nur für Forschungszwecke
SAG (Smoothened Agonist) Hydrochloride Smoothened Agonist
Kat.-Nr.S7779
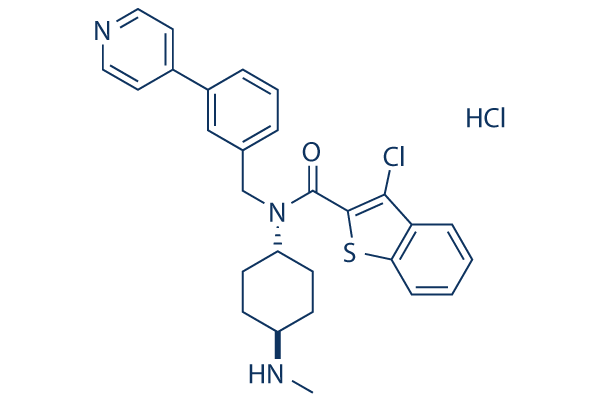
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 526.52
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | JAK TGF-beta/Smad Wnt/beta-catenin ERK GSK-3 ROCK PKA Secretase STAT Casein Kinase |
|---|---|
| Weitere Hedgehog/Smoothened Inhibitoren | Purmorphamine Cyclopamine (11-Deoxojervine) GANT61 SAG (Smoothened Agonist) SANT-1 HPI-4 (Ciliobrevin A) BMS-833923 Taladegib (LY2940680) Ciliobrevin D PF-5274857 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mouse Shh-Light II cell | Function assay | 48 hrs | Activation of Shh pathway in mouse Shh-Light II cells assessed as induction of gli1 expression after 48 hrs by renilla luminescence assay, EC50=0.0088 μM | 22985958 | ||
| HUVEC | Cytotoxicity assay | 24 h | Cytotoxicity against HUVEC after 24 hrs by WST-1 assay, IC50=22 μM | 22985958 | ||
| Shh-Light II | Function assay | 48 hrs | Activation of Shh pathway in mouse Shh-Light II cells assessed as induction of gli1 expression after 48 hrs by renilla luminescence assay, EC50 = 0.0618 μM. | 22985958 | ||
| NIH/3T3 | Function assay | Agonist activity at Smo in mouse NIH/3T3 cells transfected with Gli-dependent firefly luciferase reporter assessed as stimulation of Gli transcription factor, EC50 = 0.03 μM. | 27429255 | |||
| C3H10T1/2 | Function assay | 6 days | Agonist activity at Smo in mouse C3H10T1/2 cells assessed as induction of cell differentiation into osteoblast incubated for 6 days by alkaline phosphatase assay, EC50 = 0.13 μM. | 27429255 | ||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 526.52 | Formel | C28H29Cl2N3OS |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 2095432-58-7 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | CNC1CCC(CC1)N(CC2=CC(=CC=C2)C3=CC=NC=C3)C(=O)C4=C(C5=CC=CC=C5S4)Cl.Cl | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 82 mg/mL
(155.73 mM)
Water : 50 mg/mL Ethanol : 27 mg/mL |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Smoothened
(mouse cultured cell assay) 3 nM(EC50)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
SAG reguliert die Smo-Aktivität, indem es direkt an das heptahelikale Smo-Bündel bindet. SAG induziert eine Smo-abhängige Signalgebung über Gli auf GRK2-abhängige Weise. SAG induziert auch (1 nM) die Proliferation von neuronalen und glialen Vorläufern, ohne das Differenzierungsmuster neu produzierter Zellen zu beeinflussen. |
| Kinase-Assay |
Zellbasierte Assays zur Hh-Signalweg-Aktivierung
|
|
Assays zur Hh-Signalweg-Aktivierung in Shh-LIGHT2-Zellen, einer klonalen NIH 3T3-Zelllinie, die Gli-abhängige Firefly-Luciferase und konstitutive Renilla-Luciferase-Reporter stabil integriert, werden durchgeführt. Für Studien von SAG (ein Chlorobenzothiophen-haltiger Hh-Signalweg-Agonist) und PA-SAG werden Shh-LIGHT2-Zellen bis zur Konfluenz in 96-Well-Platten kultiviert und dann mit verschiedenen Konzentrationen dieser Verbindungen in DMEM, das 0,5 % (Vol./Vol.) Rinderkälberserum enthält, behandelt.
