nur für Forschungszwecke
PR-171 (Carfilzomib) Proteasome Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S2853
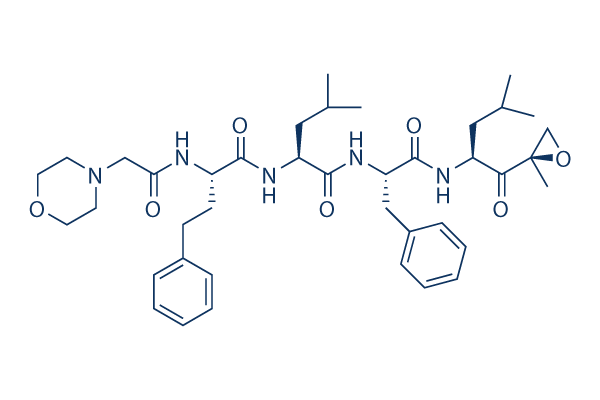
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 719.91
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | HDAC Caspase Secretase MMP HCV Protease Cysteine Protease DPP Tyrosinase HIV Protease Serine Protease |
|---|---|
| Weitere Proteasome Inhibitoren | MG132 Celastrol Epoxomicin (BU-4061T) ONX-0914 (PR-957) Oprozomib Delanzomib VR23 Marizomib (Salinosporamide A) PI-1840 KSQ-4279 (USP1-IN-1) |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MM.1S | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-100 nM | 48 h | IC50 = 10 nM | 25312543 | |
| NCI-H929 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-100 nM | 48 h | IC50 = 14 nM | 25312543 | |
| SUDHL16 | Apoptosis Asssay | 2.5–3.5 nM | 48 h | enhances the cell death co-treatment with ACY1215 | 25239935 | |
| SUDHL14 | Apoptosis Asssay | 2.5–3.5 nM | 48 h | enhances the cell death co-treatment with ACY1215 | 25239935 | |
| U2932 | Apoptosis Asssay | 2.5–3.5 nM | 48 h | enhances the cell death co-treatment with ACY1215 | 25239935 | |
| P-UMSCC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.2 nM | 24915039 | |||
| R-UMSCC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=2294 nM | 24915039 | |||
| P-Cal33 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17.3 nM | 24915039 | |||
| R-Cal33 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1112 nM | 24915039 | |||
| Jurkat | Growth Inhibition Assay | 1-11nM | 48 h | inhibits the cell proliferation co-treatment with vorinostat | 24801128 | |
| Jurkat | Apoptosis Asssay | 8 nM | 24/48 h | induces apoptosis, caspase activation, and PARP cleavage co-treatment with vorinostat | 24801128 | |
| UMSCC-22A | Apoptosis Asssay | 200 nM | 24 h | induce the cell apoptosis co-treatment with ONX 0912 | 22929803 | |
| UMSCC-22B | Apoptosis Asssay | 200 nM | 24 h | induce the cell apoptosis co-treatment with ONX 0912 | 22929803 | |
| 1483 | Apoptosis Asssay | 200 nM | 24 h | induce the cell apoptosis co-treatment with ONX 0912 | 22929803 | |
| UMSCC-1 | Apoptosis Asssay | 200 nM | 24 h | induce the cell apoptosis co-treatment with ONX 0912 | 22929803 | |
| UMSCC-22A | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38.7 ± 1.0 nM | 22929803 | |||
| UMSCC-22B | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.7 ± 9.3 nM | 22929803 | |||
| 1483 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=50.5 ± 11.9 nM | 22929803 | |||
| UMSCC-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34.6 ± 2.6 nM | 22929803 | |||
| Cal33 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=49.3 ± 8.9 nM | 22929803 | |||
| PCI-15A | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=70.4 ± 22.6 nM | 22929803 | |||
| PCI-15B | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=39.5 ± 11.0 nM | 22929803 | |||
| OSC-19 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18.3 ± 4.2 nM | 22929803 | |||
| SUDHL16 | Apoptosis Asssay | 2.0-4.0 nM | 48 h | induces cell death co-treatment with obatoclax | 22411899 | |
| SUDHL16 | Function Assay | 2.5 nM | 24 h | activates JNK, inactivates AKT, up-regulates Noxa, and induces γH2A.X co-treatment with obatoclax | 22411899 | |
| Granta | Growth Inhibition Assay | 0-4 nM | 48 h | induce cell death co-treatment with HADCIs | 21750224 | |
| SUDHL16 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 1-4 nM | 36 h | induce cell death co-treatment with HADCIs | 20233973 | |
| MOLT4 | Function assay | 1 hr | Inhibition of chymotrypsin-like activity of 20S proteasome in human MOLT4 cells after 1 hr by CellTiter-Glo luminescent assay, IC50 = 0.0051 μM. | 19348473 | ||
| MESSA | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MESSA cells assessed as cell viability after 72 hrs by CellTiter-Glo luminescent assay, IC50 = 0.018 μM. | 19348473 | ||
| MESSA | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against multidrug resistance transporter expressing doxorubicin resistant human MESSA cells assessed as cell viability after 72 hrs by CellTiter-Glo luminescent assay, IC50 = 0.413 μM. | 19348473 | ||
