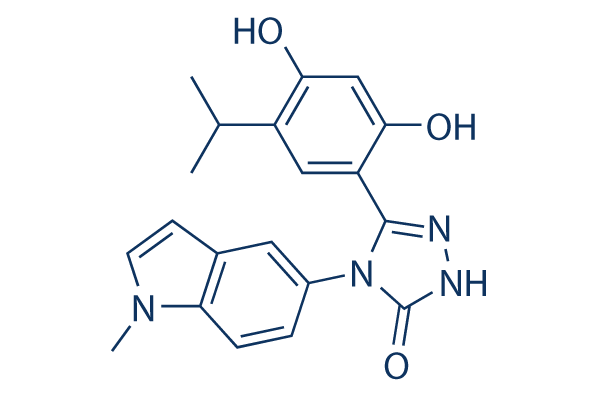
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 364.4
Qualitätskontrolle
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCI-H1975 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=8 nM | 22144665 | ||
| NCI-H1975 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=16 nM | 22144665 | ||
| Calu-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=64 nM | 23012248 | |||
| Calu-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=58 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2122 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=53 nM | 23012248 | |||
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H358 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H1734 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H727 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28 nM | 23012248 | |||
| COR-L23 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H1792 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2009 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19 nM | 23012248 | |||
| SK-LU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2212 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H441 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2030 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H23 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11 nM | 23012248 | |||
| HOP-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11 nM | 23012248 | |||
| IA-LM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H460 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H157 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H1355 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5 nM | 23012248 | |||
| VCaP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7 nM | 23152004 | |||
| LNCaP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 23152004 | |||
| Ramos-RA1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Karpas-299 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Kasumi-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.8 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CCRF-CEM (2) | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.2 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CCRF-CEM (1) | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.5 nM | 23303741 | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| RS4;11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.5 nM | 23303741 | |||
| COG-LL-317 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| NALM-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.7 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-136 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.2 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-90 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.3 nM | 23303741 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.8 nM | 23303741 | |||
| NB-1643 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.9 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-258 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.7 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-9 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| TC-71 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.5 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-266 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.1 nM | 23303741 | |||
| BT-12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.3 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Rh30 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Rh18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.2 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Rh41 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| RD | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 23303741 | |||
| K033 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| M23 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K029 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K028 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K008 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K033 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces a modest increase in G1 population | 23418523 | |
| M23 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G1 and G2/M arrest | 23418523 | |
| K029 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G1 arrest | 23418523 | |
| K028 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G2 arrest | 23418523 | |
| K008 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G2 arrest | 23418523 | |
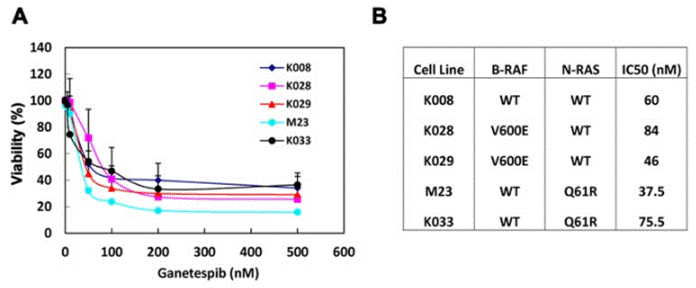
| K033 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=75.5 nM | 23418523 | |||
| M23 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=37.5 nM | 23418523 | |||
| K029 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=46 nM | 23418523 | |||
| K028 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=84 nM | 23418523 | |||
| K008 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=60 nM | 23418523 | |||
| H3122 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | IC50=10 nM | 23533265 | |
| H2228 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | IC50=13 nM | 23533265 | |
| A1847 | Apoptosis Assay | 10-100 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces apoptosis time and dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-8 | Apoptosis Assay | 10-100 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces apoptosis time and dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-5 | Apoptosis Assay | 10-100 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces apoptosis time and dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| SKOV-3 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| A1847 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-8 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-5 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| H146 | Function Assay | 30 nM | 72 h | induces persistent G2/M phase arrest | 24166505 | |
| GLC4 | Function Assay | 30 nM | 72 h | induces persistent G2/M phase arrest | 24166505 | |
| H82 | Function Assay | 30 nM | 72 h | induces persistent G2/M phase arrest | 24166505 | |
| AC3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.9 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H1173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.62 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H792 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.07 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H620 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.67 nM | 24166505 | |||
| N592 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.12 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H526 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.64 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H187 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.99 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H146 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.51 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H128 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=69.55 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H69 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=83.36 nM | 24166505 | |||
