nur für Forschungszwecke
PF-562271 Besylate FAK Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S2672
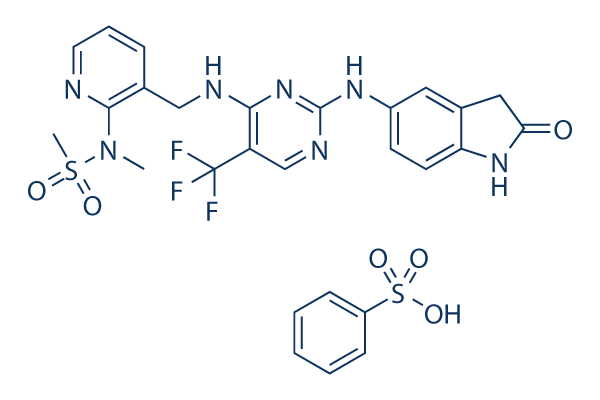
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 665.66
Qualitätskontrolle
| Verwandte Ziele | EGFR VEGFR JAK PDGFR FGFR Src HIF FLT FLT3 HER2 |
|---|---|
| Weitere FAK Inhibitoren | Defactinib (VS-6063) PF-562271 (VS-6062) PF-573228 VS-4718 (PND-1186) PF-562271 HCl TAE226 (NVP-TAE226) GSK2256098 PF-431396 Y15 Solanesol (Nonaisoprenol) |
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MV-4-11 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MV-4-11 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.2766 μM | ||||
| human SW982 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW982 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.3282 μM | ||||
| human KM12 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KM12 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.38557 μM | ||||
| human COLO-205 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human COLO-205 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.48658 μM | ||||
| human COLO-829 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human COLO-829 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.76176 μM | ||||
| human MG-63 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MG-63 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.80637 μM | ||||
| human IGROV-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human IGROV-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.81038 μM | ||||
| human NCI-H650 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H650 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.83154 μM | ||||
| human RT-112 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human RT-112 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=0.9846 μM | ||||
| human BCPAP cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BCPAP cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.01288 μM | ||||
| ALL-PO cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ALL-PO cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.01584 μM | ||||
| human KYSE-270 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-270 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.04714 μM | ||||
| human 8305C cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human 8305C cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.09904 μM | ||||
| NCI-H810 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H810 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.10776 μM | ||||
| human CAL-33 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-33 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.12938 μM | ||||
| human AN3-CA cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human AN3-CA cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.21867 μM | ||||
| human NKM-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NKM-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.27506 μM | ||||
| human BPH-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BPH-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.28766 μM | ||||
| human MES-SA cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MES-SA cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.30682 μM | ||||
| human CAL-62 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CAL-62 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.31909 μM | ||||
| human KYSE-150 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human KYSE-150 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.35236 μM | ||||
| human SK-UT-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SK-UT-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.44647 μM | ||||
| human HUTU-80 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HUTU-80 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.44886 μM | ||||
| human SIG-M5 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SIG-M5 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.48487 μM | ||||
| human AGS cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human AGS cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.52124 μM | ||||
| human ST486 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human ST486 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.53278 μM | ||||
| human HSC-2 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human HSC-2 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.5395 μM | ||||
| human BC-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human BC-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.61664 μM | ||||
| human CGTH-W-1 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human CGTH-W-1 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.61679 μM | ||||
| human MZ1-PC cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MZ1-PC cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.62312 μM | ||||
| human SW1710 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SW1710 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.62628 μM | ||||
| human EW-13 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human EW-13 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.63466 μM | ||||
| human U251 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human U251 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=1.74031 μM | ||||
| human NCI-H460 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human NCI-H460 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.04839 μM | ||||
| human DU-4475 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DU-4475 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.14759 μM | ||||
| human MFE-296 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MFE-296 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.47792 μM | ||||
| human DU-145 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human DU-145 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.49118 μM | ||||
| human MDA-MB-231 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human MDA-MB-231 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.49572 μM | ||||
| human SNU-387 cell | Growth inhibition assay | Inhibition of human SNU-387 cell growth in a cell viability assay, IC50=2.5282 μM | ||||
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 665.66 | Formel | C21H20F3N7O3S.C6H6O3S |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 939791-38-5 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | PF-00562271 Besylate | Smiles | CN(C1=C(C=CC=N1)CNC2=NC(=NC=C2C(F)(F)F)NC3=CC4=C(C=C3)NC(=O)C4)S(=O)(=O)C.C1=CC=C(C=C1)S(=O)(=O)O | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
4-Methylpyridine : 25 mg/mL
DMSO
: 0.4 mg/mL
(0.6 mM)
Water : Insoluble |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
FAK
(Cell-free assay) 1.5 nM
PYK2
(Cell-free assay) 13 nM
CDK2/CyclinE
(Cell-free assay) 30 nM
CDK3/CyclinE
(Cell-free assay) 47 nM
CDK1/CyclinB
(Cell-free assay) 58 nM
CDK7/CyclinH/MAT1
(Cell-free assay) 97 nM
FLT3
(Cell-free assay) 97 nM
GSK-3α
(Cell-free assay) 101 nM
CDK5/p35
(Cell-free assay) 120 nM
GSK-3β
(Cell-free assay) 133 nM
Aurora A
(Cell-free assay) 145 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
PF-562271 Besylate zeigt selektive Hemmwirkungen auf die FAK- und Pyk2-Tyrosinkinase-Aktivität mit IC50-Werten von 1,5 nM bzw. 14 nM. In zellbasierten Assays beträgt der IC50-Wert von PF-562271 für FAK 5 nM, was selektiver ist als bei anderen Kinase-Targets. In zweidimensionalen (2D) Kulturen führt PF-562271 zu einer dosisabhängigen Hemmung der Zellproliferation in FAK WT, FAK−/− und FAK Kinase-defizienten (KD) Zellen mit IC50-Werten von 3,3 μM, 2,08 μM bzw. 2,01 μM.