| RPMI8226 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxic activity against human RPMI8226 cells after 72 hrs by MTS assay, IC50 = 0.01319 μM. | 24767818 | ||
| NCI-H929 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxic activity against human NCI-H929 cells after 72 hrs by MTS assay, IC50 = 0.02132 μM. | 24767818 | ||
| CCRF-CEM | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human CCRF-CEM cells after 72 hrs by oxyluciferin luminescence assay, IC50 = 0.0061 μM. | 26231162 | ||
| RPMI8266 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human RPMI8266 cells after 72 hrs by oxyluciferin luminescence assay, IC50 = 0.0139 μM. | 26231162 | ||
| HCT116 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human HCT116 cells after 72 hrs by oxyluciferin luminescence assay, IC50 = 0.0193 μM. | 26231162 | ||
| A431 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human A431 cells after 72 hrs by oxyluciferin luminescence assay, IC50 = 0.0238 μM. | 26231162 | ||
| TOV21G | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human TOV21G cells after 72 hrs by oxyluciferin luminescence assay, IC50 = 0.0238 μM. | 26231162 | ||
| RKO | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human RKO cells after 72 hrs by oxyluciferin luminescence assay, IC50 = 0.0271 μM. | 26231162 | ||
| MM1S | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human MM1S cells measured after 72 hrs by MTS assay, IC50 = 0.0015 μM. | 27765408 | ||
| RPMI8226 | Antiproliferative assay | 72 hrs | Antiproliferative activity against human RPMI8226 cells measured after 72 hrs by MTS assay, IC50 = 0.0132 μM. | 27765408 | ||
| LCL | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human LCL cells harboring wild type p53 assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by 7AAD-staining based FACS analysis, LD50 = 0.03 μM. | 27994734 | ||
| RD-ES | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human RD-ES cells harboring p53 mutant assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by 7AAD-staining based FACS analysis, LD50 = 0.043 μM. | 27994734 | ||
| U266 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human U266 cells harboring mutant p53 assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by 7AAD-staining based FACS analysis, LD50 = 0.06 μM. | 27994734 | ||
| WE68 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human WE68 cells harboring wild type p53 assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by 7AAD-staining based FACS analysis, LD50 = 0.08 μM. | 27994734 | ||
| IMR90 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human IMR90 cells harboring wild type p53 assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by 7AAD-staining based FACS analysis, LD50 = 0.13 μM. | 27994734 | ||
| MCF10A | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MCF10A cells harboring wild type p53 assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by 7AAD-staining based FACS analysis, LD50 = 0.32 μM. | 27994734 | ||
| SKOV3 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against p53 deficient human SKOV3 cells assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by 7AAD-staining based FACS analysis, LD50 = 0.32 μM. | 27994734 | ||
| MDA-MB-468 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MDA-MB-468 cells harboring mutant p53 assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by 7AAD-staining based FACS analysis, LD50 = 0.33 μM. | 27994734 | ||
| HNDF | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against HNDF cells harboring wild type p53 assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by 7AAD-staining based FACS analysis, LD50 = 0.35 μM. | 27994734 | ||
| KGN | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human KGN cells harboring wild type p53 assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by 7AAD-staining based FACS analysis, LD50 = 0.45 μM. | 27994734 | ||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MCF7 cells harboring wild type p53 assessed as reduction in cell viability after 48 hrs by 7AAD-staining based FACS analysis, LD50 = 4.5 μM. | 27994734 | ||
