nur für Forschungszwecke
NVP-AEW541 IGF-1R Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1034
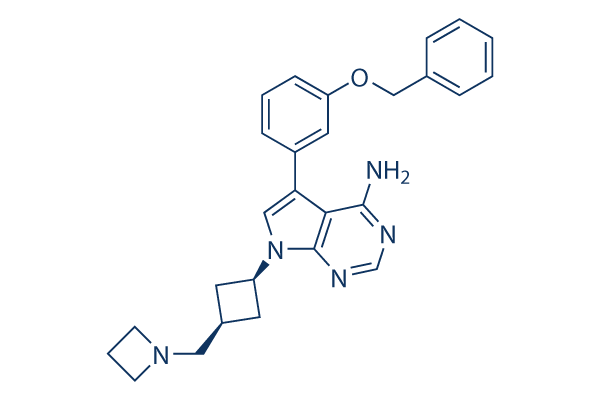
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 439.55
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | EGFR VEGFR PDGFR FGFR c-Met Src MEK CSF-1R FLT3 HER2 |
|---|---|
| Weitere IGF-1R Inhibitoren | Linsitinib (OSI-906) BMS-536924 BMS-754807 Picropodophyllin (AXL1717) GSK1904529A AG-1024 NVP-ADW742 NT157 PQ 401 MSDC-0160 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NWT-21 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-IR with IC50 of 0.086 ± 0.028 μM | 15050915 | |
| A14 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | inhibits InsR with IC50 of 2.3 ± 0.163 μM | 15050915 | |
| A431 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | inhibits HER1 with IC50 of >10 μM | 15050915 | |
| A31 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | inhibits PDGFR with IC50 of >10 μM | 15050915 | |
| GIST882 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | inhibits c-Kit with IC50 of >5 μM | 15050915 | |
| 32D-Bcr-Abl | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | inhibits Bcr-Abl p210 with IC50 of >10 μM | 15050915 | |
| MCF-7 | Cytoxicity assay | DMSO | IC50=1.64 μM | 15050915 | ||
| NWT-21 | Growth inhibitory assay | DMSO | IC50=0.163 μM | 15050915 | ||
| TC-71 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | inhibits insulin-like growth factor-I–mediated growth | 15867386 | |
| TC-71 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| Saos-2 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<3 μM | 15867386 | |
| U-2OS | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| SK-ES-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| SK-N-MC | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| RD-ES | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| SJ-Rh 30 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| SJ-Rh 4 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| 6647 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| SARG | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<3 μM | 15867386 | |
| MOS | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<4 μM | 15867386 | |
| IOR/OS7 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<1 μM | 15867386 | |
| IOR/OS9 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<6 μM | 15867386 | |
| IOR/OS10 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<5 μM | 15867386 | |
| IOR/OS14 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<4 μM | 15867386 | |
| LAP35 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| IOR/BRZ | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| IOR/CAR | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<1 μM | 15867386 | |
| IOR/NGR | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| IOR/RCH | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| RMZ-RC2 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<0.5 μM | 15867386 | |
| CCA | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<2 μM | 15867386 | |
| RD/18 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~7 μM | DMSO | IC50<4 μM | 15867386 | |
| OVCAR-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~15 μM | DMSO | inhibits cell proliferation | 16300820 | |
| OVCAR-4 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~15 μM | DMSO | inhibits cell proliferation | 16300820 | |
| OVCAR-3 | Apoptosis assay | ~15 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 16300820 | |
| OVCAR-4 | Apoptosis assay | ~15 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 16300820 | |
| OVCAR-3 | Function assay | ~15 μM | DMSO | Decreases phosphorylation of AKT | 16300820 | |
| Huh-7 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=1.4 μM | 16530734 | |
| Hep-G2 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=1.8 μM | 16530734 | |
| Hep-3B | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=1.9 μM | 16530734 | |
| SK-Hep-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=6.9 μM | 16530734 | |
