nur für Forschungszwecke
Vinblastine sulfate Antineoplastic and Immunosuppressive Antibiotics Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S4505
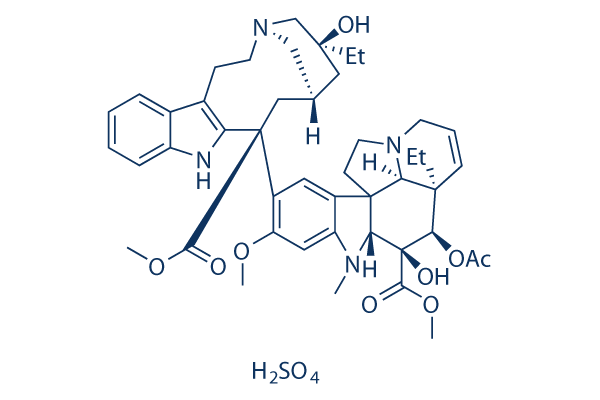
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 909.05
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | Akt Wnt/beta-catenin PKC HSP ROCK Microtubule Associated Integrin Bcr-Abl Actin FAK |
|---|---|
| Weitere Antineoplastic and Immunosuppressive Antibiotics Inhibitoren | Staurosporine (STS) Cyclosporin A Oligomycin A (MCH 32) Puromycin Dihydrochloride Nigericin sodium salt Geldanamycin (NSC 122750) Honokiol Streptozotocin (STZ) Sodium Monensin (NSC 343257) Cephalomannine |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COLO 320 human colorectal carcinoma cell line | Function assay | In vitro concentration required to kill 50% of COLO 320 human colorectal carcinoma cell line, EC50=0.08 μM | ||||
| LNCaP human prostate cancer cell line | Function assay | In vitro concentration required to kill 50% of LNCaP human prostate cancer cell line, EC50=0.5 μM | ||||
| K562 cell | Growth inhibition assay | In vitro inhibitory concentration against human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cell growth, IC50=0.001 μM | ||||
| T47D cells | Function assay | In vitro concentration required to kill 50% of T47D human breast ductal carcinoma cell line, EC50=0.08 μM | ||||
| K562 cell | Proliferation assay | 48 h | Antiproliferative activity against human K562 cells after 48 hrs, IC50=0.001 μM | |||
| ACHN cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 h | Cytotoxicity against human ACHN cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, IC50=22.7 μM | |||
| A375 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 h | Cytotoxicity against human A375 cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, IC50=7.2 μM | |||
| C32 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 h | Cytotoxicity against human C32 cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, IC50=3 μM | |||
| LNCAP cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 h | Cytotoxicity against human LNCAP cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, IC50=29.3 μM | |||
| Huh-7D12 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 h | Cytotoxicity against human Huh-7D12 cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, IC50=45.6 μM | |||
| COR-L23 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 h | Cytotoxicity against human COR-L23 cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, IC50=45.5 μM | |||
| 142BR cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 h | Cytotoxicity against human 142BR cells after 48 hrs by SRB assay, IC50=37.6 μM | |||
| HT-29 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 h | Cytotoxicity against human HT-29 cells after 48 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=0.55 μM | |||
| A549 cells | Proliferation assay | 48 h | Antiproliferative activity against human A549 cells after 48 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=2.36 μM | |||
| DU145 cells | Proliferation assay | 48 h | Antiproliferative activity against human DU145 cells after 48 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=4.25 μM | |||
| SK-MEL-5 cells | Proliferation assay | 48 h | Antiproliferative activity against human SK-MEL-5 cells after 48 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=1.74 μM | |||
| HepG2 cells | Proliferation assay | 48 h | Antiproliferative activity against human HepG2 cells after 48 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=0.16 μM | |||
| HT-29 cells | Proliferation assay | 48 h | Antiproliferative activity against human HT-29 cells after 48 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=11.18 μM | |||
| MCF7 cells | Proliferation assay | 48 h | Antiproliferative activity against human MCF7 cells after 48 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=24.08 μM | |||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Proliferation assay | 48 h | Antiproliferative activity against human MDA-MB-231 cells after 48 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=31.52 μM | |||
