nur für Forschungszwecke
GSK126 EZH2-Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S7061
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 526.67
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | HDAC JAK BET Histone Methyltransferase PKC PARP HIF PRMT AMPK Histone Acetyltransferase |
|---|---|
| Weitere EZH2 Inhibitoren | PF-06821497 Tulmimetostat (CPI-0209) Valemetostat (DS-3201) GSK343 Lirametostat (CPI-1205) EBI-2511 EZH2/HSP90-IN-29 SHR2554 |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| human U87MG cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human U87MG cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by WST-1 assay, GI50=28.5 μM. | 24767850 | ||
| human A549 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human A549 cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by WST-1 assay, GI50=18.7 μM. | 24767850 | ||
| human T98G cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human T98G cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by WST-1 assay, GI50=12.6 μM. | 24767850 | ||
| human Daudi cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human Daudi cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by WST-1 assay, GI50=11.2 μM. | 24767850 | ||
| human PC3 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human PC3 cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by WST-1 assay, GI50=9.4 μM. | 24767850 | ||
| human U2932 cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human U2932 cells assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by WST-1 assay, GI50=6.7 μM. | 24767850 | ||
| human HeLa cells | Function assay | 72 h | Inhibition of EZH2 in human HeLa cells assessed as reduction in H3K27me3 levels incubated for 72 hrs by ELISA method, IC50=0.28 μM. | 26189078 | ||
| human Pfeiffer cells | Cytotoxic assay | 72 h | Cytotoxicity against human Pfeiffer cells expressing EZH2 A667G mutant assessed as growth inhibition after 72 hrs by WST-1 assay, GI50=0.18 μM. | 24767850 | ||
| infected SF9 cells | Binding affinity to EZH2 (unknown origin) expressed in baculovirus infected SF9 cells co-expressing SUZ12/EED/RbAp48 complex assessed as binding off-rate at 0.4 uM incubated for 20 mins by Q-TOF mass spectrometry | 27512831 | ||||
| A673 cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | ||||
| DAOY cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | ||||
| Saos-2 cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | ||||
| BT-37 cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | ||||
| RD cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | ||||
| SK-N-SH cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | ||||
| BT-12 cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | ||||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | ||||
| NB1643 cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | ||||
| OHS-50 cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | ||||
| Rh41 cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | ||||
| SK-N-MC cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | ||||
| LAN-5 cells | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | ||||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 526.67 | Formel | C31H38N6O2 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 1346574-57-9 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | GSK2816126A, GSK2816126 | Smiles | CCC(C)N1C=C(C2=C(C=C(C=C21)C3=CN=C(C=C3)N4CCNCC4)C(=O)NCC5=C(C=C(NC5=O)C)C)C | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 5 mg/mL
(9.49 mM)
Ethanol : 4 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
EZH2
(Cell-free assay) 9.9 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
