nur für Forschungszwecke
RAF265 (CHIR-265) Raf Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S2161
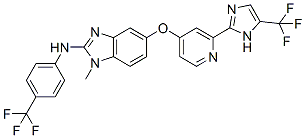
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 518.41
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | ERK p38 MAPK JNK MEK Ras KRas S6 Kinase MAP4K TAK1 Mixed Lineage Kinase |
|---|---|
| Weitere Raf Inhibitoren | LY3009120 Exarafenib (KIN-2787) GDC-0879 Avutometinib (Ro5126766, CH5126766) PLX-4720 AZ 628 SB590885 TAK-632 GW5074 PLX8394 (Plixorafenib, FORE8394) |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SK-MEL-28 | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of SK-MEL-28 cells, IC50=0.14μM. | 21576023 | |||
| MALME-3M | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of MALME-3M cells, IC50=0.14μM. | 21576023 | |||
| A375M | Growth inhibition assay | Growth inhibition of A375M cells, IC50=0.14μM. | 21576023 | |||
| A375 | Function assay | Inhibition of B-RAF V600E mutant in human A375 cells assessed as phosphorylation of ERK, IC50=0.04μM. | 26396681 | |||
| Malme-3M | Function assay | Inhibition of B-RAF V600E mutant in human Malme-3M cells assessed as phosphorylation of ERK, IC50=0.04μM. | 26396681 | |||
| WM-1799 | Function assay | Inhibition of B-RAF V600E mutant in human WM-1799 cells assessed as phosphorylation of ERK, IC50=0.04μM. | 26396681 | |||
| MALME-3M | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human MALME-3M cells harboring B-RAF V600E mutant, IC50=0.04μM. | 26396681 | |||
| A375 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human A375 cells harboring B-RAF V600E mutant, IC50=0.04μM. | 26396681 | |||
| WM1799 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human WM1799 cells harboring B-RAF V600E mutant, IC50=0.04μM. | 26396681 | |||
| SK-MEL-28 | Function assay | Inhibition of B-RAF V600E mutant in human SK-MEL-28 cells assessed as phosphorylation of ERK, IC50=0.14μM. | 26396681 | |||
| SK-MEL-28 | Antiproliferative assay | Antiproliferative activity against human SK-MEL-28 cells harboring B-RAF V600E mutant, IC50=0.16μM. | 26396681 | |||
| A375M | Function assay | 100 mg/kg | fCmin in mouse xenografted with human A375M cells at 100 mg/kg, po q2d, fCmin=0.5μM. | 26396681 | ||
| A375M | Function assay | 100 mg/kg | 48 hrs | Inhibition of B-RAF V600E mutant in mouse xenografted with human A375M cells assessed as reduction of phospho-MEK level in tumor at 100 mg/kg, po q24 after 48 hrs by Western blot analysis | 26396681 | |
| A375M | Function assay | 100 mg/kg | 48 hrs | Inhibition of B-RAF V600E mutant in mouse xenografted with human A375M cells assessed as reduction of phospho-MEK level in tumor at 100 mg/kg, po q2d after 48 hrs by Western blot analysis | 26396681 | |
| A375M | Function assay | 30 to 100 mg/kg | 4 hrs | Inhibition of B-RAF V600E mutant in mouse xenografted with human A375M cells assessed as reduction of phospho-MEK level in tumor at 30 to 100 mg/kg, po q2d measured after 4 hrs post-third dose by Western blot analysis | 26396681 | |
| A375M | Antitumor assay | 10 to 100 mg/kg | 30 days | Antitumor activity against human A375M cells xenografted in mouse assessed as tumor regression at 10 to 100 mg/kg, po q2d measured up to 30 days | 26396681 | |
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| VERO-E6 | Function assay | 48 hrs | Toxicity CC50 against VERO-E6 cells determined at 48 hours by high content imaging (same conditions as 2_LEY without exposure to 0.01 MOI SARS CoV-2 virus), CC50=9.19μM. | ChEMBL | ||
| VERO-E6 | Function assay | 48 hrs | Determination of IC50 values for inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 induced cytotoxicity of VERO-E6 cells after 48 hours exposure to 0.01 MOI SARS CoV-2 virus by high content imaging, IC50=14.64μM. | ChEMBL | ||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 518.41 | Formel | C24H16F6N6O |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 927880-90-8 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | CN1C2=C(C=C(C=C2)OC3=CC(=NC=C3)C4=NC=C(N4)C(F)(F)F)N=C1NC5=CC=C(C=C5)C(F)(F)F | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 100 mg/mL