| GLC4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.47 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.27 nM | 24166505 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 100 nM | 24 h | inhibits the migratory and invasive capacity | 24173541 | |
| BT-20 | Function Assay | 100/250 nM | 24 h | resulted in a dose-dependent destabilization of EGFR, IGF-IR, MET, and CRAF | 24173541 | |
| MDA-MB-435 | Function Assay | 100 nM | 30 min | inhibits accumulation of HIF-1α | 24248265 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 100 nM | 30 min | inhibits accumulation of HIF-1α | 24248265 | |
| HCC2998 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=128 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SK-CO-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=81 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LS-123 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=73 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SNU-C2B | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LS-1034 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LoVo | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22 nM | 24682747 | |||
| COLO-678 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21 nM | 24682747 | |||
| NCI-H747 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17 nM | 24682747 | |||
| COLO-205 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14 nM | 24682747 | |||
| HCT 116 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14 nM | 24682747 | |||
| HuTu-80 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13 nM | 24682747 | |||
| HCT-15 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SW620 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LS-411 N | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5 nM | 24682747 | |||
| RKO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SW780 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3451 nM | 24784839 | |||
| RT4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1733 nM | 24784839 | |||
| TCCSUP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=142 nM | 24784839 | |||
| MGH-U3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=53 nM | 24784839 | |||
| HT-1197 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=53 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 5637 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 35612 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38 nM | 24784839 | |||
| KU-19-19 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36 nM | 24784839 | |||
| LB831-BLC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34 nM | 24784839 | |||
| UM-UC3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 647-V | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27 nM | 24784839 | |||
| HT-1376 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21 nM | 24784839 | |||
| J82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18 nM | 24784839 | |||
| BFTC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17 nM | 24784839 | |||
| SCaBER | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 639-V | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10 nM | 24784839 | |||
| RT112 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9 nM | 24784839 | |||
| T24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7 nM | 24784839 | |||
| SW-1710 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6 nM | 24784839 | |||
| DSH1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6 nM | 24784839 | |||
| CAL27 | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| Detroit562 | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| FUDA | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| SCC25 | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| HT-29 | Function Assay | 50nM | 24 h | DMSO | induced G0/G1 arrest | 25210794 |
| HCT-116 | Function Assay | 50nM | 24 h | DMSO | induced G0/G1 arrest | 25210794 |
| MGC-803 | Function Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 24 h | induces G2/M cell-cycle arrest | 25590805 | |
| MKN-28 | Cell Viability Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 25590805 | |
| SGC-7901 | Cell Viability Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 25590805 | |
| MGC-803 | Cell Viability Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 25590805 | |
| MV411 | Apoptosis Assay | 30/80/150/250 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces dose dependant induction of apoptosis | 25882550 | |
| HL60 | Apoptosis Assay | 30/80/150/250 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces dose dependant induction of apoptosis | 25882550 | |
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 364.4 | Formel | C20H20N4O3 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 888216-25-9 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | CC(C)C1=C(C=C(C(=C1)C2=NNC(=O)N2C3=CC4=C(C=C3)N(C=C4)C)O)O | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 40 mg/mL
(109.76 mM)
Ethanol : 9 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
HSP90
(OSA 8 cells) 4 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Die 50%igen Hemmkonzentrationen (IC50) f
Gan Ganetespib (STA-9090) gegen maligne Mastzelllinien sind 10-50-mal niedriger als die f
17-AAG, was darauf hinweist, dass Triazolon-Klasse von HSP90-Inhibitoren wahrscheinlich eine gr
e Wirksamkeit als Geldanamycin-basierte Inhibitoren aufweist. Diese Verbindung hemmt MG63-Zelllinien mit IC50 von 43 nM. Sie bindet an die ATP-Bindungsdomäne am N-Terminus von Hsp90 und dient als potenter Hsp90-Inhibitor, indem sie den Abbau mehrerer onkogener Hsp90-Client-Proteine wie HER2/neu, mutiertes EGFR, Akt, c-Kit, IGF-1R, PDGFR
Jak1, Jak2, STAT3, STAT5, HIF-1
CDC2 und c-Met sowie Wilms-Tumor 1 verursacht. Bei niedrigen nanomolaren Konzentrationen hemmt es die Zellproliferation und induziert Apoptose in einer Vielzahl von menschlichen Krebszelllinien, einschlie
lich vieler Tyrosinkinase-Inhibitor- und Tanespimycin-resistenter Zelllinien. Es zeigt eine potente Zytotoxizit in einer Reihe von soliden und h matologischen Tumorzelllinien, einschlie
lich solcher, die mutierte Kinasen exprimieren, die Resistenz gegen niedermolekulare Tyrosinkinase-Inhibitoren verleihen. Seine Behandlung verursachte schnell den Abbau bekannter Hsp90-Client-Proteine, zeigt eine
berlegene Wirksamkeit gegenüber dem Ansamycin-Inhibitor 17-AAG und zeigt eine anhaltende Aktivität auch bei kurzen Expositionszeiten. In einer anderen Studie induziert es die Apoptose maligner Mastzelllinien von Hunden. Es ist bei deutlich niedrigeren Konzentrationen für C2- und BR-Mastzelllinien von Hunden mit IC50 von 19 bzw. 4 nM aktiv, w rend 17-AAG C2- und BR-Mastzelllinien von Hunden mit IC50 von 958 bzw. 44 nM hemmt. Sowohl die Expression von WT als auch die von mutiertem Kit werden durch 100 nM dieser Verbindung nach 24 Stunden in allen behandelten Linien, einschlie
lich C2- und BMCMCs-Zellen, herunterreguliert. Es wurden jedoch keine Auswirkungen auf die PI3K- oder HSP90-Expression nach der Behandlung mit dieser Verbindung beobachtet.
