nur für Forschungszwecke
MLN2238 (Ixazomib) Proteasome Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S2180
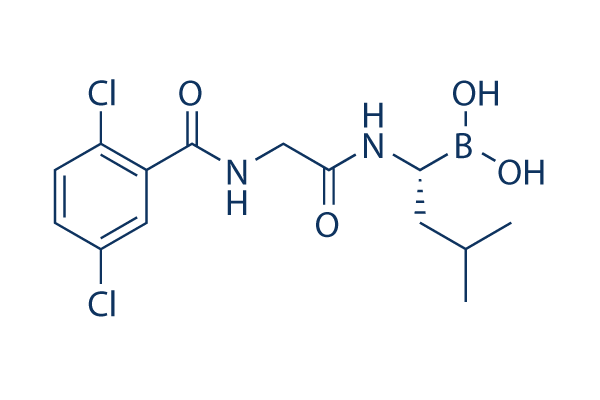
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 361.03
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | HDAC Caspase Secretase MMP HCV Protease Cysteine Protease DPP Tyrosinase HIV Protease Serine Protease |
|---|---|
| Weitere Proteasome Inhibitoren | MG132 Celastrol Epoxomicin (BU-4061T) ONX-0914 (PR-957) Oprozomib Delanzomib VR23 Marizomib (Salinosporamide A) PI-1840 KSQ-4279 (USP1-IN-1) |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HEK293 | Function assay | 1 hr | Inhibition of NFkappaB in HEK293 cells incubated for 1 hr prior to TNF-alpha challenge measured after 3 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay relative to control, IC50 = 0.0062 μM. | ChEMBL | ||
| Calu6 | Function assay | 1 hr | Inhibition of 26S proteasome beta5 subunit in human Calu6 cells using Suc-LLVY-aminoluciferin as substrate after 1hr by luminescence assay, IC50 = 0.009 μM. | ChEMBL | ||
| Calu6 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human Calu6 cells after 72 hrs by luminescence assay, LC50 = 0.014 μM. | ChEMBL | ||
| U266B1 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human U266B1 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 72 hrs by CellTiter 96 aqueous one solution assay, IC50 = 0.05215 μM. | 29934218 | ||
| RPMI8226 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human RPMI8226 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 72 hrs by CellTiter 96 aqueous one solution assay, IC50 = 0.05532 μM. | 29934218 | ||
| ARH77 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human ARH77 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 72 hrs by CellTiter 96 aqueous one solution assay, IC50 = 0.0655 μM. | 29934218 | ||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| fibroblast cells | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for control Hh wild type fibroblast cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 361.03 | Formel | C14H19BCl2N2O4 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 1072833-77-2 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | B(C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C1=C(C=CC(=C1)Cl)Cl)(O)O | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 72 mg/mL
(199.42 mM)
Ethanol : 72 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Merkmale |
A first-in-class proteasome inhibitor that has improved pharmacokinetics (PK), pharmacodynamics(PD), and antitumor activity in preclinical studies.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
20S proteasome
(Cell-free assay) 0.93 nM(Ki)
20S proteasome
(Cell-free assay) 3.4 nM
|
| In vitro |
Bei höheren Konzentrationen hemmt diese Verbindung auch die Caspase-ähnlichen (β1) und Trypsin-ähnlichen (β2) proteolytischen Stellen mit IC50-Werten von 31 nM bzw. 3,5 uM. Es hemmt Calu-6-Zellen mit einem IC50-Wert von 9,7 nM. MLN2238 ist ein selektiver, potenter und reversibler Inhibitor des Proteasome in Tumorzellen. Diese Verbindung zeigt eine zeitabhängige reversible Proteasome-Hemmung. Sowohl diese Verbindung als auch Bortezomib zeigen eine zeitabhängige reversible Proteasome-Hemmung; jedoch ist die Dissoziationshalbwertszeit des Proteasome für sie etwa 6-mal schneller als die von Bortezomib (18 bzw. 110 Minuten). Es dissoziiert schneller vom Proteasome als Bortezomib, was mit einer schnelleren Wiederherstellung der Proteasome-Aktivität übereinstimmt, die im Proteasome-Glo-Assay beobachtet wurde. Es hat einen größeren gesamten Tumor-pharmakodynamischen Effekt als Bortezomib, bewertet durch 20S-Hemmung. Diese Verbindung ist die biologisch aktive Form von MLN9708.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
Kinase-Assay
|
|
Calu-6-Zellen werden in MEM, das 10 % fötales Rinderserum und 1 % Penicillin/Streptomycin enthält, kultiviert und 1 Tag vor Beginn des Experiments mit 1 × 104 Zellen pro Vertiefung in einer 384-Well-Platte ausplattiert. Die Proteasome-Aktivität wird durch Überwachung der Hydrolyse des Chymotrypsin-ähnlichen Substrats Suc-LLVY-aminoluciferin in Gegenwart von Luciferase unter Verwendung der Proteasome-Glo-Assay-Reagenzien gemäß den Anweisungen des Herstellers bewertet. Die Lumineszenz wird mit einem LEADseeker-Instrument gemessen.
