nur für Forschungszwecke
JNK Inhibitor VIII JNK Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S7794
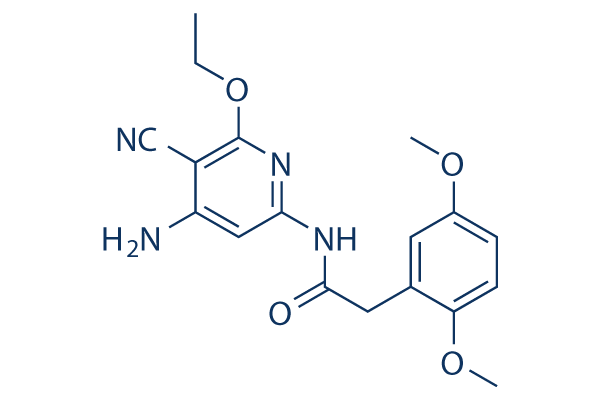
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 356.38
Qualitätskontrolle
- In Nature Medicine für seine erstklassige Qualität zitiert
- COA
- NMR
- SDS
- Datenblatt
| Verwandte Ziele | ERK p38 MAPK Raf MEK Ras KRas S6 Kinase MAP4K TAK1 Mixed Lineage Kinase |
|---|---|
| Weitere JNK Inhibitoren | CC-90001 SP600125 JNK-IN-8 Anisomycin (Flagecidin) JNK Inhibitor IX Tanzisertib Hydrochloride (CC-930) Polyphyllin I DTP3 BI-78D3 Bentamapimod (AS602801) |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB7 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB7 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.27473μM | SANGER | |||
| LB2241-RCC | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LB2241-RCC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=6.57739μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1299 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1299 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=13.2019μM | SANGER | |||
| BV-173 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BV-173 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=14.0505μM | SANGER | |||
| HPAF-II | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HPAF-II cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=14.5873μM | SANGER | |||
| RS4-11 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RS4-11 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=16.6795μM | SANGER | |||
| EW-1 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human EW-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=17.1883μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1581 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1581 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=17.2588μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-PN-DW | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-PN-DW cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=17.9485μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-4 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KP-4 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=19.1087μM | SANGER | |||
| DU-145 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DU-145 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=19.8748μM | SANGER | |||
| ACHN | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ACHN cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=20.6213μM | SANGER | |||
| A172 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human A172 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=21.263μM | SANGER | |||
| HuO-3N1 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HuO-3N1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=21.4318μM | SANGER | |||
| QIMR-WIL | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human QIMR-WIL cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.3274μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1650 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1650 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=22.7873μM | SANGER | |||
| SW1088 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1088 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.1641μM | SANGER | |||
| Mewo | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human Mewo cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=23.3997μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H1355 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H1355 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=24.6365μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-LU-1 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-LU-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.058μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-70 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-70 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.125μM | SANGER | |||
| KP-N-YS | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KP-N-YS cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.5706μM | SANGER | |||
| HTC-C3 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HTC-C3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.7345μM | SANGER | |||
| NB17 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB17 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.9113μM | SANGER | |||
| GOTO | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human GOTO cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=27.9415μM | SANGER | |||
| BEN | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BEN cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=29.865μM | SANGER | |||
| HMV-II | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HMV-II cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=30.1553μM | SANGER | |||
| SF295 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SF295 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=32.156μM | SANGER | |||
| MPP-89 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MPP-89 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=33.5199μM | SANGER | |||
| LCLC-103H | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human LCLC-103H cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=34.2223μM | SANGER | |||
