nur für Forschungszwecke
R788 (Fostamatinib) Disodium Syk Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S2206
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 624.42
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | EGFR VEGFR JAK PDGFR FGFR Src HIF FLT FLT3 HER2 |
|---|---|
| Weitere Syk Inhibitoren | R406 R406 (free base) PRT062607 (P505-15) HCl Entospletinib (GS-9973) Piceatannol BAY 61-3606 dihydrochloride PRT-060318 2HCl TAK-659 Hydrochloride Lanraplenib (GS-SYK) RO9021 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ramos | Function assay | Inhibition of SYK in human Ramos cells, IC50 = 0.267 μM. | 23350847 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 624.42 | Formel | C23H24FN6O9P.2Na |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 1025687-58-4 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | Tamatinib Fosdium | Smiles | CC1(C(=O)N(C2=C(O1)C=CC(=N2)NC3=NC(=NC=C3F)NC4=CC(=C(C(=C4)OC)OC)OC)COP(=O)([O-])[O-])C.[Na+].[Na+] | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 12 mg/mL
(19.21 mM)
Water : Insoluble Ethanol : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Merkmale |
Clinically used oral formulation of R406.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
Syk
(Cell-free assay) 41 nM
|
| In vitro |
R935788 ist ein Methylenphosphat-Prodrug von R406, das in vivo schnell in R406 umgewandelt werden kann. R406 (in vitro aktive Form von R935788) hemmt selektiv die Syk-abhängige Signalübertragung mit EC50-Werten im Bereich von 33 nM bis 171 nM, stärker als Syk-unabhängige Signalwege in verschiedenen Zellen. R406 hemmt die Zellproliferation einer Vielzahl von diffusen großzelligen B-Zell-Lymphom-Zelllinien (DLBCL) mit EC50-Werten von 0,8 μM bis 8,1 μM. Die Behandlung mit R406 reduziert die basale Phosphorylierung von BLNK, Akt, Glykogensynthasekinase-3 (GSK-3), Forkhead-Box O (FOXO) und ERK nicht nur in Zellen mit hohen (TCL-002), sondern auch in Zellen mit niedrigen Spiegeln von phosphoryliertem Syk (TCL1-551). Darüber hinaus hemmt R406 das Anti-IgM-induzierte Bcr-Signal bei TCL1-Leukämien vollständig. Trotz der höheren Spiegel an konstitutiv aktivem Syk bei TCL1-Leukämien ist R406 nicht selektiv zytotoxisch für die Leukämiezellen.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
In-vitro-Fluoreszenzpolarisations-Kinase-Assays
|
|
R406 (in vitro aktive Form von R935788) wird in DMSO seriell verdünnt und dann auf 1% DMSO in Kinasepuffer (20 mM HEPES, pH 7,4, 5 mM MgCl2, 2 mM MnCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0,1 mg/mL acetyliertes BGG) verdünnt. ATP und Substrat in Kinasepuffer werden bei Raumtemperatur zugegeben, was zu einer finalen DMSO-Konzentration von 0,2% führt. Die Kinase-Reaktionen werden in einem Endvolumen von 20 μL durchgeführt, das 5 μM HS1-Peptidsubstrat und 4 μM ATP enthält, und durch Zugabe von 0,125 ng Syk in Kinasepuffer gestartet. Die Reaktion wird 40 Minuten bei Raumtemperatur ablaufen gelassen. Die Reaktion wird durch Zugabe von 20 μL PTK-Quench-Mix gestoppt, der EDTA/Anti-Phosphotyrosin-Antikörper (1× final)/fluoreszierenden Phosphopeptid-Tracer (0,5× final) in FP-Dilutionspuffer verdünnt enthält. Die Platte wird 30 Minuten im Dunkeln bei Raumtemperatur inkubiert und dann auf einem Polarion-Fluoreszenzpolarisations-Plattenlesegerät abgelesen. Die Daten werden umgewandelt, um die Menge des vorhandenen Phosphopeptids unter Verwendung einer Kalibrierungskurve zu bestimmen, die durch Konkurrenz mit dem im Tyrosinkinase-Assay-Kit bereitgestellten Phosphopeptid-Kompetitor erzeugt wurde. Zur IC50-Bestimmung wird R406 in elf Konzentrationen in Duplikaten getestet, und die Kurvenanpassung wird durch nichtlineare Regressionsanalyse unter Verwendung der Prism GraphPad Software durchgeführt.
