nur für Forschungszwecke
Y-27632 Dihydrochloride ROCK Inhibitor
Kat.-Nr.S1049
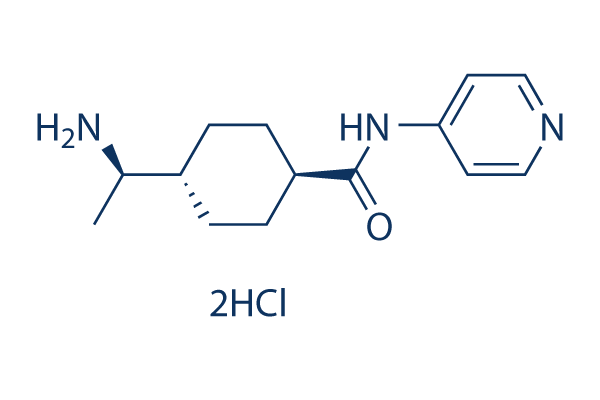
Chemische Struktur
Molekulargewicht: 320.26
Qualitätskontrolle
Produkte, die oft zusammen verwendet werden mit Y-27632 Dihydrochloride
Zellkultur, Behandlung & Arbeitskonzentration
| Zelllinien | Assay-Typ | Konzentration | Inkubationszeit | Formulierung | Aktivitätsbeschreibung | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salivary gland stem cells | Function Assay | 10 µM | 7 d | Reduces SGSC senescence | 25804560 | |
| HT22 | Cytotoxic Assay | 10 µM | 13 h | Protects against glutamate-induced neuronal death | 22810835 | |
| Swiss3T3 | Colony-forming Assay | 10 µM | 13 d | Increases prostate cell colony-forming activity | 21464902 | |
| TSGH 8301 | Migration Assay | 20 µM | 1 h | Increases cell migration | 19896475 | |
| Cynomolgus monkey embryonic stem cells | Cytotoxic Assay | 20 µM | 24 h | Promotes cyES cell survival | 18940855 | |
| PC 12 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 24 h | Attenuates catecholamine biosynthesis | 16219424 | |
| C2C12 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 6 h | Prevents the serine phosphorylation of IRS-1 induced by insulin and/or TNF-α | 16267124 | |
| Pancreatic acinar cells | Function Assay | 10 μM | 70 min | Potentiates CCK-stimulated pancreatic enzyme secretion | 12745080 | |
| Rat hepatic stellate cells | Function Assay | 30 μM | 48 h | Diminishes the phosphorylation of Erk2, and decreases new DNA synthesis | 10845663 | |
| LNCaP | Growth Inhibition Assay | 25 μM | 17 h | Does not inhibit cell growth | 10720471 | |
| PC3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 25 μM | 17 h | Does not inhibit cell growth | 10720471 | |
| PC3 | Migration Assay | 25 μM | 1 h | Inhibits the BMFB-CM and the EGF-stimulated migration | 10720471 | |
| PC3 | Function Assay | 25 μM | 1 h | Induces morphological changes | 10720471 | |
| Rat Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells | Function Assay | 10 μM | 2 h | Inhibits angiotensin II-induced hypertrophy | 10642317 | |
| Stellate Cell | Function Assay | 25 μM | 15 min | Inhibits formation of F-actin stress fibers and phosphorylation of myosin light chain | 10600496 | |
| Neonatal rat ventricular myocytes | Function Assay | 10 μM | 48 h | Inhibits ET-1-induced increases in protein synthesis, cell size and myofibrillar organization | 10386613 | |
| LS174T | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Moderately inhibits cell growth | 10021386 | |
| HCT116 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Strongly inhibits cell growth | 10021386 | |
| HCT15 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Does not inhibit cell growth | 10021386 | |
| SW620 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Does not inhibit cell growth | 10021386 | |
| Src-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Does not inhibit cell growth | 10021386 | |
| Src-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Does not inhibit cell growth | 10021386 | |
| NIH3T3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Does not inhibit cell growth | 10021386 | |
| Src-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Does not inhibit cell growth | 10021386 | |
| Src-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Does not inhibit cell growth | 10021386 | |
| Ras-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Strongly inhibits cell growth | 10021386 | |