| MN-60 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MN-60 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=36.0139μM | SANGER | |||
| BB65-RCC | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BB65-RCC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=36.1528μM | SANGER | |||
| BHY | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BHY cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=36.9645μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-3 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-MEL-3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.7324μM | SANGER | |||
| NY | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NY cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.7592μM | SANGER | |||
| CAL-72 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-72 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=37.9289μM | SANGER | |||
| ES3 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ES3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=38.1949μM | SANGER | |||
| NBsusSR | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NBsusSR cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=39.3132μM | SANGER | |||
| NB10 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NB10 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=40.1731μM | SANGER | |||
| ChaGo-K-1 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ChaGo-K-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=41.1576μM | SANGER | |||
| KYSE-450 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-450 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=41.4514μM | SANGER | |||
| SK-MEL-1 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-MEL-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=41.9927μM | SANGER | |||
| PC-3 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human PC-3 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=42.2752μM | SANGER | |||
| KARPAS-299 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KARPAS-299 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=44.5948μM | SANGER | |||
| DBTRG-05MG | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DBTRG-05MG cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=44.6546μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC1806 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HCC1806 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=45.2169μM | SANGER | |||
| NCI-H2009 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H2009 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=45.2843μM | SANGER | |||
| HCC2157 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HCC2157 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=45.7976μM | SANGER | |||
| EM-2 | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human EM-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=47.4011μM | SANGER | |||
| DOK | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DOK cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=48.3877μM | SANGER | |||
| HepG2 | Function assay | Inhibition of cJun phosphorylation in HepG2 cell line, Ki=0.004μM | 16759099 | |||
| HepG2 | Function assay | Inhibition of cJun phosphorylation in HepG2 cell line, EC50=0.92μM | 16759099 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 356.38 | Formel | C18H20N4O4 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | 3 years -20°C powder |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 894804-07-0 | -- | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | TCS JNK 6o | Smiles | CCOC1=C(C(=CC(=N1)NC(=O)CC2=C(C=CC(=C2)OC)OC)N)C#N | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 71 mg/mL
(199.22 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
JNK1
(Cell-free assay) 2 nM(Ki)
JNK2
(Cell-free assay) 4 nM(Ki)
JNK1
(Cell-free assay) 45 nM
JNK3
(Cell-free assay) 52 nM(Ki)
JNK2
(Cell-free assay) 160 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
JNK Inhibitor VIII (TCS-JNK-6a) bindet kompetitiv und reversibel an die ATP-Bindungsstelle. Diese Verbindung zeigt ein bemerkenswertes Selektivitätsprofil. Zusätzlich zeigt sie eine gewisse Hemmung der c-Jun-Phosphorylierung in HepG2-Zellen. TCS-JNK-6o ist ein 2,5-Dimethoxy-Analogon dieser Chemikalie mit der Dimethoxy-Substitution des Phenylrings. Diese Verbindung zeigt weitere Potenzsteigerungen. |
| Kinase-Assay |
Ser/Thr-Kinase
|
|
Ser/Thr-Kinase-Assays werden unter Verwendung einer radioaktiven FlashPlate-basierten Assay-Plattform durchgeführt. In diesem Format werden biotinyliertes Substratpeptid (2 μM), γ-[33P]-ATP (5 μM, 2 mCi/μmol), diese Verbindung (3-10000 nM in 2% DMSO) und Enzym für 1 Stunde in einem Puffer inkubiert, der 25 mM Hepes, pH 7,5, 1 mM DTT, 10 mM MgCl2, 100 μM Na3VO4 und 0,075 mg/mL Triton X-100 enthält, mit 80 μL Stoppuffer, der 100 mM EDTA und 4 M NaCl enthält, gestoppt, auf Streptavidin-beschichtete 384-Well-FlashPlates übertragen, die dann 3-mal gewaschen und mit einem TopCount-Mikroplattenleser ausgelesen werden.
|
|
| In vivo |
Pharmakokinetische Profile werden für JNK Inhibitor VIII (TCS-JNK-6o) in Sprague-Dawley-Ratten bestimmt. Diese Verbindung zeigt eine kurze Halbwertszeit von etwa 1 Stunde, mit schneller Clearance und kaum messbarer Bioverfügbarkeit. Mikrosomale Inkubationsstudien ergaben, dass der oxidative Metabolismus mit dieser Verbindung sehr schnell ist. |
Literatur |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