|
|
| In vivo |
Angesichts der Plasmahalbwertszeit von R406 bei Mäusen von weniger als 2 Stunden wird R935788 in 3 geteilten Dosen im Abstand von 3 Stunden verabreicht, um während jedes Behandlungstages eine kontinuierliche Syk-Hemmung zu gewährleisten, was die längere Plasmahalbwertszeit beim Menschen (15 Stunden) nachahmt. Trotz der relativ geringen zytotoxischen Wirkung in vitro hemmt R935788 signifikant die Proliferation und das Überleben von Leukämiezellen in vivo, was mit der Blockierung der antigenabhängigen B-Zell-Rezeptor-Signalübertragung (Bcr) und nicht mit der Hemmung der konstitutiven Syk-Aktivität verbunden ist. Die R935788-Behandlung mit 80 mg/kg/Tag über 18-21 Tage hemmt das Tumorwachstum von TCL1-002, TCL1-551 und TCL1-870 bei Mäusen mit nicht nachweisbaren leukämischen CD5+/B220+-Zellen am letzten Behandlungstag, verlängert das Überleben der behandelten Mäuse signifikant, wobei das mittlere Überleben von 45/46 Tagen auf 170/172 Tage anstieg, und eliminiert die malignen Zellen bei einem erheblichen Teil der Mäuse nach einer 6-monatigen Nachbeobachtungszeit vollständig, ohne die Produktion normaler B-Lymphozyten zu beeinflussen. Die R935788-Behandlung induziert auch eine frühe und vorübergehende Migration sowohl normaler als auch maligner B-Zellen aus Milz und Lymphknoten in das periphere Blut, gefolgt von einer selektiven Wachstumshemmung der malignen B-Zell-Population. Darüber hinaus ist R935788 auch wirksam gegen spontan auftretende TCL1-Leukämien bei Eμ-TCL1-transgenen Mäusen.
|
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | p-JAK2 / JAK2 / p-SRC / SRC / p-FAK / FAK / p-SYK / SYK / p-ERK / ERK p-SYK(525-526) / t-SYK / p-SYK(323) / p-BTK / t-BTK p-MEK / MEK / p-ERK / ERK / p-AKT / AKT |

|
29340070 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
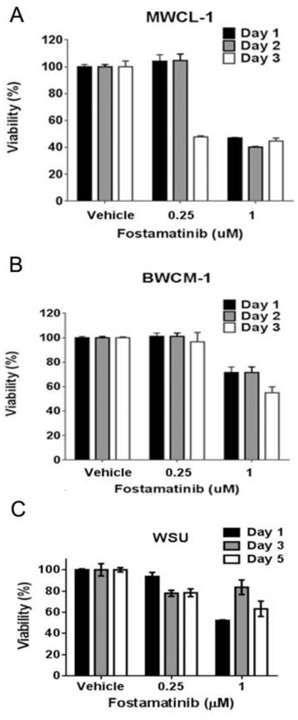
|
25748087 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05904093 | Not yet recruiting | Sickle Cell Disease|Hb-SS Disease|Hemoglobin S|Disease Sickle Cell Anemia|Sickle Cell Disorders|Hemoglobin Beta Thalassemia Disease |
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
May 15 2024 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05509582 | Enrolling by invitation | Immune Mediated Anemia|Immune Mediated Thrombocytopenia|Chronic GVHD |
National Heart Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
May 15 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06071520 | Completed | Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia |
Fundación Pública Andaluza para la gestión de la Investigación en Sevilla |
March 1 2023 | -- |
| NCT05613296 | Not yet recruiting | ITP - Immune Thrombocytopenia|Chronic ITP|Refractory ITP |
Gruppo Italiano Malattie EMatologiche dell''Adulto |
February 2023 | -- |
| NCT04543279 | Terminated | Myelofibrosis|Thrombocytopenia |
Washington University School of Medicine|Rigel Pharmaceuticals |
May 3 2021 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04904276 | Terminated | ITP|Immune Thrombocytopenia |
Rigel Pharmaceuticals |
May 18 2021 | -- |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
What’s the difference between S2625 and S2206?
Antwort:
The differences between S2625 and S2206: 1. S2206 is more stable than S2625; 2. The water solubility of S2206 is better than S2625; 3. The absorption of S2206 is harder than S2625, so you need to test the suitable dosage if you use it in animal assays; 4. The potency of S2206 and S2625 is similar.