| Ras-2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Strongly inhibits cell growth | 10021386 | |
| mNET1-e | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Strongly inhibits cell growth | 10021386 | |
| mNET1-d | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Strongly inhibits cell growth | 10021386 | |
| Dbl-e | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Moderately inhibits cell growth | 10021386 | |
| Dbl-d | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Strongly inhibits cell growth | 10021386 | |
| NIH3T3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 10 μM | 18 d | Does not inhibit cell growth | 10021386 | |
| Mesothelial cells from rat mesentery | Invasive Assay | 30 μM | 20 h | Blocks invasive activity | 9930872 | |
| CCL39 | Function Assay | 30 μM | 30 min | Completely abolishes activation of Na-H exchanger NHE1 by integrins | 9693382 | |
| HeLa | Function Assay | 10 μM | 30 min | Inhibits the formation of stress fibers and the assembly of vinculin-containing focal adhesions | 9668072 | |
| N1E-115 | Function Assay | 10 μM | 2 h | DMSO | Inhibits the assembly of microtubules and intermediate filaments to form extended processes | 9647654 |
| Swiss 3T3 cells | Function Assay | 10 μM | 2 h | DMSO | Inhibits the assembly of microtubules and intermediate filaments to form extended processes | 9647654 |
| Klicken Sie hier, um weitere experimentelle Daten zu Zelllinien anzuzeigen | ||||||
Chemische Informationen, Lagerung & Stabilität
| Molekulargewicht | 320.26 | Formel | C14H21N3O.2HCl |
Lagerung (Ab dem Eingangsdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-Nr. | 129830-38-2 | SDF herunterladen | Lagerung von Stammlösungen |
|
|
| Synonyme | N/A | Smiles | CC(C1CCC(CC1)C(=O)NC2=CC=NC=C2)N.Cl.Cl | ||
Löslichkeit
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 64 mg/mL
(199.83 mM)
Water : 64 mg/mL Ethanol : 4 mg/mL |
Molaritätsrechner
|
In vivo |
|||||
In-vivo-Formulierungsrechner (Klare Lösung)
Schritt 1: Geben Sie die untenstehenden Informationen ein (Empfohlen: Ein zusätzliches Tier zur Berücksichtigung von Verlusten während des Experiments)
Schritt 2: Geben Sie die In-vivo-Formulierung ein (Dies ist nur der Rechner, keine Formulierung. Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn es im Abschnitt "Löslichkeit" keine In-vivo-Formulierung gibt.)
Berechnungsergebnisse:
Arbeitskonzentration: mg/ml;
Methode zur Herstellung der DMSO-Stammlösung: mg Wirkstoff vorgelöst in μL DMSO ( Konzentration der Stammlösung mg/mL, Bitte kontaktieren Sie uns zuerst, wenn die Konzentration die DMSO-Löslichkeit der Wirkstoffcharge überschreitet. )
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügenμL PEG300, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügenμL Tween 80, mischen und klären, dann hinzufügen μL ddH2O, mischen und klären.
Methode zur Herstellung der In-vivo-Formulierung: Nehmen Sie μL DMSO Stammlösung, dann hinzufügen μL Maisöl, mischen und klären.
Hinweis: 1. Bitte stellen Sie sicher, dass die Flüssigkeit klar ist, bevor Sie das nächste Lösungsmittel hinzufügen.
2. Achten Sie darauf, das/die Lösungsmittel der Reihe nach hinzuzufügen. Sie müssen sicherstellen, dass die bei der vorherigen Zugabe erhaltene Lösung eine klare Lösung ist, bevor Sie mit der Zugabe des nächsten Lösungsmittels fortfahren. Physikalische Methoden wie Vortex, Ultraschall oder ein heißes Wasserbad können zur Unterstützung des Lösens verwendet werden.