| Huh-7 | Function assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | Induces cell cycle arrest | 16530734 | |
| Hep-G2 | Function assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | Induces cell cycle arrest | 16530734 | |
| SK-Hep-1 | Function assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | Induces cell cycle arrest | 16530734 | |
| BON | Kinase assay | ~6 μM | DMSO | induces dephosphorylation of IGF-1R | 16601284 | |
| BON | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=6.6 μM | 16601284 | |
| CM | Growth inhibitory assay | ~5 μM | DMSO | IC50=3.3 μM | 16601284 | |
| BON | Function assay | ~7.5 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest | 16601284 | |
| CM | Function assay | ~5 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest | 16601284 | |
| BON | Apoptosis assay | ~7.5 μM | DMSO | induces Apoptosis | 16601284 | |
| CM | Apoptosis assay | ~5 μM | DMSO | induces Apoptosis | 16601284 | |
| HT-29 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=1.7 μM | 17007015 | |
| HCT-116 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | IC50=2.5 μM | 17007015 | |
| primary colorectal cancer cells | Function assay | ~5 μM | DMSO | alters the morphology of the remaining cells | 17007015 | |
| HTLA-230 | Function assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-II-mediated stimulation of IGF-IR and Akt | 17121898 | |
| KCNR | Function assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-II-mediated stimulation of IGF-IR and Akt | 17121898 | |
| SK-N-BE2c | Function assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-II-mediated stimulation of IGF-IR and Akt | 17121898 | |
| SK-N-BE | Function assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-II-mediated stimulation of IGF-IR and Akt | 17121898 | |
| LAN-5 | Function assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-II-mediated stimulation of IGF-IR and Akt | 17121898 | |
| GI-CA-N | Function assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-II-mediated stimulation of IGF-IR and Akt | 17121898 | |
| SH-EP | Function assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-II-mediated stimulation of IGF-IR and Akt | 17121898 | |
| SK-N-AS | Function assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-II-mediated stimulation of IGF-IR and Akt | 17121898 | |
| RN-GA | Function assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-II-mediated stimulation of IGF-IR and Akt | 17121898 | |
| SY-5Y(N) | Function assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-II-mediated stimulation of IGF-IR and Akt | 17121898 | |
| GI-CA-N | Growth inhibitory assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | IC50= 6.8 μM | 17121898 | |
| SH-EP | Growth inhibitory assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | IC50= 3 μM | 17121898 | |
| HTLA-230 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | IC50= 0.5 μM | 17121898 | |
| SK-N-BE2c | Growth inhibitory assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | IC50= 1.1 μM | 17121898 | |
| SK-N-BE2 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | IC50= 3 μM | 17121898 | |
| SY-5Y (N) | Growth inhibitory assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | IC50= 2.4 μM | 17121898 | |
| LAN-5 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | IC50= 0.4 μM | 17121898 | |
| KCNR | Growth inhibitory assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | IC50= 0.4 μM | 17121898 | |
| RN-GA | Growth inhibitory assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | IC50= 1.3 μM | 17121898 | |
| SK-N-AS | Growth inhibitory assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 17121898 | |
| KCNR | Apoptosis assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 17121898 | |
| GI-CA-N | Apoptosis assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 17121898 | |
| HTLA-230 | Apoptosis assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 17121898 | |
| SK-N-BE2c | Apoptosis assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 17121898 | |