|
| Kinase-Assay |
Rekombinanter Kinase-Assay und Enzymkinetik
|
|
Kurz gesagt, die gereinigte, aktivierte FAK-Kinase-Domäne (Aminosäuren 410–689) wird 15 Minuten lang in Kinase-Puffer [50 mM HEPES (pH 7,5), 125 mM NaCl und 48 mM MgCl2] mit 50 μM ATP und 10 μg pro Vertiefung eines zufälligen Peptidpolymers aus Glu und Tyr, p(Glu/Tyr), umgesetzt. Die Phosphorylierung von p(Glu/Tyr) wird mit seriell verdünntem PF-562271 in 1/2-Log-Konzentrationen beginnend mit einer Höchstkonzentration von 1 μM herausgefordert. Jede Konzentration wird in dreifacher Ausführung getestet. Die Phosphorylierung von p(Glu/Tyr) wird mit einem allgemeinen Anti-Phospho-Tyrosin (PY20)-Antikörper, gefolgt von einem Meerrettichperoxidase (HRP)-konjugierten Ziegen-Anti-Maus-IgG-Antikörper, nachgewiesen. HRP-Substrat wird hinzugefügt, und die Absorptionswerte bei 450 nm werden nach Zugabe der Stopplösung (2 M H2SO4) erhalten. IC50-Werte werden unter Verwendung des Hill-Slope-Modells bestimmt. Ein breites Kinase-Selektivitätsprofiling wird intern und unter Verwendung des KinaseProfiler Selectivity Screening Service von UpState Biotechnology durchgeführt.
|
|
| In vivo |
In mehreren humanen s.c. Xenograft-Modellen zeigt PF-562271 eine dosisabhängige Tumorwachstumshemmung und bewirkt eine maximale Tumorinhibition für PC-3M, BT474, BxPc3 und LoVo im Bereich von 78% bis 94% Hemmung bei Dosen von 25 bis 50 mg/kg zweimal täglich, ohne Gewichtsverlust, Morbidität oder Tod. PF-562271 (25 mg/kg p.o.) führt zu einer signifikanten Abnahme der Tumorprogression sowohl in subkutanen als auch in Knochenmetastasen-PC3M-luc-C6-Xenograft-Modellen. In einem Huh7.5-hepatozellulären Karzinom-Xenograft-Modell zielt die Kombinationstherapie aus Sunitinib und PF-562271 auf Angiogenesis und Tumoraggressivität ab und erzielt einen signifikant stärkeren Antitumor-Effekt als Einzelwirkstoffe, indem sie das Tumorwachstum blockiert und die Fähigkeit des Tumors, sich nach Absetzen der Therapie zu erholen, beeinflusst.
|
Literatur |
|
Klinische Studieninformationen
(Daten von https://clinicaltrials.gov, aktualisiert am 2024-05-22)
| NCT-Nummer | Rekrutierung | Erkrankungen | Sponsor/Kooperationspartner | Startdatum | Phasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00666926 | Completed | Head and Neck Neoplasm|Prostatic Neoplasm|Pancreatic Neoplasm |
Verastem Inc. |
December 2005 | Phase 1 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
We are planning both in vitro and in vivo experiments and want to know how to reconstitute it for these purposes?
Antwort:
It has poor solubility in DMSO and water, with solubility in DMSO being only 0.4mg/ml. In a previous literature report (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18339875), the author used 5% Gelucire to formulate this compound. You can also consider other co-solvents such as PEG400, CMC, Tween80, and Captisol.
Frage 2:
Can you provide with a few common vehicles for it, S2672 for use as oral gavage?
Antwort:
It can be dissolved in 0.5% CMC Na at 30 mg/ml as a suspension. If 4% DMSO can be used in your experiment, it will help dissolving the suspension more homogeneously.
