nur für Forschungszwecke
I-BET151 (GSK1210151A) BET Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S2780
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 415.44
Qualitätskontrolle
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MV4;11 | cytotoxicity assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | IC50=26 nM | 21964340 | |
| RS4;11 | cytotoxicity assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | IC50=192 nM | 21964340 | |
| MOLM13 | cytotoxicity assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | IC50=120 nM | 21964340 | |
| NOMO1 | cytotoxicity assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | IC50=15 nM | 21964340 | |
| HEL | cytotoxicity assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | IC50=1 μM | 21964340 | |
| K562 | cytotoxicity assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | IC50>100 μM | 21964340 | |
| MEG01 | cytotoxicity assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | IC50=25 μM | 21964340 | |
| HL60 | cytotoxicity assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | IC50=890 nM | 21964340 | |
| MV4;11 | Apoptosis assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 21964340 | |
| MOLM13 | Apoptosis assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 21964340 | |
| MV4;11 | Function assay | DMSO | decreases the recruitment of BRD3/4 and impaired recruitment of CDK9 and PAF1 to the transcriptional start site | 21964340 | ||
| PBMC | Function assay | DMSO | inhibits IL-6 with pIC50 of 6.7 | 22437115 | ||
| A2 | Function assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | reactivates latent HIV-1 | 23255218 | |
| A72 | Function assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | reactivates latent HIV-1 | 23255218 | |
| BC1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | IC50=220 nM | 23792448 | |
| BC3 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | IC50=460 nM | 23792448 | |
| BCBL1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | IC50=330 nM | 23792448 | |
| BJAB | Growth inhibitory assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | IC50=970 nM | 23792448 | |
| Namalwa | Growth inhibitory assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | IC50=970 nM | 23792448 | |
| Jurkat | Growth inhibitory assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | IC50=1220 nM | 23792448 | |
| MM1S | Growth inhibitory assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | IC50=760 nM | 23792448 | |
| U266 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | IC50=950 nM | 23792448 | |
| UM-PEL-1 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | IC50=210 nM | 23792448 | |
| UM-PEL-3 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | IC50=180 nM | 23792448 | |
| BC1 | Function assay | 500 nM | DMSO | induces cell-cycle arrest | 23792448 | |
| BC3 | Function assay | 500 nM | DMSO | induces cell-cycle arrest | 23792448 | |
| BC1 | Function assay | 800 nM | DMSO | reduces c-Myc protein levels | 23792448 | |
| BC3 | Function assay | 800 nM | DMSO | reduces c-Myc protein levels | 23792448 | |
| H929 | Function assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest | 24335499 | |
| KMS12PE | Function assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest | 24335499 | |
| KMS12BM | Function assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest | 24335499 | |
| KMS18 | Function assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest | 24335499 | |
| KMS11 | Function assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest | 24335499 | |
| RPMI8226 | Function assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest | 24335499 | |
| H929 | Apoptosis assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell apoptosis | 24335499 | |
| KMS12PE | Apoptosis assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell apoptosis | 24335499 | |
| KMS12BM | Apoptosis assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell apoptosis | 24335499 | |
| KMS18 | Apoptosis assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell apoptosis | 24335499 | |
| KMS11 | Apoptosis assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell apoptosis | 24335499 | |
| RPMI8226 | Apoptosis assay | ~1 μM | DMSO | induces cell apoptosis | 24335499 | |
| U87MG | Function assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | reduces U87MG cellular ATP with IC50 of 1.05 μM | 24496381 | |
| A172 | Function assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | reduces cellular ATP with IC50 of 1.28 μM | 24496381 | |
| SW1783 | Function assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | reduces cellular ATP with IC50 of 2.68 μM | 24496381 | |
| U87MG | Function assay | ~10 μM | DMSO | increases proportion of cells in the G1/S transition | 24496381 | |
| RAW267.4 | Function assay | 1 μM | DMSO | reduces IL-6 production induced by LPS | 24859008 | |
| RAW267.4 | Function assay | 1 μM | DMSO | reduces the association between BRD4 and acetylated p65 | 24859008 | |
| Me007 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | inhibits the growth | 24906137 | |
| SK-Mel-28 | Growth inhibitory assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | inhibits the growth | 24906137 | |