| SY-5Y (N) | Apoptosis assay | ~8 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 17121898 | |
| HL60AR | Function assay | 160 nM | enhances the levels of p27Kip1 | 17361225 | ||
| HL60AR | Apoptosis assay | ~200 nM | induces apoptosis | 17361225 | ||
| HPAF-II | Kinase assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-I-mediated signalling | 18445520 | |
| HPAF-II | Growth inhibitory assay | ~2 μM | DMSO | inhibits cell proliferation | 18445520 | |
| HPAF-II | Function assay | ~2 μM | DMSO | inhibits basal and IGF-I-mediated pancreatic cancer cell migration | 18445520 | |
| TFK-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~250 nM | DMSO | IC50=0.26 μM | 20066734 | |
| EGI-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~250 nM | DMSO | IC50=0.28 μM | 20066734 | |
| CC-LP-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~250 nM | DMSO | IC50=0.15 μM | 20066734 | |
| CC-SW-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~250 nM | DMSO | IC50=0.54 μM | 20066734 | |
| Sk-ChA-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~250 nM | DMSO | IC50=0.2 μM | 20066734 | |
| Mz-ChA-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~250 nM | DMSO | IC50=1.39 μM | 20066734 | |
| Mz-ChA-2 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~250 nM | DMSO | IC50=0.73 μM | 20066734 | |
| ECC-1 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-IR activation by 98% | 21295335 | |
| Ishikawa | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-IR activation by 93% | 21295335 | |
| USPC-1 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-IR activation by 100% | 21295335 | |
| USPC-2 | Kinase assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | inhibits IGF-IR activation by 96% | 21295335 | |
| ECC-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | decreases cell proliferation | 21295335 | |
| Ishikawa | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | decreases cell proliferation | 21295335 | |
| USPC-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | decreases cell proliferation | 21295335 | |
| USPC-2 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | decreases cell proliferation | 21295335 | |
| Ba/F3 | Function assay | Inhibition of full length IGF-1 receptor (unknown origin) transfected in Ba/F3 cells assessed as cell proliferation, IC50=0.02μM | 26951753 | |||
| HEK293 | Function assay | 60 mins | Inhibition of full length IGF-1 receptor (unknown origin) autophosphorylation transfected in HEK293 cells pretreated for 60 mins followed by IGF-1 stimulation measured after 10 mins by quantitative Western blot analysis, IC50=0.065μM | 26951753 | ||
| HEK293 | Function assay | Displacement of [3H]-dofetilide from human ERG channel expressed in HEK293 cells, IC50=0.13μM | 26951753 | |||
| Ba/F3 | Function assay | Inhibition of full length insulin receptor (unknown origin) transfected in Ba/F3 cells assessed as cell proliferation, IC50=0.244μM | 26951753 | |||
| HEK293 | Function assay | 60 mins | Inhibition of full length insulin receptor (unknown origin) autophosphorylation transfected in HEK293 cells pretreated for 60 mins followed by IGF-1 stimulation measured after 10 mins by quantitative Western blot analysis, IC50=0.892μM | 26951753 | ||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 439.55 | Formel | C27H29N5O |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 475489-16-8 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | AEW541 | Smiles | C1CN(C1)CC2CC(C2)N3C=C(C4=C(N=CN=C43)N)C5=CC(=CC=C5)OCC6=CC=CC=C6 | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 88 mg/mL
(200.2 mM)
Ethanol : 24 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Insulin Receptor
(Cell-free assay) 0.14 μM
IGF-1R
(Cell-free assay) 0.15 μM
FLT3
(Cell-free assay) 0.42 μM
Tek
(Cell-free assay) 0.53 μM
FLT1
(Cell-free assay) 0.6 μM
HER4
(Cell-free assay) 1.4 μM
PDGFR
(Cell-free assay) 2.0 μM
KDR
(Cell-free assay) 2.3 μM
c-Src
(Cell-free assay) 2.4 μM
FLT4
(Cell-free assay) 2.4 μM
c-Kit