|
| In vivo |
Die Verabreichung von Ganetespib (STA-9090) f
rt zu einer signifikanten Tumorregression in mehreren Tumor-Xenograft-Modellen bei Mäusen und scheint weniger toxisch zu sein. Dar
ber hinaus zeigte diese Verbindung eine bessere Tumorp
netration im Vergleich zu Tanespimycin. Es hemmt das in vivo Tumorwachstum sowohl in malignen Mastzell- als auch in OSA-Xenograft-Modellen. Ganetespib hemmt das Tumorwachstum signifikant, wenn es in zwei sich wiederholenden Zyklen von 25 mg/kg/Tag
ber 3 Tage dosiert wird, mit einem %T/C-Wert von 18. Es wird gut vertragen, wobei die Vehikel- und Ganetespib-Gruppen am Tag 17 durchschnittliche K
rpergewichtsver nderungen relativ zum Studienbeginn von +0,3% bzw. -8,1% aufweisen.
|
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
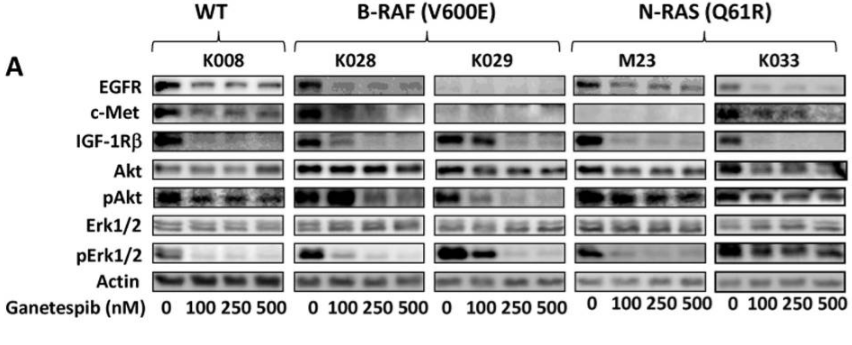
| Western blot | EGFR / c-Met / IGF-1Rβ/ Akt / p-Akt / ERK / p-ERK p27(Kip1) / p21 (Cip1) / Cyclin D1 / Cyclin E / Cyclin B1 / CDK1 / CDK2 / CDK4 Survivin / Bcl-2 / Bcl-xl / Mcl-1 B-RAF / C-RAF / N-RAS HER2 / p-STAT3 / BIM CDK1 / Cyclin D1 / Cyclin B1 / p27 c-PARP / c-caspase 3 / caspase 8 / c-caspase 8 / caspase 9 / c-caspase 9 ErbB2 / pErbB2 / Src / pSrc / mTOR / pmTOR / Bad / pBad / GSK3 / pGSK3 Wee1 / p-Wee1 / Chk1 / p-Chk1 |
|
23418523 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
23418523 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02192541 | Terminated | Neoplasms |
National Cancer Institute (NCI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
December 2 2014 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02008877 | Completed | Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors (MPNST)|Sarcoma |
Sarcoma Alliance for Research through Collaboration|Synta Pharmaceuticals Corp.|United States Department of Defense |
December 2013 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
Does this inhibitor inhibit both isoforms of HSP90?
Antwort:
We don't have the information now and it is not very clear in the literature either. From following two references, it indicates that it might be specific to the alpha form “It binds to the ATP binding site of Hsp90 alpha with a Kd of 110 nM” http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3477583/