| Mel-RMU | Growth inhibitory assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | inhibits the growth | 24906137 | |
| Mel-JD | Growth inhibitory assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | inhibits the growth | 24906137 | |
| Mel-RM | Growth inhibitory assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | inhibits the growth | 24906137 | |
| Me007 | Apoptosis assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 24906137 | |
| SK-Mel-28 | Apoptosis assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 24906137 | |
| Mel-RMU | Apoptosis assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 24906137 | |
| Mel-JD | Apoptosis assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 24906137 | |
| Mel-RM | Apoptosis assay | ~100 μM | DMSO | induces apoptosis | 24906137 | |
| Me007 | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest by upregulation of p21 | 24906137 | |
| SK-Mel-28 | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest by upregulation of p21 | 24906137 | |
| Mel-RMU | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest by upregulation of p21 | 24906137 | |
| Mel-JD | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest by upregulation of p21 | 24906137 | |
| Mel-RM | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | induces cell cycle arrest by upregulation of p21 | 24906137 | |
| Me007 | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | upregulates proapoptotic and cell cycle arrest genes | 24906137 | |
| SK-Mel-28 | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | upregulates proapoptotic and cell cycle arrest genes | 24906137 | |
| Mel-RMU | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | upregulates proapoptotic and cell cycle arrest genes | 24906137 | |
| Mel-JD | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | upregulates proapoptotic and cell cycle arrest genes | 24906137 | |
| Mel-RM | Function assay | 10 μM | DMSO | upregulates proapoptotic and cell cycle arrest genes | 24906137 | |
| HepG2 | Function assay | 18 hrs | Upregulation of ApoA1 expression in human HepG2 cells assessed as concentration required to increase 70% of luciferase activity after 18 hrs by luciferase reporter gene assay, EC170 = 0.09 μM. | 22386529 | ||
| Raji | Function assay | 4 hrs | Inhibition of BRD4 in human Raji cells assessed as reduction of MYC expression after 4 hrs, IC50 = 0.13 μM. | 24900758 | ||
| MV4-11 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 hrs | Growth inhibition of human MV4-11 cells after 72 hrs by SRB assay, IC50 = 0.119 μM. | 25559428 | ||
| MM1S | Growth inhibition assay | 72 hrs | Growth inhibition of human MM1S cells after 72 hrs by SRB assay, IC50 = 0.299 μM. | 25559428 | ||
| HT-29 | Growth inhibition assay | 72 hrs | Growth inhibition of human HT-29 cells after 72 hrs by SRB assay, IC50 = 0.945 μM. | 25559428 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Displacement of FAM-labeled ZBA248 from BRD4 BD1 (44 to 168 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by fluorescence polarization assay, IC50 = 0.0317 μM. | 26080064 | ||
| MV4-11 | Cytotoxicity assay | 4 days | Cytotoxicity against human MV4-11 cells harboring MLL1 fusion gene assessed as growth inhibition after 4 days by CellTiter-Glo luminescent assay, IC50 = 0.162 μM. | 26080064 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Displacement of FAM-labeled ZBA248 from BRD4 BD2 (333 to 460 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by fluorescence polarization assay, IC50 = 0.226 μM. | 26080064 | ||
| MOLM13 | Cytotoxicity assay | 4 days | Cytotoxicity against human MOLM13 cells harboring MLL1 fusion gene assessed as growth inhibition after 4 days by CellTiter-Glo luminescent assay, IC50 = 0.228 μM. | 26080064 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of FAM-labeled ZBA248 binding to recombinant human N-terminal His6-tagged BRD4 bromodomain 1 (44 to 168 residues) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by Flourescence polarization assay, IC50 = 0.0317 μM. | 28463487 | ||
| MV4-11 | Growth inhibition assay | 4 days | Growth inhibition of human MV4-11 cells after 4 days by WST-8 assay, IC50 = 0.162 μM. | 28463487 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of FAM-labeled ZBA248 binding to recombinant human N-terminal His6-tagged BRD4 bromodomain 2 (333 to 460 residues) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by Flourescence polarization assay, IC50 = 0.226 μM. | 28463487 | ||