(192.89 mM)
Ethanol : 33 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
VEGFR2
(Cell-free assay) 30 nM(EC50)
B-Raf
(Cell-free assay) 3 nM-60 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
RAF265 (CHIR-265) hemmt C-Raf, Wildtyp B-Raf und mutiertes (V600E) B-Raf. Diese Verbindung blockiert effektiv die Phosphorylierung der nachgeschalteten Substrate von Raf, MEK und ERK, in Zellen und tötet auch Melanom- und Darmkrebszelllinien ab, die B-Raf-Mutationen unabhängig vom PTEN-Mutationsstatus aufweisen. Die Raf-Kinase-Hemmung durch dieses Mittel in mutierten B-Raf-Melanomzelllinien führt zu einem Zellzyklusarrest und induziert Apoptosis, was den Effekt von Raf RNAi in diesen Zellen nachahmt. Es hemmt auch potent die Phosphorylierung von VEGFR2 und die Proliferation von VEGF-stimulierten hMVEC. In HT29- und MDAMB231-Zellen zeigt diese Chemikalie eine hemmende Aktivität mit einer IC20 von 1 bis 3 μM bzw. einer IC50 von 5 bis 10 μM. Während sie zu einem signifikanten Rückgang des klonogenen Überlebens in allen getesteten Zelllinien führt, was bedeutet, dass diese Verbindung einen dominanten Effekt auf das klonogene Überleben induziert. Die Zugabe dieses Mittels zu RAD001 in HCT116-Zellen könnte zu einer moderat verringerten Phosphorylierung von AKT, S6-Protein und 4EBP1 führen. Es reduziert deutlich den Proteingehalt von Bcl-2 und wirkt stark hemmend in CM- und NCI-H727-Zellen, während es keinen Einfluss auf die TRAIL-Empfindlichkeit von BON1- und GOT1-Zellen hat. Proteinkinase D3 (PRKD3), die bei Hemmung die Zellabtötung durch diese Verbindung in A2058-Melanomzellen verstärken könnte, was die Reaktivierung der MAPK-Signalübertragung verhindert, PARP-Spaltung induziert, die Caspase-Aktivität erhöht, die Zellzyklusprogression unterbricht und die Koloniebildung hemmt.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
Assay-Protokoll
|
|
Raf und Mek werden in 2 × Endkonzentrationen in Assay-Puffer (50 mM Tris, pH 7,5, 15 mM MgCl2, 0,1 mM EDTA und 1 mM DTT) kombiniert und 15 μL pro Vertiefung in Polypropylen-Assay-Platten dosiert. Hintergrundwerte werden in Vertiefungen bestimmt, die Mek und DMSO ohne Raf enthalten. Zu den Raf/Mek-haltigen Vertiefungen werden 3 μL dieser Verbindung, 10 × in 100 % DMSO verdünnt, hinzugefügt. Die Raf-Kinase-Aktivitätsreaktion wird durch die Zugabe von 12 μL pro Vertiefung von 2,5 × 33P-ATP, verdünnt in Assay-Puffer, gestartet. Nach 45–60 Minuten werden die Reaktionen durch Zugabe von 70 μL Stoppreagenz (30 mM EDTA) gestoppt. Filtrationsplatten werden 5 Minuten lang mit 70 % Ethanol vorgewässert und dann durch Filtration mit Waschpuffer gespült. Proben (90 μL) aus den Reaktionsvertiefungen werden dann auf die Filtrationsplatten überführt. Die Filtrationsplatten werden 6 × mit Waschpuffer unter Verwendung eines Millipore-Filtrationsapparates gewaschen. Die Platten werden getrocknet und 100 μL pro Vertiefung Szintillationsflüssigkeit hinzugefügt. Die CPM wird dann mit einem Wallac Microbeta 1450-Lesegerät bestimmt.
|
|
| In vivo |
RAF265 (CHIR-265) zeigt 71 % bis 72 % TVI% (Hemmung des Tumorvolumens) in HCT116-Xenotransplantaten bei 12 mg/kg. Die Kombination dieser Verbindung und RAD001 zeigt eine verstärkte Antitumoraktivität mit erhöhtem T10 (Zeit, um ein relatives Tumorvolumen des 10-fachen des anfänglichen Tumorvolumens zu erreichen) und einer Verzögerung des Tumorwachstums. Die Kombination von RAD001 und dieser Chemikalie verstärkt auch signifikant die Aktivierung von Caspase-3 in HCT116 und MDAMB231, jedoch nicht in A549-Xenotransplantaten. Diese Verbindung hemmt die FDG-Akkumulation (2-Desoxy-2-[18F]fluor-d-glucose) und verringert die Tumorvolumina in A375M-Xenotransplantaten bei oraler Verabreichung von 100 mg/kg.
|
Literatur |
|
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT01352273 | Completed | Advanced Solid Tumors |
Array Biopharma now a wholly owned subsidiary of Pfizer|Array BioPharma |
June 2011 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