| MCF7 | Function assay | 35 nM | 4 hrs | Inhibition of 26S proteasome in human MCF7 cells assessed as accumulation of high molecular weight polyubiquitin-conjugated proteins at 35 nM after 4 hrs by Western blot analysis | 27994734 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | Function assay | 35 nM | 4 hrs | Inhibition of 26S proteasome in human MDA-MB-468 cells assessed as accumulation of high molecular weight polyubiquitin-conjugated proteins at 35 nM after 4 hrs by Western blot analysis | 27994734 | |
| MM1S | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MM1S cells measured after 72 hrs by MTS assay, IC50 = 0.0015 μM. | 28027531 | ||
| RPMI8226 | Cytotoxicity assay | 72 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human RPMI8226 cells measured after 72 hrs by MTS assay, IC50 = 0.0132 μM. | 28027531 | ||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| fibroblast cells | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for control Hh wild type fibroblast cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| fibroblast cells | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for control Hh wild type fibroblast cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Daoy | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for Daoy cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D caspase screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Orthogonal 3D viability screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| ANBL-6 | Function assay | Inhibition of 20S proteasome activity in human ANBL-6 cells, IC50 = 0.01 μM. | 29652143 | |||
| MCF7 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MCF7 cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 0.0041 μM. | 30165344 | ||
| MDA-MB-231 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human MDA-MB-231 cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 0.0044 μM. | 30165344 | ||
| RPMI8226 | Cytotoxicity assay | 48 hrs | Cytotoxicity against human RPMI8226 cells after 48 hrs by MTT assay, IC50 = 0.0067 μM. | 30165344 | ||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 719.91 | Formel | C40H57N5O7 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 868540-17-4 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | CC(C)CC(C(=O)C1(CO1)C)NC(=O)C(CC2=CC=CC=C2)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CCC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)CN4CCOCC4 | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 100 mg/mL
(138.9 mM)
Ethanol : 50 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Proteasome
(ANBL-6 cells) 5 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Carfilzomib (PR-171) hemmt die Proliferation in einer Vielzahl von Zelllinien und von Patienten abgeleiteten neoplastischen Zellen, einschließlich multiplem Myelom, und induzierte intrinsische und extrinsische apoptotische Signalwege sowie die Aktivierung der c-Jun-N-terminalen Kinase (JNK). Es zeigt eine erhöhte Anti-MM-Aktivität, überwindet Resistenzen gegenüber anderen Wirkstoffen und wirkt synergistisch mit (Dex). Diese Verbindung zeigt eine präferenzielle In-vitro-Hemmwirkung gegen die ChT-L-Aktivität in der β5-Untereinheit, mit über 80 % Hemmung bei Dosen von 10 nM. Kurze Exposition gegenüber niedrig dosiertem Carfilzomib führt zu einer präferenziellen Bindungsspezifität für das β5-konstitutive 20S Proteasome und die β5i-Immunproteasome-Untereinheiten. Die Messung der Caspase-Aktivität in mit ihm gepulsten ANBL-6-Zellen zeigt nach 8 Stunden erhebliche Anstiege der Caspase-8-, Caspase-9- und Caspase-3-Aktivität, was eine 3,2-, 3,9- bzw. 6,9-fache Zunahme gegenüber den Kontrollzellen nach 8 Stunden ergibt. In mit Carfilzomib-pulsbehandelten Zellen ist die mitochondriale Membranintegrität auf 41 % (Q1 + Q2) reduziert, verglichen mit 75 % in Vehikel-behandelten Kontrollzellen. In einer anderen Studie hat es auch präklinische Wirksamkeit gegen hämatologische und solide Malignome gezeigt. Es hemmt direkt die Osteoklastenbildung und den Knochenabbau. |