| MOLM13 | Growth inhibition assay | 4 days | Growth inhibition of human MOLM13 cells after 4 days by WST-8 assay, IC50 = 0.228 μM. | 28463487 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | Binding affinity to biotinylated BRD3 BD1 (24 to 144 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells by bio-layer interferometry method, Kd = 0.0298 μM. | 26080064 | |||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | Binding affinity to biotinylated BRD3 BD2 (306 to 417 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells by bio-layer interferometry method, Kd = 0.0405 μM. | 26080064 | |||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | Binding affinity to biotinylated BRD4 BD1 (44 to 168 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells by bio-layer interferometry method, Kd = 0.0528 μM. | 26080064 | |||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | Binding affinity to biotinylated BRD2 BD1 (72 to 205 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells by bio-layer interferometry method, Kd = 0.0548 μM. | 26080064 | |||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | Binding affinity to biotinylated BRD2 BD2 (349 to 460 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells by bio-layer interferometry method, Kd = 0.0703 μM. | 26080064 | |||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | Binding affinity to biotinylated BRD4 BD2 (333 to 460 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells by bio-layer interferometry method, Kd = 0.215 μM. | 26080064 | |||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | Binding affinity to biotinylated CREBBP (1043 to 1159 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells by bio-layer interferometry method, Kd = 3.084 μM. | 26080064 | |||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Displacement of FAM-labeled ZBA248 from BRD3 BD1 (24 to 144 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by fluorescence polarization assay, Ki = 0.0072 μM. | 26080064 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Displacement of FAM-labeled ZBA248 from BRD4 BD1 (44 to 168 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by fluorescence polarization assay, Ki = 0.009 μM. | 26080064 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Displacement of FAM-labeled ZBA248 from BRD2 BD1 (72 to 205 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by fluorescence polarization assay, Ki = 0.009 μM. | 26080064 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Displacement of FAM-labeled ZBA248 from BRD3 BD2 (306 to 417 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by fluorescence polarization assay, Ki = 0.0223 μM. | 26080064 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Displacement of FAM-labeled ZBA248 from BRD2 BD2 (349 to 460 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by fluorescence polarization assay, Ki = 0.0496 μM. | 26080064 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Displacement of FAM-labeled ZBA248 from BRD4 BD2 (333 to 460 amino acid residues) (unknown origin) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by fluorescence polarization assay, Ki = 0.0748 μM. | 26080064 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of FAM-labeled ZBA248 binding to recombinant human N-terminal His6-tagged BRD4 bromodomain 1 (44 to 168 residues) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by Flourescence polarization assay, Ki = 0.009 μM. | 28463487 | ||
| Rosetta2 DE3 | Function assay | 30 mins | Inhibition of FAM-labeled ZBA248 binding to recombinant human N-terminal His6-tagged BRD4 bromodomain 2 (333 to 460 residues) expressed in Rosetta2 DE3 cells after 30 mins by Flourescence polarization assay, Ki = 0.0748 μM. | 28463487 | ||
| THP1 | Antiinflammatory assay | Antiinflammatory activity in human THP1 cells | 22386529 | |||
| HT-29 | Function assay | 0.3125 uM to 5 uM | 24 hrs | Inhibition of BRD4 in human HT-29 cells assessed as reduction in c-Myc protein expression at 0.3125 uM to 5 uM uM after 24 hrs by Western blotting method | 25559428 | |
| MV4-11 | Function assay | Inhibition of BRD4 in human MV4-11 cells assessed as downregulation of BCL2 RNA expression by RNA-seq analysis | 29259751 | |||
| MV4-11 | Function assay | Inhibition of BRD4 in human MV4-11 cells assessed as downregulation of cMYC RNA expression by RNA-seq analysis | 29259751 | |||
| U-2 OS | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for U-2 OS cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| DAOY | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for DAOY cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-12 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-12 cells | 29435139 | |||
| MG 63 (6-TG R) | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for MG 63 (6-TG R) cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| fibroblast cells | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for control Hh wild type fibroblast cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh41 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh41 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh30 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh30 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 415.44 | Formel | C23H21N5O3 |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 1300031-49-5 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | CC1=C(C(=NO1)C)C2=C(C=C3C(=C2)N=CC4=C3N(C(=O)N4)C(C)C5=CC=CC=N5)OC | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 83 mg/mL
(199.78 mM)
Ethanol : 83 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Merkmale |
Optimized to retain excellent BET target potency and selectivity while enhancing the in vivo pharmacokinetics and terminal half-life to enable prolonged in vivo studies.