| rat REF52 cells | Function assay | 0.1 μM | 30 mins | Induction of microtubule depolymerization in rat REF52 cells at 0.1 uM after 30 mins by fluorescence assay | ||
| HepG2 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against adriamycin-resistant human HepG2 cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.056 μM | |||
| HepG2 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human HepG2 cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.019 μM | |||
| K562 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human K562 cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.016 μM | |||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human MDA-MB-231 cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.0083 μM | |||
| MCF7 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human MCF7 cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by MTT assay, IC50=0.007 μM | |||
| SCL6 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human SCL6 cells by MTT assay, ED50=6.1 Μm | ||||
| SCL9 | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human SCL9 cells by MTT assay, ED=5.3 μM | ||||
| KATO III cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human KATO III cells by MTT assay, ED50=6.1 μM | ||||
| NUGC4 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human NUGC4 cells by MTT assay, ED50=5.3 μM | ||||
| UACC903 cells | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 h | Cytotoxicity against human UACC903 cells after 48 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=1.65 μM | |||
| K562 cells | Function assay | Inhibition of tubulin polymerization in human K562 cells, IC50=0.13 μM | ||||
| BxPC3 cells | Proliferation assay | 48 h | Antiproliferative activity against human BxPC3 cells after 48 hrs by MTS assay, IC50=1.13 μM | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 909.05 | Formel | C46H58N4O9.H2SO4 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 143-67-9 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | NSC-49842, Vincaleukoblastine, 29060-LE | Smiles | CCC1(CC2CC(C3=C(CCN(C2)C1)C4=CC=CC=C4N3)(C5=C(C=C6C(=C5)C78CCN9C7C(C=CC9)(C(C(C8N6C)(C(=O)OC)O)OC(=O)C)CC)OC)C(=O)OC)O.OS(=O)(=O)O | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 100 mg/mL
(110.0 mM)
Water : 50 mg/mL Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
nAChR
(Adrenal Chromaffin Cells) 8.9 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Die durchschnittliche terminale Halbwertszeit von Vinblastine sulfate beträgt 14,3 h. Bei Inkubation in frisch isolierten Rattenhepatozyten dringt diese Verbindung schnell und intensiv in die Zellen ein, wahrscheinlich durch einen passiven Diffusionsmechanismus, gefolgt von einer engen zellulären Bindung. Es hemmt die durch Adrenomedullin induzierte angiogene Reaktion und ist auch positiv für den mitotischen Schlupf, wodurch Mikronuklei in einkernigen Zellen mit Zytokinese-Blockade entstehen. Diese Chemikalie führt zu einem signifikanten Anstieg mikronukleierter einkerniger Zellen bei Konzentrationen, die etwa 50 % Zelltod und Zytostase oder weniger verursachten, berechnet mit RPD, RICC und RCC.
|
| In vivo |
Vinblastine ist ein weit verbreitetes Krebsmedikament mit unerwünschten Nebenwirkungen . Eine Kombination dieser Verbindung und RAP in sehr niedrigen Dosen gegen menschliches HCC erzielt in vivo eine zufriedenstellende antiangiogene Wirkung. Die klinisch relevante Dosis dieser Chemikalie hemmt die Palmitoylierung von Tubulin in vivo in CEM-Zellen (Wirkung auf die Depalmitoylierung von Tubulin).
|
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
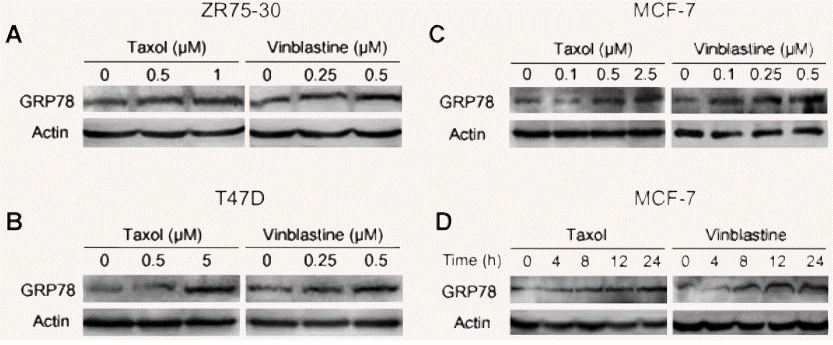
| Western blot | GRP78 p-eIF2 p-JNK / c-Caspase-7 / c-PARP ERK / p-ERK / Mcl-1 / Bad / Bid / Noxa |
|
19674193 |
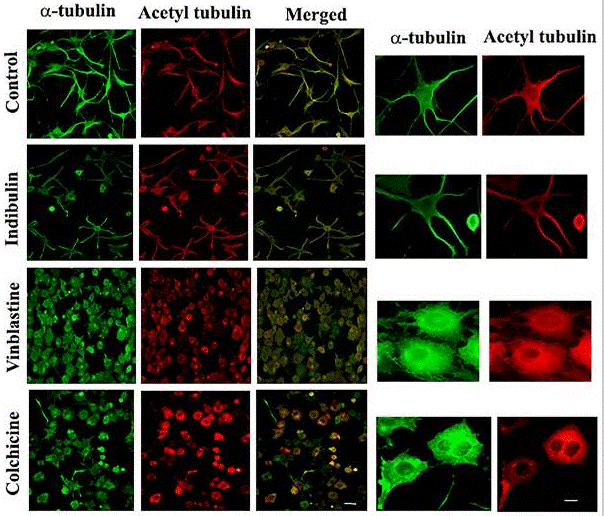
| Immunofluorescence | α-tubulin / Acetyl tubulin |
|
30120268 |
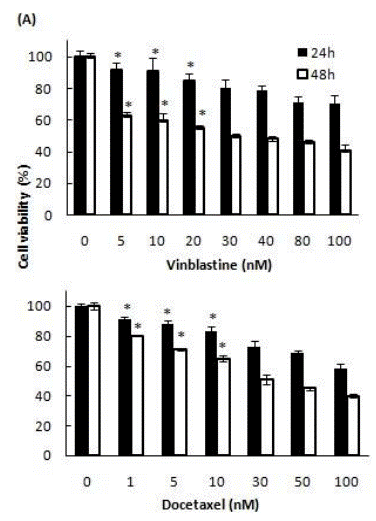
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
27114800 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06381570 | Recruiting | Low-grade Glioma |
Daniel Morgenstern|The Hospital for Sick Children |
March 21 2024 | Early Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