|
|
| In vivo |
Im Hippocampus erwachsener Ratten erhöht die intrazerebroventrikuläre Verabreichung von SAG (2,5 nM) die Anzahl der neu gebildeten Zellen signifikant und verlängert das Überleben der Hippocampuszellen. Bei Mäusen verhindert SAG (20 μg/g, i.p.) effektiv GC-induzierte neonatale zerebelläre Entwicklungsstörungen. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | LC3I / LC3II |
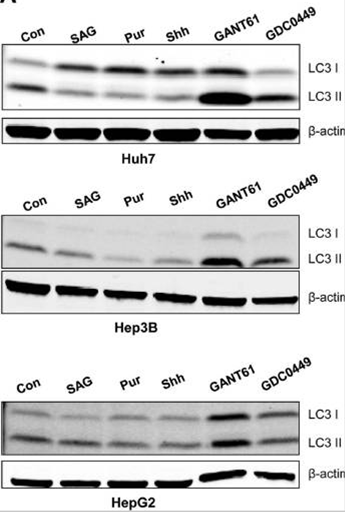
|
23504944 |
| Immunofluorescence | acetylated alpha tubulin Smo |
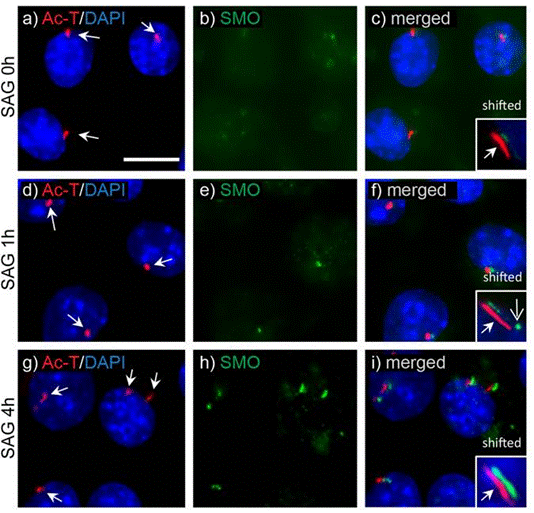
|
25992706 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05937178 | Recruiting | Hepatitis B Chronic |
Huashan Hospital|The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University|Anhui Provincial Hospital|Beijing YouAn Hospital|Peking University People''s Hospital|Peking University First Hospital|Xiamen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine|First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University|LanZhou University|Third Affiliated Hospital Sun Yat-Sen University|First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University|The Affiliated Hospital Of Guizhou Medical University|Hainan General Hospital|Hebei Medical University Third Hospital|The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine|Henan Provincial People''s Hospital|The Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University|Tongji Hospital|Wuhan Union Hospital China|Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University|Central South University|Xiangya Hospital of Central South University|The First Hospital of Jilin University|the Second Hospital of Nangjing|The Affiliated Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School|The First Affiliated Hospital with Nanjing Medical University|The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University|The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University|Shengjing Hospital|Qingdao Sixth People''s Hospital|Shandong Provincial Hospital|The Second Hospital of Shandong University|The First Affiliated Hospital of Shanxi Medical University|Tang-Du Hospital|First Affiliated Hospital Xi''an Jiaotong University|Ruijin Hospital|West China Hospital|Tianjin Second People''s Hospital|First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University|The First People''s Hospital of Yunnan|Shulan (Hangzhou) Hospital|Zhejiang University|Southwest Hospital China|The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University|Sichuan Provincial People''s Hospital |
January 31 2023 | -- |
| NCT05701592 | Recruiting | Posterior Cruciate Ligament Tear |
Konrad Malinowski MD|Artromedical Konrad Malinowski Clinic |
December 20 2022 | -- |
| NCT03645044 | Active not recruiting | Hiv|HBV Coinfection |
University of Melbourne|National Health and Medical Research Council Australia|The University of Western Australia|University of Adelaide|The HIV Netherlands Australia Thailand Research Collaboration|University of Malaya|YR Gaitonde Centre for AIDS Research and Education|Melbourne Health |
May 24 2018 | -- |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