In vitro hemmt GSK126 am stärksten H3K27me3, gefolgt von H3K27me2 in sowohl EZH2-Wildtyp- als auch mutierten DLBCL-Zelllinien. Diese Verbindung hemmt auch effektiv die Proliferation von EZH2-mutierten DLBCL-Zelllinien und induziert die Transkriptionsaktivierung von EZH2-Zielgenen in sensitiven Zelllinien. In A687V EZH2-mutanten Zellen führt diese Behandlung zu einer globalen Abnahme von H3K27me3, einer robusten Genaktivierung, Caspase-Aktivierung und einer verminderten Proliferation. In den Eltern-H2087-Zellen hemmt es die Expression von VEGF-A und phosphoryliertem Ser(473)-AKT und bewirkt somit die Hemmung der Zellproliferation, Migration und Metastasierung.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
EZH2-Assay
|
|
Der fünfköpfige PRC2-Komplex (Flag–EZH2, EED, SUZ12, AEBP2, RbAp48), der entweder Wildtyp- oder mutiertes EZH2 enthält, wird hergestellt. GSK126 wird in DMSO gelöst und in Konzentrationen von 0,6 nM bis 300 nM mit einer finalen DMSO-Konzentration von 2,5 % getestet. Im Gegensatz zum Wildtyp-EZH2, das in vitro H3K27me0 als Substrat bevorzugt, bevorzugen EZH2 Y641-Mutanten H3K27me2 und zeigen wenig Aktivität mit H3K27me0 oder H3K27me1. Der A677G-Mutant unterscheidet sich sowohl von der Wildtyp- als auch von den Y641-Mutantenformen von EZH2 dadurch, dass er H3K27me0, H3K27me1 und H3K27me2 effizient methyliert; daher werden Histon-H3-Peptide (Reste 21–44; 10 μM final) mit entweder K27me0 (Wildtyp, A677G EZH2), K27me1 (A677G EZH2) oder K27me2 (A677G, Y641N, Y641C, Y641H, Y641S und Y641F EZH2) als methyltransferase-Substrate verwendet. Diese Verbindung wird zu den Platten gegeben, gefolgt von der Zugabe von 6 nM EZH2-Komplex und Peptid. Da die Potenz dieser Chemikalie an oder nahe der engen Bindungsgrenze eines Assays liegt, der bei [SAM] = Km durchgeführt wird, werden IC50-Werte bei einer hohen Konzentration des kompetitiven Substrats SAM relativ zu seinem Km (7,5 μM SAM, wobei der SAM Km 0,3 μM beträgt) gemessen. Unter diesen Bedingungen wird der Beitrag der Enzymkonzentration relativ gering, und genaue Schätzungen von Ki können berechnet werden. Reaktionen werden mit [3H]-SAM initiiert, 30 Minuten inkubiert, durch Zugabe eines 500-fachen Überschusses an unmarkiertem SAM gequencht und das methylierte Produktpeptid wird auf Phosphozellulosefiltern gemäß dem vom Hersteller gelieferten Protokoll für MSPH Multiscreen-Platten eingefangen. Die Platten werden auf einem TopCount ausgelesen, nachdem 20 μL Microscint-20-Cocktail hinzugefügt wurden. Apparente Ki-Werte werden unter Verwendung der Cheng–Prusoff-Beziehung für einen kompetitiven Inhibitor berechnet. IC50=Ki (1+[S]/Km)+[E]/2, wobei E das Enzym und S das Substrat ist.
|
|
| In vivo |
Bei Mäusen mit KARPAS-422- und Pfeiffer-Xenografts senkt GSK126 (150 mg/kg/d, i.p.) das globale H3K27me3, erhöht die Genexpression und führt somit zu einer deutlichen Tumorrückbildung.
|
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
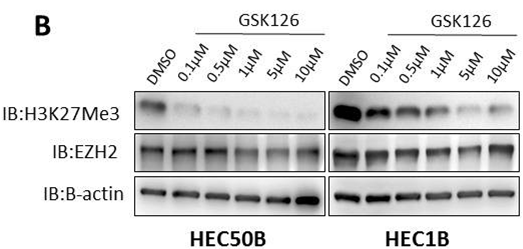
| Western blot | H3K27Me3 / EZH2 XIAP / Survivin / MCL-1 / BID / BIM / BAX / BCL-xl/ Bcl-2 β-catenin / c-Myc / LEF1 / DVL2 / DVL3 / p-GSK3β |
|
28418882 |
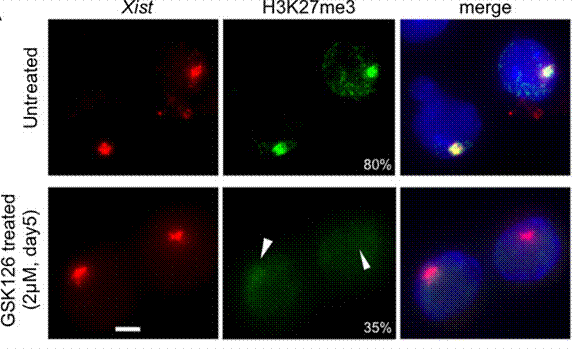
| Immunofluorescence | H3K27me3 |
|
25053977 |
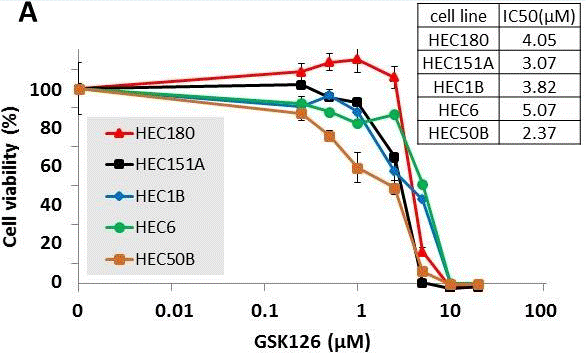
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability Cell proliferation |
|
28418882 |
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02082977 | Terminated | Cancer|Neoplasms |
GlaxoSmithKline |
April 24 2014 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
Could you please suggest a vehicle for in vivo uses of this compound without oil?
Antwort:
It could be dissolved in 4% DMSO+30% PEG 300+ddH2O (0.5mg/ml).
Frage 2:
Does this compound require an activation step to be functional? For example, an acidic or basic environment.
Antwort:
It does not require an activation step to be functional.