|
|---|---|
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
BRD3
(Cell-free assay) 0.25 μM
BRD2
(Cell-free assay) 0.5 μM
BRD4
(Cell-free assay) 0.79 μM
|
| In vitro |
I-BET151 (GSK1210151A) zeigt eine potente Selektivität über eine Vielzahl unterschiedlicher Proteintypen wie COX-2, P450, Aurora B, GSK3β, PI3K-γ, GPCR, Ionenkanäle und Transporter. Ähnlich wie I-BET762 (GSK525762A) zeigt es eine potente Bindungsaffinität zu BRD2, BRD3 und BRD4 mit einem KD von 0,02-0,1 μM und hemmt signifikant die Lipopolysaccharid-stimulierte IL-6-Zytokinproduktion in humanen peripheren mononukleären Zellen (PBMC) und Vollblut (WB) sowie Ratten-WB mit einem IC50 von 0,16 μM, 1,26 μM bzw. 1,26 μM. Diese Verbindung (0,5 oder 5 μM) hemmt die Bindung von BETs (BRD2, BRD3, BRD4 und BRD9), aber nicht die Bindung von 23 anderen Bromodomänenproteinen im HL60-Kernextrakt an acetylierte Histonpeptide. Es hat eine potente Wirksamkeit gegen Zelllinien, die verschiedene MLL-Fusionen wie MV4;11, RS4;11, MOLM13 und NOMO1-Zellen mit einem IC50 von 15-192 nM aufweisen. Konsistenterweise ablatiert es vollständig das Kolonie-bildende Potenzial von MLL-Fusions-getriebenen Leukämien (MOLM13), aber nicht von Leukämien, die durch Tyrosinkinase-Aktivierung (K562) angetrieben werden. I-BET151 zeigt auch eine potente Wirksamkeit in sowohl Flüssigkeitskultur- als auch klonogenen Assays unter Verwendung primärer muriner Vorläuferzellen, die entweder mit MLL-ENL oder MLL-AF9 transformiert wurden. Die Behandlung mit dieser Verbindung induziert signifikant Apoptose und einen prominenten G0/G1-Arrest in MLL-Fusionszelllinien, die durch unterschiedliche MLL-Fusionen angetrieben werden (MOLM13 und MV4;11, die MLL-AF9 bzw. MLL-AF4 enthalten), aber nicht in K562-Zellen, wahrscheinlich aufgrund der Hemmung der Transkription von BCL2, C-MYC und CDK6 durch Blockierung der Rekrutierung von BRD3/4-, PAFc- und SEC-Komponenten an die Transkriptionsstartstelle (TSS).
|
| Kinase-Assay |
Fluoreszenzanisotropie (FP) Ligandenverdrängungsassay
|
|
Alle Komponenten werden in einem Puffer der Zusammensetzung 50 mM HEPES pH 7,4, 150 mM NaCl und 0,5 mM CHAPS gelöst, mit Endkonzentrationen von BRD 2/3/4 75 nM, fluoreszierendem Liganden 5 nM. 10 μL dieser Reaktionsmischung werden mit einem Mikro-Multidrop in Vertiefungen gegeben, die 100 nL verschiedener Konzentrationen von I-BET151 (GSK1210151A) oder DMSO-Träger (1 % final) in einer Greiner 384-Well Black Low Volume Mikrotiterplatte enthalten und 60 Minuten bei Raumtemperatur im Dunkeln äquilibriert werden. Die Fluoreszenzanisotropie wird im Envision (lex = 485 nm, lEM = 530 nm; Dichroit = 505 nM) abgelesen.
|
|
| In vivo |
I-BET151 (GSK1210151A) hemmt, wenn es in einer Dosis von 30 mg/kg/Tag verabreicht wird, signifikant das Tumorwachstum von muriner MLL-AF9- und humaner MLL-AF4-Leukämie bei Mäusen und bietet einen deutlichen Überlebensvorteil.
|
Literatur |
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western blot | α-SMA / Fibronectin / Collagen-1 FoxM1 / AURKB / Survivin / cyclin B / PLK1 HP1α / HP1β / HP1γ |
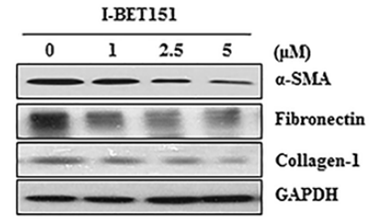
|
27732564 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