Wirkmechanismus
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
ROCK1 (p160ROCK)
(Cell-free assay) 140 nM(Ki)
ROCK2
(Cell-free assay) 300 nM(Ki)
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
Y-27632 2HCl hemmt ROCK-II, während es wenig Aktivität gegen PKC, cAMP-abhängige Proteinkinase und Myosin-Leichtketten-Kinase (MLCK) mit Ki von 26 μM, 25 μM bzw. > 250 μM sowie PKA, die durch ein anderes Rho-Familien-GTPase-Mitglied, Cdc42, aktiviert wird, zeigt. Diese Verbindung hemmt die durch verschiedene Agonisten wie Phenylephrin, Histamin, Acetylcholin, Serotonin, Endothelin und Thromboxan induzierte Kontraktion der glatten Muskulatur mit einer IC50 von 0,3-1 μM, indem sie selektiv die Ca2+-Sensibilisierung hemmt. Sie unterdrückt die Rho-induzierte, p160ROCK-vermittelte Bildung von Stressfasern in kultivierten Zellen. |
| Kinase-Assay |
Diese chemische Behandlung blockiert sowohl die Rho-vermittelte Aktivierung von Aktomyosin als auch die LPA-stimulierte invasive Aktivität von MM1-Zellen konzentrationsabhängig. |
|
Diese Verbindung ist nicht nur ausreichend, um die Bildung von üppigen axonalen Prozessen einzuleiten, sondern fördert auch die axonale Reifung in den sehr frühen Stadien der Axonogenese, während die Axonverlängerung weitgehend verschont bleibt. |
|
| In vivo |
In humanen embryonalen Stammzellen (hES-Zellen) verringert diese chemische Behandlung bei 10 μM die dissoziationsinduzierte Apoptose selbst in serumfreier Suspensionskultur (SFEB) deutlich, erhöht die Kloneffizienz (von ~1% auf ~27%), erleichtert die Subklonierung nach Gentransfer und ermöglicht es SFEB-kultivierten hES-Zellen, zu überleben und sich in Bf1+ kortikale und basale telenzephale Vorläufer zu differenzieren. |
Literatur |
|
Anwendungen
| Methoden | Biomarker | Bilder | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Western Blot | p-LIMK1(Thr508) p-LIMK2(Thr505) p-Cofilin(Ser3) CDK2 KRT7 ROCK2 E-cadherin p-MLC2(Ser19) |
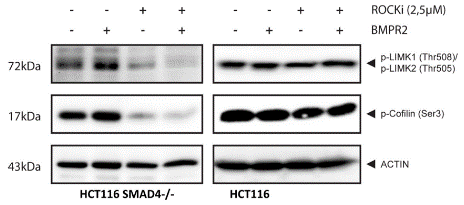
|
24704720 |
| Transwell migration assay | cell migration inhibition |
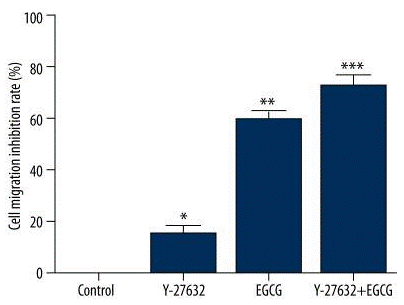
|
27694793 |
| Immunofluorescence | Neurotoxicity Assay E-cadherin beta-catenin Phalloidin |
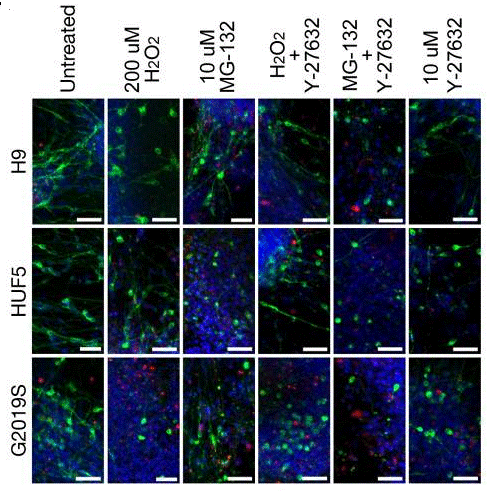
|
21362567 |
| Growth inhibition assay | cell proliferation |
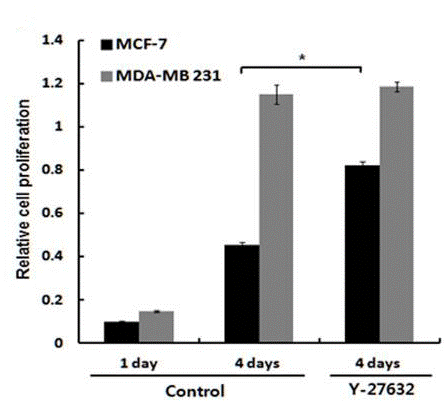
|
24523903 |
| ELISA | caspase-9 |
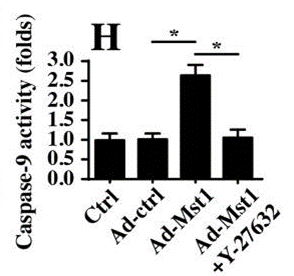
|
30320378 |
Technischer Support
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Wenn Sie weitere Fragen haben, hinterlassen Sie bitte eine Nachricht.
Häufig gestellte Fragen
Frage 1:
Is there any data about the Amax (maximum attraction luminosity) and extinction coefficient of it?
Antwort:
The wavelength used to test its HPLC is 260nm, while the extinction coefficient is unknown.
Frage 2:
Could it be used in cell culture? Do you have any reference for this application?
Antwort:
Yes. It can be used in cell culture certainly. Here is the reference website: http://molpharm.aspetjournals.org/content/57/5/976.full.
