nur für Forschungszwecke
Picropodophyllin (AXL1717) IGF-1R Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S7668
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 414.41
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | EGFR VEGFR PDGFR FGFR c-Met Src MEK CSF-1R FLT3 HER2 |
|---|---|
| Weitere IGF-1R Inhibitoren | Linsitinib (OSI-906) BMS-536924 NVP-AEW541 BMS-754807 GSK1904529A AG-1024 NVP-ADW742 NT157 PQ 401 MSDC-0160 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-549 (human lung carcinoma) neoplastic cell line | Cytotoxic assay | In vitro cytotoxicity against the A-549 (human lung carcinoma) neoplastic cell line, IC50=60 nM | 14980682 | |||
| P-388 neoplastic cell line | Cytotoxic assay | In vitro cytotoxicity against the P-388 (from DBA/2 mouse) neoplastic cell line, IC50=60 nM | 14980682 | |||
| HT-29 (human colon carcinoma) neoplastic cell line | Cytotoxic assay | In vitro cytotoxicity against the HT-29 (human colon carcinoma) neoplastic cell line, IC50=60 nM | 14980682 | |||
| amnion cells | Antiviral assay | Antiviral activity against HSV1 infected in human primary amnion cells assessed as inhibition of virus-induced pathogenic effect, Activity = 1.9 μM. | 9834179 | |||
| P388 | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against mouse P388 cells, IC50 = 6 μM. | 7673931 | |||
| A549 | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells, IC50 = 6 μM. | 7673931 | |||
| HT-29 | Cytotoxicity assay | Cytotoxicity against human HT-29 cells, IC50 = 6 μM. | 7673931 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 414.41 | Formel | C22H22O8 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 477-47-4 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | AXL1717 | Smiles | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1OC)OC)C2C3C(COC3=O)C(C4=CC5=C(C=C24)OCO5)O | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 83 mg/mL
(200.28 mM)
Ethanol : 1.5 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
IGF-1R
(Cell-free assay) 1 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
In intakten Zellen hemmt PPP effizient die IGF-1-stimulierte IGF-1R-, Akt (Ser 473)- und Erk1/2-Phosphorylierung. Es hemmt spezifisch das Zellwachstum und induziert Apoptose in kultivierten IGF-1R-positiven Tumorzellen. Diese Verbindung sensibilisiert HMCL, primäre menschliche MM- und murine 5T33MM-Zellen synergetisch für ABT-737 und ABT-199, indem sie die Zellviabilität weiter verringert und die Apoptose verstärkt. Sie unterdrückt auch synergetisch die Proliferation und Motilität von hepatozellulären Karzinomzellen. |
| Kinase-Assay |
In-vitro-Tyrosinkinase-Assays.
|
|
Der Assay der IGF-1R-katalysierten Substratphosphorylierung von pTG wird unter Verwendung eines 96-Well-Platten-Tyrosinkinase-Assay-Kits durchgeführt. Wir verwenden rekombinanten epidermalen Wachstumsfaktorrezeptor, immunpräzipitiertes IR aus HEPG2, immunpräzipitiertes IGF-1R aus P6-Zellen und IGF-1R-immunodepletierten Überstand aus P6 (repräsentiert „Nicht-IGF-1R-Tyrosinkinasen“). Nach 30-minütiger Behandlung der Rezeptoren mit den gewünschten Verbindungen im Kinasepuffer [50 mM HEPES-Puffer (pH 7,4), 20 mM MgCl2, 0,1 MnCl2 und 0,2 Na3VO4] wird die Kinase-Reaktion durch Zugabe von ATP aktiviert. Das phosphorylierte Polymersubstrat wird mit einem Phosphotyrosin-spezifischen monoklonalen Antikörper, der an Meerrettichperoxidase gekoppelt ist (Klon PT-66), nachgewiesen. Die Farbentwicklung erfolgt mit dem Meerrettichperoxidase-chromogenen Substrat O-Phenylendiamindihydrochlorid und wird mittels Spektrophotometrie (ELISA-Reader) quantifiziert. Die IGF-1R-Tyrosin-Autophosphorylierung wird mittels eines Sandwich-ELISA-Assays analysiert. Kurz gesagt, 96-Well-Platten werden über Nacht bei 4 °C mit 1 μg/Well eines Antikörpers gegen die IGF-1R β-Untereinheit beschichtet. Die Platten werden 1 Stunde lang mit 1 % BSA in PBS Tween blockiert, und dann werden 80 μg/Well des gesamten Proteinlysats aus der P6-Zelllinie hinzugefügt. Als negative Kontrolle verwenden wir das gesamte Proteinlysat aus der R-Zelllinie. Die untersuchten Verbindungen werden in Tyrosinkinase-Puffer ohne ATP bei Raumtemperatur 30 Minuten vor der Kinaseaktivierung mit ATP hinzugefügt. Der Kinase-Assay wird mit dem Sigma-Kit (siehe oben) durchgeführt. Nach der Spektrophotometrie werden die IC50-Werte der Inhibitoren mit der REGRESSION-Funktion des Statistica-Programms bestimmt.