| Kinase-Assay |
Enzymimmunoassays zur Untereinheitenprofilierung von Carfilzomib
|
|
ANBL-6-Zellen (2 × 106/Well) werden in 96-Well-Platten ausgesät und 1 Stunde lang mit Carfilzomib (PR-171) in Dosen von 0,001 bis 10 μM behandelt. Die Zellen werden anschließend lysiert (20 mM Tris-HCl, 0,5 mM EDTA) und die geklärten Lysate in Polymerase-Kettenreaktions (PCR)-Platten überführt. Eine Standardkurve wird unter Verwendung unbehandelter ANBL-6-Zelllysate, beginnend mit einer Proteinkonzentration von 6 μg/μL, erstellt. Die aktive Sondenstelle [Biotin-(CH2)4-Leu-Leu-Leu-Epoxyketon; 20 μM] wird hinzugefügt und 1 Stunde lang bei Raumtemperatur inkubiert. Die Zelllysate werden dann durch Zugabe von 1 % Natriumdodecylsulfat (SDS) und Erhitzen auf 100°C denaturiert, gefolgt von der Mischung mit 20 μL pro Well Streptavidin-Sepharose-Hochleistungsperlen in einer 96-Well-Multiscreen-DV-Platte und einer Inkubation von 1 Stunde. Diese Perlen werden anschließend mit Enzym-Linked-Immunosorbent-Assay (ELISA)-Puffer (PBS, 1 % Rinderserumalbumin und 0,1 % Tween-20) gewaschen und über Nacht bei 4°C auf einem Plattenschüttler mit Antikörpern gegen Proteasome-Untereinheiten inkubiert. Die verwendeten Antikörper umfassten monoklonale Maus-Anti-β1, Anti-β2, Anti-β1i und Anti-β5i, polyklonale Ziegen-Anti-β2i und polyklonale Kaninchen-Anti-β5 (affinitätsgereinigtes Antiserum gegen KLH-CWIRVSSDNVADLHDKYS-Peptid). Die Perlen werden gewaschen und 2 Stunden lang mit Meerrettichperoxidase-konjugierten sekundären Ziegen-Anti-Kaninchen-, Ziegen-Anti-Maus- oder Kaninchen-Anti-Ziegen-Antikörpern inkubiert. Nach dem Waschen werden die Perlen unter Verwendung des Supersignal-ELISA-Picochemilumineszenz-Substrats entwickelt. Es wird eine Lumineszenzdetektion durchgeführt. Die Roh-Lumineszenz wird durch Vergleich mit der Standardkurve in μg/mL umgerechnet und als %-Hemmung relativ zur Vehikelkontrolle ausgedrückt. Kurvenanpassungen werden unter Verwendung der folgenden nicht-sigmoidalen Dosis-Wirkungs-Gleichung erstellt: Y = Boden + (Spitze-Boden)/(1 + 10̂((LogEC50 − X) × HillSlope)), wobei X der Logarithmus der Konzentration, Y die %-Hemmung und EC50 die Dosis dieser Verbindung ist, die einen 50%-Effekt zeigt.
|
|
| In vivo |
Carfilzomib (PR-171) reduziert das Tumorwachstum in einem In-vivo-Xenograft-Modell mäßig. Es verringert die Lebensfähigkeit von multiplem Myelom-Zellen nach kontinuierlicher oder transienter Behandlung effektiv. Diese Verbindung erhöht auch das trabekuläre Knochenvolumen, verringert den Knochenabbau und verbessert die Knochenbildung bei nicht-tumorbelasteten Mäusen. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
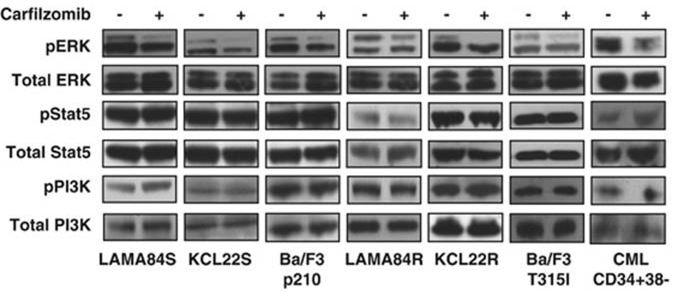
| Western blot | pERK / ERK / pSTAT5 / STAT5 / pPI3K / PI3K caspase-9 / caspase-8 c-PARP / PARP / caspase-3 Bcl-2 / Bcl-Xl / Mcl-1 / Bik / Bim / Bax / Bak Atg5 / Atg12 / Beclin-1 / LC3-II Noxa / Bik / Puma / Mcl-1 EGFR / HER2 / ER alpha / p-Akt(Ser473) / Akt / p-ERK / ERK / p53 BDP1 / HER2(Tyr1248) / HER2(Tyr1221/Tyr1222) / PARP1 / caspase-7 / p53 Mut HLA class I |
|
24590311 |
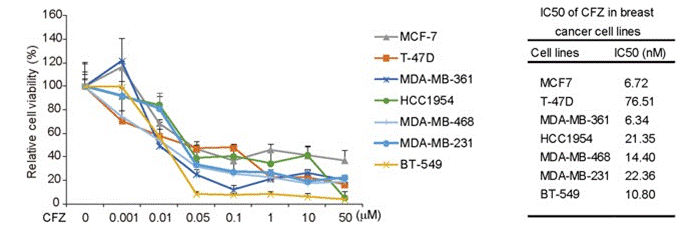
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
27655642 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05552976 | Recruiting | Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma |
Bristol-Myers Squibb |
January 10 2023 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05675449 | Recruiting | Multiple Myeloma |
Pfizer |
December 14 2022 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05041933 | Unknown status | Hematological Diseases |
University Hospital Limoges |
September 15 2021 | -- |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
How should I prepare a solution of it for an ongoing in vivo study?
Antwort:
It can be dissolved in 2% DMSO/30% PEG 300/dd H₂O at 10 mg/ml as a suspension, and can be dissolved in 2% DMSO/castor oil at 10 mg/ml as a clear solution.