(Cell-free assay) 3.3 μM
c-Met
(Cell-free assay) 3.8 μM
HER2
(Cell-free assay) 4.1 μM
FGFR1
(Cell-free assay) 4.1 μM
PDK-1
(Cell-free assay) 4.8 μM
HER1
(Cell-free assay) 5.8 μM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
NVP-AEW541 hemmt auch InsR, Tek, Flt1 und Flt3 mit einer IC50 von 140 nM, 530 nM, 600 nM und 420 nM in Assays mit gereinigten Kinasen/rekombinanten Kinasedomänen. Diese Verbindung ist selektiver und zeigt auf zellulärer Ebene eine 27-fach höhere Wirksamkeit als InsR. Sie unterdrückt das IGF-I-vermittelte Überleben, das Weichagar-Wachstum und die Proliferation von MCF-7-Zellen mit einer IC50 von 0,162 μM, 0,105 μM bzw. 1,64 μM. Diese Chemikalie reduziert auch den Spiegel von Phospho-IGF-1R und Phospho-PKB in NWT-21-Zellen. Sie zeigt eine wachstumshemmende Wirkung auf TC-71-Muskuloskelettalsarkomzellen in serumarmem Medium sowie in 10 % FBS-haltigem Medium. Diese Verbindung hemmt den Zellzyklus und induziert einen spezifischen G1-Arrest in Sarkomzelllinien (TC-71, SK-N-MC, SaoS-2, RD/18 und RH4). Sie könnte das Wachstum menschlicher Neuroblastomzellen mit einer IC50 von 0,4-6,8 μM hemmen. Eine Zunahme der hypodiploiden Fraktion und die Depletion der S- und G2-M-Kompartimente konnten in diesen Zelllinien nachgewiesen werden. Diese Verbindung-getriebene Hemmung von IGF-1R führt zu einer Reduktion der Phosphorylierung von Akt, aber nicht von Erk1 und Erk2 in Neuroblastomzellen. Sie hemmt das Gliomzellwachstum und stört die autokrine Schleife, die durch HIF1α-Stabilisierung initiiert wird. Eine aktuelle Studie zeigt, dass diese Chemikalie die Proliferation und Viabilität von PC3-, DU145- und 22Rv1-Prostatakrebszellen unterdrückt, ohne dass ein assoziierter Zelltod erforderlich ist. Sie senkt die Phospho-Akt-Spiegel in 22Rv1- und DU415-Zellen, nicht aber in PC3-Zellen, ohne die Gesamt-Akt-Spiegel zu beeinflussen, was zeigt, dass der PTEN-Status die Wirksamkeit dieser Verbindung mit essentiellem Akt bestimmen könnte. Die durch diese Verbindung induzierte Radiosensibilisierung ist vom Akt-Aktivierungsstatus abhängig. Sie könnte die H2AX-Phosphorylierung (ein Maß für DSBs) in PC3-, DU145- und 22Rv1-Zellen erhöhen.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
In-vitro-Kinase-Assays
|
|
NVP-AEW541 wird in DMSO (10 mM) gelöst und bei -20 °C gelagert. Verdünnungen werden frisch in DMSO/Wasser 1:1 hergestellt. Die Endkonzentration von DMSO in den Enzymassays beträgt <0,5 %. Die Proteinkinase-Assays werden in 96-Well-Platten bei RT durchgeführt und durch Zugabe von 20 μL 125 mM EDTA beendet. Anschließend werden 30 μL (c-Abl, c-Src, IGF-1R) des Reaktionsgemisches auf Immobilon-PVDF übertragen, das 5 Minuten mit Methanol vorbehandelt, mit Wasser gespült, dann 5 Minuten mit 0,5 % H3PO4 getränkt und auf ein Vakuummanifold montiert wurde. Nach dem Auftragen aller Proben wird ein Vakuum angelegt und jede Vertiefung mit 200 μL 0,5 % H3PO4 gespült. Die Membranen werden entfernt und 4-mal auf einem Schüttler mit 1,0 % H3PO4 und einmal mit Ethanol gewaschen. Nach dem Trocknen, Montieren in einem Packard TopCount 96-Well-Rahmen und Zugabe von 10 μL/Well Microscint werden die Membranen gezählt. IC50-Werte werden durch lineare Regressionsanalyse der prozentualen Hemmung dieser Verbindung in Duplikaten bei vier Konzentrationen (üblicherweise 0,01, 0,1, 1 und 10 μM) berechnet. Eine Einheit Proteinkinase-Aktivität ist definiert als 1 nmol 33P, das pro Minute pro mg Protein bei 37 °C von [γ33P]ATP auf das Substratprotein übertragen wird.
|
|
| In vivo |
NVP-AEW541 (50 mg/kg, p.o.) führt zur Aufhebung der basalen und IGF-I-induzierten Rezeptor-, sowie PKB- und MAPK-Phosphorylierung, mit einem T/C-Wert von 14 % im NWT-21-Tumorxenograft. Diese Verbindung (50 mg/kg) verursacht eine Tumorschrumpfung sowohl in HTLA-230- als auch in SK-N-BE2c-Xenografts, ohne Anzeichen systemischer Toxizität. Sie könnte die Tumorinvasion sowohl in Matrigel-beschichteten Kammern als auch in HTLA-230-Xenografts hemmen.
|
Literatur |
|
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