|
|
| In vivo |
In SCID-Mäusen, die mit humanen ES-1-, BE- und PC3-Xenografts transplantiert wurden, bewirkt Picropodophyllin (PPP) (20 mg/kg/12 h, i.p.) eine vollständige Tumorregression. Diese Verbindung zeigt auch eine deutliche Antitumoraktivität und führt zu einer signifikanten Überlebensverlängerung im 5T33MM-Mausmodell. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-IGFR1 / p-AKT / p-ERK |
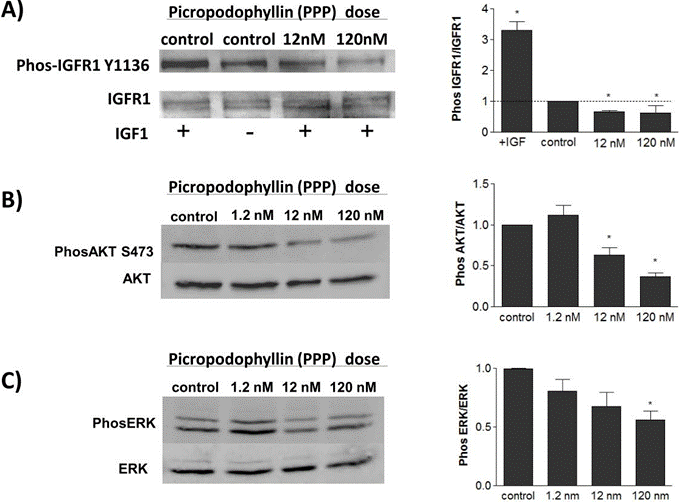
|
22363814 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
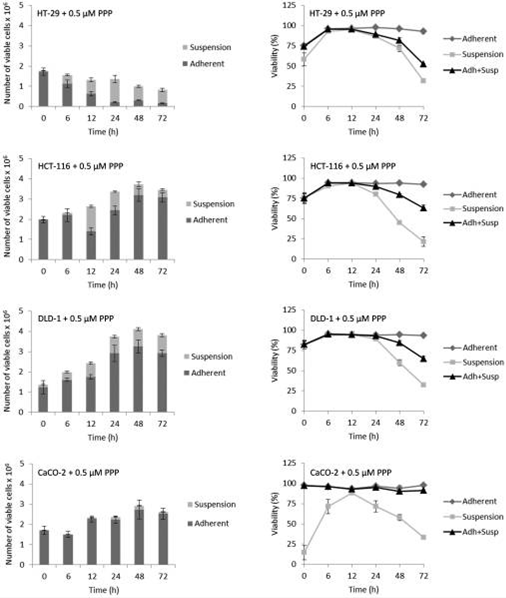
|
22159423 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT06357884 | Recruiting | Diabetic Neuropathies|Plantar Callus |
Chinese University of Hong Kong|Princess Margaret Hospital Hong Kong |
February 23 2024 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05710185 | Recruiting | Palmoplantar Pustulosis |
Brigham and Women''s Hospital|University of Pennsylvania |
July 1 2023 | Phase 4 |
| NCT06025422 | Recruiting | Diabetic Foot Ulcer|Diabetic Neuropathies |
University Hospitals Leicester|University of Salford |
March 13 2023 | -- |
| NCT04433052 | Recruiting | Coronary Heart Disease |
Tampere University |
February 1 2023 | Not Applicable |
| NCT05740137 | Active not recruiting | Colorectal Cancer|Colorectal Adenoma|Colorectal Neoplasms |
Ismail Gögenur|Nykøbing Falster County Hospital|Naestved Hospital|Holbaek Sygehus|Slagelse Hospital|Zealand University Hospital |
October 1 2022 | Not Applicable |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
I am currently setting the conditions for in vivo experiments, how should I reconstitute it?
Antwort:
Other than DMSO:vegetable oil 10:1 (v/v) cited from reference. We tested another formulation: 4% DMSO+corn oil. This compound can be dissolved in it at 5 mg/ml clearly. But after stayed for about 20-30 min, the two phase would separate and wouldn't get together again. So if you are going to use this formulation, please prepare the fresh solution just before use.
