nur für Forschungszwecke
Eprenetapopt (APR-246) p53 Aktivator
Kat.-Nr.S7724
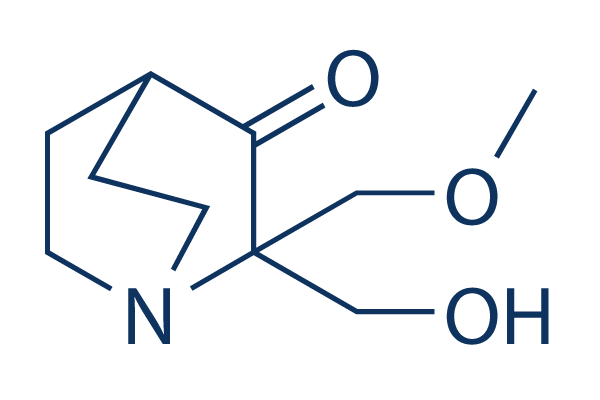
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 199.25
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | Bcl-2 Caspase PD-1/PD-L1 Ferroptosis Apoptosis related Synthetic Lethality STAT TNF-alpha Ras KRas |
|---|---|
| Weitere p53 Inhibitoren | CBL0137 Hydrochloride Pifithrin-α (PFTα) Hhydrobromide Pifithrin-μ Serdemetan (JNJ-26854165) RITA PRIMA-1 NSC 319726 (ZMC1) NSC348884 Tenovin-6 Tenovin-1 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NALM-6 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| UoCB-6 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| EU-3 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| MUTZ-5 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| KOPN-8 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| RS4;11 | Cell viability assay | high sensitivity and cell death induction in all TP53mut leukemias, but low APR-246 sensitivity in TP53wt ALL | 31073076 | |||
| SKBR3 | Cell cycle assay | 5 µM | 2 weeks | lapatinib in combination with APR-246 caused a lower level of G1 arrest and an increase in the sub-G1 fraction | 30743996 | |
| BT549 | Cell viability assay | IC50=3.1 μM | 30196236 | |||
| MDA-MB-468 | Cell viability assay | IC50=5 μM | 30196236 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Cell viability assay | IC50=4.1 μM | 30196236 | |||
| HCC1143 | Cell viability assay | IC50=6.8 μM | 30196236 | |||
| MDA-MB-453 | Cell viability assay | IC50=0.9 μM | 30196236 | |||
| SKBR3 | Cell viability assay | IC50=5.1 μM | 30196236 | |||
| UACC812 | Cell viability assay | IC50=11.3 μM | 30196236 | |||
| MCF7 | Cell viability assay | IC50=31.1 μM | 30196236 | |||
| MCF10A | Cell viability assay | IC50=5.2 μM | 30196236 | |||
| UMSCC10A | Cell viability assay | 0-50 μM | 72 h | suppressed cell survival and bore a modest effect on the killing of HNSCC cells | 29348462 | |
| FaDu | Cell viability assay | 0-50 μM | 72 h | suppressed cell survival and bore a modest effect on the killing of HNSCC cells | 29348462 | |
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 199.25 | Formel | C10H17NO3 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 5291-32-7 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | PRIMA-1MET | Smiles | COCC1(C(=O)C2CCN1CC2)CO | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 40 mg/mL
(200.75 mM)
Water : 40 mg/mL Ethanol : 40 mg/mL |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Mutant p53
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Eprenetapopt (APR-246), auch bekannt als PRIMA-1MET, ist die erste klinische Verbindung, die mutiertes p53 reaktiviert und Apoptosis induziert. Es ist ein Prodrug, das in die aktive Verbindung Methylenchinuklidinon (MQ) umgewandelt wird, einen Michael-Akzeptor, der an Cysteinreste in mutiertem p53 bindet und seine Wildtyp-Konformation wiederherstellt. Diese Verbindung reaktiviert nicht nur p53, sondern senkt auch die intrazellulären Glutathionspiegel dosisabhängig. Es kann Apoptosis auf p53-unabhängige Weise auslösen, indem es ROS und endoplasmatischen Retikulum (ER)-Stress induziert und die Thioredoxinreduktase 1 (TrxR1) hemmt. Es wurde auch berichtet, dass APR-246 den Zelltod in Myelomzellen unabhängig vom p53-Status induziert, indem es das GSH/ROS-Gleichgewicht beeinträchtigt. PRIMA-1Met/APR-246 hemmte effizient das Wachstum der SCLC-Zelllinien, die mutiertes p53 in vitro exprimierten, und induzierte Apoptosis, verbunden mit einem erhöhten Anteil von Zellen mit fragmentierter DNA, Caspase-3-Aktivierung, PARP-Spaltung, Bax- und Noxa-Hochregulation und Bcl-2-Herunterregulation in den Zellen. |
| In vivo |
In einer klinischen Phase-I/II-Dosisfindungsstudie zu hämatologischen Malignomen und Prostatakrebs zeigte Eprenetapopt (APR-246) ein gutes Sicherheitsprofil, und es wurden sowohl klinische als auch p53-abhängige biologische Reaktionen beobachtet. Es wird in Tierstudien gut vertragen, und die einmalige Behandlung mit dieser Verbindung hemmt das Tumorwachstum um 21 % bei Mäusen mit aggressiv wachsenden A2780-CP20-Tumor-Xenografts. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | FL-PARP / Cleaved PARP p-p53 |
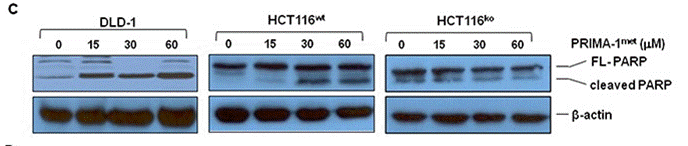
|
26452133 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
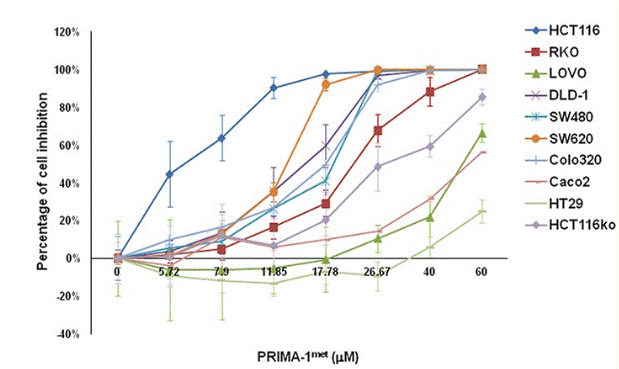
|
26452133 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04383938 | Completed | Bladder Cancer|Gastric Cancer|Non Small Cell Lung Cancer|NSCLC|Urothelial Carcinoma|Advanced Solid Tumor |
Aprea Therapeutics |
June 25 2020 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT04214860 | Completed | Myeloid Malignancy |
Aprea Therapeutics |
December 13 2019 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03391050 | Terminated | Melanoma |
Aprea Therapeutics|Jules Bordet Institute |
January 18 2018 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
| NCT02999893 | Terminated | Oesophageal Carcinoma |
Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre Australia |
April 11 2017 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