|
|
| In vivo |
MLN2238 induziert eine größere pharmakodynamische Reaktion als Bortezomib in Xenograft-Tumoren. Diese Verbindung zeigt eine größere maximale und anhaltende Tumor-Proteasome-Hemmung im Vergleich zu Bortezomib in Xenograft-Modellen. Diese Ergebnisse bestätigen, dass die verbesserte Tumorexposition, die mit diesem Mittel beobachtet wird, sich in eine verbesserte tumorpharmakodynamische Reaktion sowohl auf der Ebene des Proteasome als auch nachgeschaltet vom Proteasome übersetzt. Es zeigt Antitumoraktivität im CWR22-Xenograft-Modell. Diese Chemikalie zeigt im Vergleich zu Bortezomib größere tumorpharmakodynamische Reaktionen in WSU-DLCL2-Xenografts. In ähnlicher Weise führte die Bortezomib-Behandlung nur zu einem geringfügigen Anstieg der GADD34-Spiegel in WSU-DLCL2-Xenograft-Tumoren, während sie dessen Expression stark induziert. Diese Verbindung hat ein verbessertes pharmakodynamisches Profil und eine verbesserte Antitumoraktivität im Vergleich zu Bortezomib in beiden OCI-Ly10- und PHTX22L-Modellen.
|
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
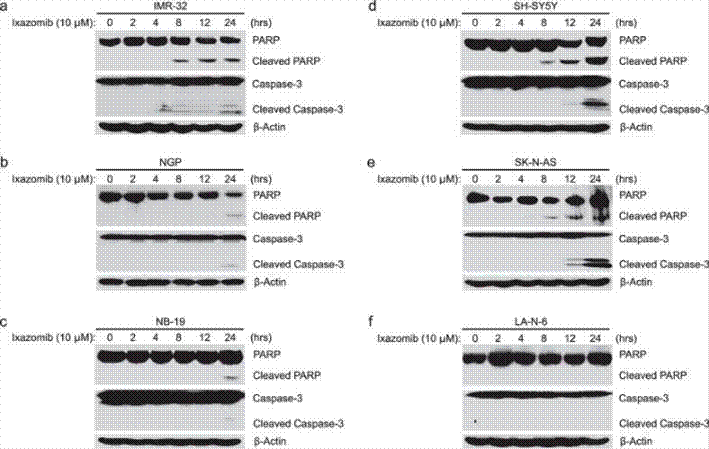
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | PARP / Cleaved PARP / Caspase-3 / Cleaved Caspase-3 Mcl-1 / Bcl-2 p53 / p21 / NOXA / PUMA / pRb / E2F / Cyclin D1 / CDK6 |
|
27687684 |
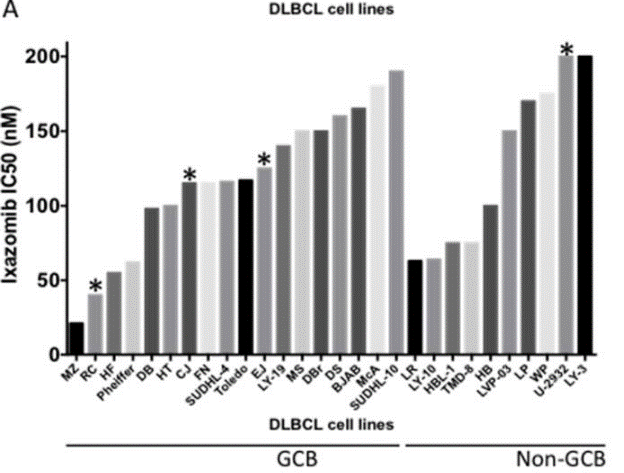
| Growth inhibition assay | IC50 |
|
29416618 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00963820 | Completed | Multiple Myeloma |
Millennium Pharmaceuticals Inc.|Takeda |
October 2009 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
